Navigating the complexities of healthcare affordability can be daunting, but understanding the Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit (HIPTC) can significantly ease the burden. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of the HIPTC, explaining its eligibility criteria, application process, and impact on individuals and families across various scenarios. We’ll explore how it works, its connection to the Affordable Care Act, and its potential future trajectory, offering a clear and concise understanding of this vital financial assistance program.
From its inception as a key component of the Affordable Care Act, the HIPTC has played a pivotal role in expanding access to affordable health insurance. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to determine your eligibility, understand the calculation process, and ultimately navigate the system effectively. We aim to demystify the process and empower you to make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Definition of the Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit (HIPTC)
The Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit (HIPTC), often simply called the premium tax credit, helps many Americans afford health insurance purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplaces (also known as exchanges). It’s essentially a government subsidy that lowers the monthly cost of your health plan. Think of it as a discount on your health insurance bill, making coverage more accessible.
Eligibility Criteria for the HIPTC
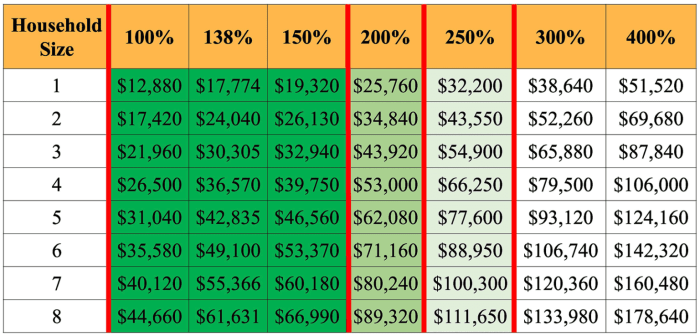
To qualify for the HIPTC, you must meet several criteria. First, you must obtain health insurance through a Health Insurance Marketplace. Second, your household income must fall within specific limits. These limits are adjusted annually and vary depending on your family size and location. Third, you cannot be eligible for affordable employer-sponsored health insurance. Finally, you must be a U.S. citizen or national, or a lawfully present immigrant. Meeting all these requirements makes you eligible to receive the tax credit. The specific income limits and other details are updated annually by the IRS and the Department of Health and Human Services.
How the HIPTC Reduces Premium Costs
The HIPTC is a refundable tax credit, meaning you can receive the credit even if you don’t owe any income tax. The amount of the credit depends on your household income and the cost of health insurance plans in your area. The Marketplace calculates your estimated credit based on your income and family size, and this is applied directly to your monthly premium. For example, if your monthly premium is $500 and your credit is $300, you would only pay $200 per month. The remaining $300 is covered by the government. The credit is calculated to keep your health insurance costs within an affordable percentage of your income.
Comparison of the HIPTC to Other Healthcare Subsidies
The following table compares the HIPTC to other healthcare subsidies available in the United States. Note that eligibility criteria and benefit amounts can change, so it’s always best to check the most current information from the relevant government agencies.
| Program Name | Eligibility Requirements | Benefit Type | Funding Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit (HIPTC) | Income-based, Marketplace enrollment, no affordable employer coverage | Reduces monthly health insurance premiums | Federal government |
| Cost-Sharing Reductions (CSRs) | Income-based, Marketplace enrollment, limited availability | Reduces out-of-pocket costs (deductibles, co-pays, etc.) | Federal government (currently limited) |
| Medicaid | Income-based, varies by state | Comprehensive health insurance coverage | Federal and state governments |
| Medicare | Age 65 or older, or certain disabilities | Comprehensive health insurance coverage for seniors and disabled | Federal government |
Impact of the HIPTC on Individuals and Families

The Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit (HIPTC) significantly impacts the lives of many individuals and families across the United States, primarily by increasing healthcare affordability and access. Its effects are multifaceted, influencing not only financial burdens but also healthcare utilization patterns. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing the program’s effectiveness and its role in achieving broader health equity goals.
The HIPTC’s primary effect is to make health insurance more affordable. By subsidizing a portion of the monthly premium, the program reduces the out-of-pocket costs for individuals and families, making it possible for them to purchase coverage they might otherwise be unable to afford. This reduction in cost can alleviate significant financial strain, particularly for those with low or moderate incomes. This allows individuals to budget for other essential needs and reduces the risk of medical debt.
Healthcare Affordability
The HIPTC directly reduces the financial burden of health insurance. For many, the difference between being able to afford insurance and being uninsured is the availability of the HIPTC. This translates to a greater ability to access necessary medical care without the fear of overwhelming medical bills. The magnitude of this impact varies depending on income level and the specific health insurance plan chosen, but even a modest reduction in premiums can make a significant difference in a household budget. For example, a family earning slightly above the poverty line might find the HIPTC makes the difference between choosing between food and medicine, and being able to afford both.
