Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. Understanding the average premium is a crucial first step, but the reality is far from a single number. Numerous factors, from age and location to the type of plan chosen, significantly influence the final cost. This guide will unravel the intricacies of health insurance premiums, providing a clear picture of what to expect and how to find the best coverage for your needs.
We’ll explore the key elements that determine your premium, offering a detailed breakdown of average costs across different plan types and demographics. Understanding these factors empowers you to make informed decisions, ensuring you secure affordable and adequate health insurance protection.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
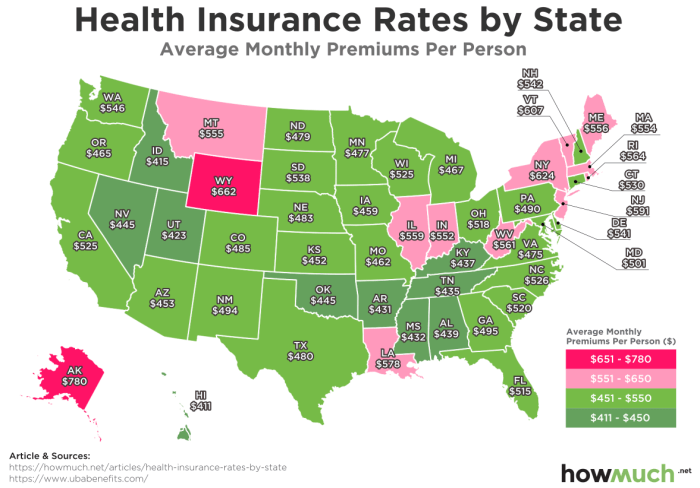
Several key factors interact to determine the cost of health insurance premiums. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions when choosing a plan. These factors are often complex and interconnected, resulting in a wide range of premium costs across different individuals and families.
Age
Age significantly impacts health insurance premiums. Older individuals generally pay more because they tend to have higher healthcare utilization rates due to increased susceptibility to chronic illnesses and age-related conditions. Insurers factor in these higher expected costs when setting premiums. For example, a 60-year-old might pay considerably more than a 30-year-old for the same plan, even if both are otherwise healthy.
Location
Geographic location plays a crucial role in determining premium costs. Areas with higher costs of living, a greater concentration of specialists, and higher healthcare service prices typically have higher insurance premiums. For instance, premiums in major metropolitan areas with high-cost hospitals and specialized medical facilities tend to be higher than those in rural areas with fewer resources and lower healthcare costs.
Individual vs. Family Plans
Family health insurance plans usually cost more than individual plans. This is because family plans cover multiple individuals, increasing the potential for healthcare utilization and claims. While economies of scale might offer some cost savings, the increased risk associated with covering a family generally leads to higher premiums compared to an individual plan. A family of four, for instance, will almost always pay significantly more than an individual with the same level of coverage.
Health Status
Pre-existing conditions and overall health status are major factors influencing premium costs. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of significant healthcare needs often face higher premiums because of the increased likelihood of needing extensive medical care. Insurers assess risk profiles to determine premiums, leading to higher costs for those deemed higher-risk. Someone with a history of heart disease, for example, will likely pay more than someone with no such history.