Healthcare Access
Increased affordability through the HIPTC translates directly into improved healthcare access. With affordable insurance, individuals are more likely to seek preventative care, routine check-ups, and necessary treatment for existing conditions. This early intervention can lead to better health outcomes and reduce the need for more expensive treatments later on. Delaying or forgoing care due to cost is a significant barrier to health for many, and the HIPTC helps mitigate this issue. Studies have shown a correlation between access to affordable insurance and improved rates of preventative care, such as vaccinations and screenings.
Healthcare Service Utilization
Comparing healthcare service utilization before and after receiving the HIPTC reveals a notable increase in the use of various services. Individuals who previously delayed or avoided care due to cost are more likely to seek medical attention once they have affordable insurance. This often results in an increase in preventative care visits, as well as more timely treatment of acute and chronic conditions. Data consistently demonstrates that the HIPTC leads to increased utilization of preventative services such as annual check-ups and screenings, potentially leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Number of Individuals and Families Benefiting from the HIPTC
The number of individuals and families benefiting from the HIPTC is substantial and fluctuates yearly depending on economic conditions and enrollment periods. Precise figures are available from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and other government sources.
- Millions of Americans have accessed affordable health insurance through the HIPTC since its inception.
- The program has particularly benefited low- and moderate-income families, reducing the uninsured rate among these populations.
- Annual enrollment numbers vary, but consistently show a large number of individuals and families utilizing the credit.
The HIPTC and the Affordable Care Act (ACA)

The Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit (HIPTC) is a cornerstone of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), playing a crucial role in expanding access to affordable health insurance for millions of Americans. Its design and implementation are intrinsically linked to the ACA’s overall goals and structure.
The HIPTC is central to the ACA’s marketplace, providing subsidies to individuals and families who purchase health insurance through the exchanges. It works by lowering the cost of monthly premiums, making coverage more attainable for those who otherwise might not be able to afford it. The amount of the subsidy is determined by several factors, including household income, location, and the cost of available plans. Without the HIPTC, the ACA’s promise of affordable health insurance would be significantly weakened for a large portion of the population.
The HIPTC’s Role in the ACA Marketplace
The HIPTC functions as a crucial mechanism for achieving the ACA’s objective of expanding health insurance coverage. By reducing the out-of-pocket cost of insurance, it enables individuals and families with moderate incomes to purchase plans that meet their healthcare needs. This subsidy is directly tied to the affordability standards set by the ACA, ensuring that a significant portion of a household’s income isn’t dedicated to healthcare premiums. The HIPTC is not a direct payment to healthcare providers; instead, it’s a reduction in the cost of purchasing a qualified health plan through the ACA marketplace.
Impact of ACA Changes on the HIPTC
Changes to the ACA, such as alterations to income eligibility thresholds or modifications to the cost-sharing reduction program, directly influence the HIPTC. For example, increasing the income limits for eligibility would expand the pool of individuals who qualify for subsidies, while decreasing them would have the opposite effect. Similarly, changes to the cost-sharing reduction program, which helps lower out-of-pocket costs like deductibles and co-pays, would indirectly affect the demand for and value of the HIPTC. The Trump administration’s efforts to weaken the ACA, including ending cost-sharing reduction payments, led to higher premiums and reduced affordability for some, highlighting the interconnectedness of these programs.
Challenges and Limitations of the HIPTC Program
The HIPTC program faces several challenges. One is the complexity of the eligibility rules and the application process, which can be daunting for some individuals. Another challenge is the variation in premium costs across different states and plans, leading to disparities in the amount of subsidy received. Furthermore, the program’s reliance on accurate income reporting can be problematic, as inaccurate reporting can lead to overpayments or underpayments of subsidies. The ongoing debate about the future of the ACA itself creates uncertainty about the long-term stability of the HIPTC.
Historical Overview of the HIPTC
The HIPTC was established as part of the Affordable Care Act, becoming effective in 2014. Initially, there were significant challenges in implementation, including technical issues with the HealthCare.gov website. Over time, the program has been refined, with adjustments made to address various issues and improve efficiency. The program’s funding and eligibility criteria have also been subject to political debate and legal challenges throughout its history, leading to periods of uncertainty and change in its implementation. For example, the previously mentioned changes under the Trump administration resulted in significant alterations to the program’s practical application and affected millions of beneficiaries.
Future of the HIPTC
The Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit (HIPTC) plays a crucial role in making health insurance affordable for millions of Americans. However, its future is subject to ongoing political and economic pressures, necessitating a careful examination of potential reforms, long-term sustainability, and the impact of external factors. Understanding these aspects is vital for ensuring the program’s continued effectiveness in achieving its goals.
Potential Reforms and Expansions of the HIPTC could involve several key areas. Expanding eligibility criteria to include more individuals and families, particularly those in the “coverage gap” between eligibility for Medicaid and subsidized marketplace plans, could significantly increase access to affordable healthcare. Adjusting the income thresholds for eligibility to reflect changes in the cost of living and inflation would ensure the program remains relevant and effective over time. Furthermore, simplifying the application process and improving outreach efforts could enhance enrollment rates and reduce administrative burdens.
Potential HIPTC Reforms
Several potential reforms could enhance the HIPTC’s effectiveness and reach. For instance, increasing the maximum subsidy amount available to individuals could significantly lower out-of-pocket costs for those with higher premiums. This would be particularly beneficial for individuals residing in areas with limited provider networks or those requiring specialized care, leading to improved access to quality healthcare. Another important reform would involve simplifying the income verification process to streamline enrollment and reduce barriers to access. This could be achieved through improved data sharing between government agencies and healthcare providers. Finally, strengthening outreach and education initiatives to better inform eligible individuals about the HIPTC would increase participation and ensure that those who need it most are aware of and can utilize the program.
Long-Term Sustainability of the HIPTC
The long-term sustainability of the HIPTC is intrinsically linked to the overall financial health of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the broader healthcare system. Continued budgetary pressures and political debates regarding the ACA’s future could impact funding for the HIPTC. Exploring alternative funding mechanisms, such as increasing taxes on high-income earners or implementing a more progressive tax system, could help ensure the program’s long-term viability. Furthermore, regular assessments of the program’s effectiveness and efficiency, coupled with data-driven adjustments, are crucial for ensuring its long-term sustainability and maximizing its impact. This includes exploring options to reduce administrative costs and fraud while maintaining program integrity.
Impact of Economic Factors on the HIPTC
Economic fluctuations significantly influence the HIPTC. During periods of economic recession or high inflation, more individuals may find themselves needing the HIPTC to afford health insurance. This increased demand could strain the program’s resources and potentially necessitate increased government funding. Conversely, periods of economic growth might reduce the number of individuals requiring assistance, freeing up resources for other healthcare initiatives. The rising cost of healthcare itself is another significant economic factor. If healthcare costs continue to rise at a faster rate than inflation, the HIPTC may need to be adjusted to ensure it continues to provide meaningful financial assistance to eligible individuals. This could involve increasing the subsidy amounts or adjusting the income thresholds periodically to maintain its effectiveness.
Hypothetical Scenario: Changes to the HIPTC and Their Consequences
Let’s imagine a scenario where Congress significantly reduces the funding for the HIPTC due to budgetary constraints. This would lead to a reduction in the maximum subsidy amount available to individuals, potentially making health insurance unaffordable for many. As a consequence, we might see a surge in the number of uninsured Americans, particularly among low- and middle-income individuals. This could lead to delayed or forgone care, resulting in poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run, potentially offsetting any short-term budget savings from reducing HIPTC funding. Conversely, a scenario where the HIPTC is expanded to cover more individuals could lead to a greater number of people gaining access to affordable health insurance, resulting in improved public health and reduced healthcare disparities. This expansion, however, would likely require increased government spending.
Final Wrap-Up
The Health Insurance Premium Tax Credit represents a crucial lifeline for many Americans seeking affordable healthcare. By understanding the eligibility requirements, application process, and potential impact on your individual circumstances, you can leverage this valuable resource to secure the health coverage you need. This guide has provided a framework for navigating the HIPTC, empowering you to make informed choices and access the support available to you. Remember to consult with relevant healthcare professionals and government resources for personalized guidance and up-to-date information.
General Inquiries
What happens if my income changes during the year?
You may need to report the change to the Marketplace. This could affect your subsidy amount for the remainder of the year.
Can I still get the HIPTC if I’m employed and have employer-sponsored insurance?
Possibly. The affordability of your employer-sponsored plan is a factor. If your employer’s plan is considered unaffordable, you may still qualify for the HIPTC to purchase a plan through the Marketplace.
What if I don’t file taxes? Do I still need to apply for the HIPTC?
Yes, even if you don’t typically file taxes, you still need to apply for the HIPTC through the HealthCare.gov marketplace. Your tax information is still required for eligibility determination.
Is the HIPTC only for low-income individuals?
No, while income is a factor, the HIPTC is available to individuals and families within a range of income levels. The exact income limits vary annually.
How long does it take to receive the HIPTC?
The timing varies. The credit is typically applied directly to your monthly premiums or issued as a tax refund after filing your taxes.