Plan Type
The type of health insurance plan chosen (e.g., HMO, PPO, EPO) also affects premium costs. HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations) generally have lower premiums but stricter network restrictions. PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations) offer greater flexibility in choosing doctors but typically have higher premiums. The trade-off between cost and flexibility is a key consideration when selecting a plan. A comprehensive PPO plan will usually have a higher premium than a more restrictive HMO plan with similar coverage.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Premium | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Older individuals generally have higher healthcare utilization. | Higher premiums with increasing age. | A 60-year-old pays more than a 30-year-old for the same plan. |
| Location | Cost of living, healthcare service prices, and specialist availability vary geographically. | Higher premiums in high-cost areas. | Premiums in New York City are typically higher than in rural Iowa. |
| Individual vs. Family | Family plans cover multiple individuals, increasing risk for insurers. | Family plans cost more than individual plans. | A family plan costs more than a comparable individual plan. |
| Health Status | Pre-existing conditions and health history influence risk assessment. | Higher premiums for individuals with pre-existing conditions or poor health. | Someone with diabetes pays more than someone without. |
| Plan Type | Different plan types offer varying levels of flexibility and cost. | HMOs typically have lower premiums than PPOs. | A PPO plan with broader network access costs more than an HMO. |
Average Premium Ranges by Plan Type
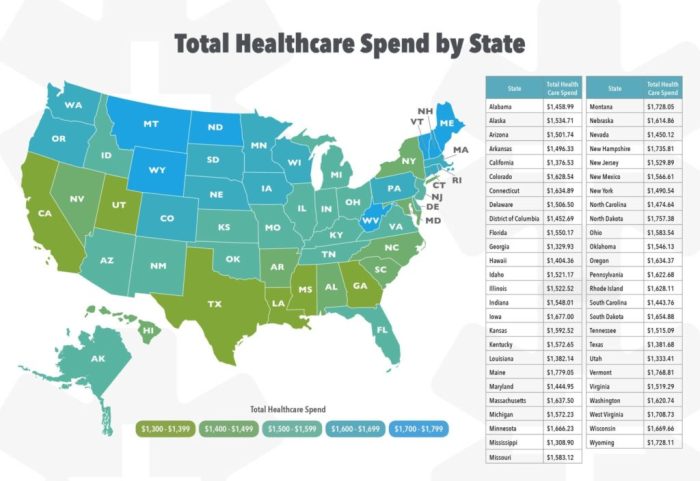
Understanding the average cost of health insurance is crucial for making informed decisions. Premiums vary significantly based on several factors, including plan type, age, location, and family size. This section provides a breakdown of average premium ranges for different health insurance plans. Keep in mind that these are averages and your actual premium may differ.
Average Premiums for HMO Plans Across Different Age Groups
HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) plans typically offer lower premiums than other plan types but often require you to see doctors within their network. The cost of an HMO plan generally increases with age, reflecting higher healthcare utilization in older populations. For example, a 30-year-old might pay an average of $500 per month, while a 60-year-old might pay closer to $800 per month. These figures are illustrative and vary based on location and specific plan details. Factors such as pre-existing conditions can also influence premium costs.
Average Premiums for PPO Plans Categorized by Family Size
PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) plans offer more flexibility in choosing doctors, even outside their network, but usually come with higher premiums. The cost typically increases with family size, as more individuals are covered under the same plan. A single individual might pay around $700 per month, while a family of four could pay upwards of $2000 per month. Again, these are averages, and actual premiums can vary widely depending on location, plan specifics, and the health status of the individuals covered.
Average Premiums for High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) Versus Traditional Plans
High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) are associated with lower monthly premiums but have significantly higher out-of-pocket costs before insurance coverage kicks in. Traditional plans, on the other hand, generally have higher monthly premiums but lower out-of-pocket maximums. For instance, a typical HDHP might have a monthly premium of $300 but a deductible of $6,000, whereas a traditional plan might cost $700 per month but have a much lower deductible, perhaps $1,000. The best choice depends on individual risk tolerance and financial situation.
Average Premium Comparison Table
| Plan Type | Age/Family Size | Average Monthly Premium | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | 30-year-old | $500 | Illustrative example; varies by location and plan |
| HMO | 60-year-old | $800 | Illustrative example; varies by location and plan |
| PPO | Single | $700 | Illustrative example; varies by location and plan |
| PPO | Family of Four | $2000 | Illustrative example; varies by location and plan |
| HDHP | Individual | $300 | Illustrative example; high deductible applies |
| Traditional | Individual | $700 | Illustrative example; lower deductible than HDHP |
Resources for Finding Health Insurance Premium Information
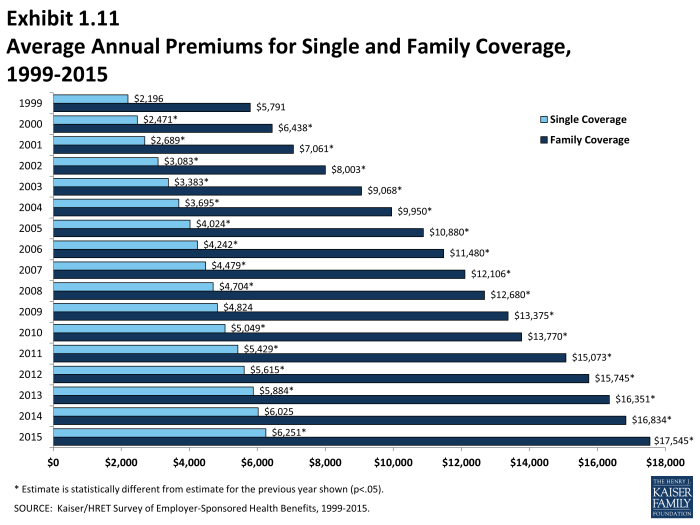
Finding accurate and up-to-date information on health insurance premiums can feel overwhelming. Fortunately, several reliable resources exist to help you navigate this process and make informed decisions about your health coverage. Understanding where to look and what information to seek is crucial for securing the best plan for your needs and budget.
Reputable Websites for Health Insurance Premium Research
Several websites offer comprehensive information on health insurance premiums. These resources provide tools for comparing plans, understanding coverage details, and accessing helpful guides. It’s important to note that the information provided is often general and may not reflect the specific premiums in your area, which are influenced by factors like location, age, and health status. However, these sites serve as excellent starting points for your research.
- Healthcare.gov: This is the official website for the Health Insurance Marketplace in the United States. It allows users to browse plans available in their area, compare costs, and enroll in coverage. The site provides detailed information on plan benefits, premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- State Insurance Department Websites: Each state maintains its own insurance department website. These sites often provide resources on health insurance, including lists of licensed insurers, consumer guides, and tools for comparing plans within the state. They can also be helpful for filing complaints or resolving disputes with insurers.
- eHealthInsurance: This is a private marketplace that allows users to compare plans from multiple insurers. It offers a user-friendly interface and provides detailed information on plan benefits and costs. Note that using a private marketplace might lead to different results than using Healthcare.gov.
Using Online Health Insurance Marketplaces to Compare Plan Costs
Online health insurance marketplaces simplify the process of comparing plan costs. These platforms typically allow users to input their location, age, and other relevant information to generate a list of available plans. Users can then sort and filter plans based on factors like premium cost, deductible, and network of doctors. Many marketplaces also provide tools to compare plans side-by-side, highlighting key differences in coverage and cost. For example, Healthcare.gov provides a detailed comparison tool that allows users to view the costs of different plans over time and under different scenarios. Remember to carefully review the details of each plan before making a decision.
Information Typically Found on Insurance Company Websites Regarding Premiums
Insurance company websites typically provide information on their health insurance plans, including premium costs. While the specific information presented may vary between insurers, common details include monthly premium amounts for different plan types (e.g., Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum), premium variations based on age and family size, and a description of factors that affect premium calculations. Many companies also provide downloadable brochures or fact sheets that detail the plan’s benefits, costs, and other important information. It’s essential to thoroughly examine the policy details to fully understand your coverage and associated costs.
Key Aspects to Consider When Comparing Premium Quotes
Before selecting a health insurance plan, carefully consider these key factors:
- Monthly Premium Cost: The amount you pay each month for coverage.
- Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins.
- Copay: The fixed amount you pay for a doctor’s visit or other healthcare services.
- Coinsurance: Your share of the costs of covered healthcare services after you’ve met your deductible.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The most you will pay out-of-pocket for covered services in a plan year.
- Network of Doctors and Hospitals: Ensuring your preferred doctors and hospitals are in the plan’s network is crucial.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: Review the formulary (list of covered medications) and associated costs.
Summary
Securing affordable and comprehensive health insurance requires careful consideration of various factors. While the average premium offers a starting point, your individual circumstances will significantly impact the final cost. By understanding the influence of age, location, plan type, and other key elements, you can effectively compare options and choose a plan that best aligns with your budget and healthcare needs. Remember to utilize the resources available to research and compare plans before making a final decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a deductible?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance coverage kicks in.
What is a co-pay?
A co-pay is a fixed amount you pay for a covered healthcare service, such as a doctor’s visit, at the time of service.
How does my credit score affect my health insurance premium?
In most states, your credit score cannot be used to determine your health insurance premium. However, some states may still allow this practice.
Can I get a subsidy to help pay for my health insurance?
Depending on your income and location, you may be eligible for a government subsidy to reduce the cost of your health insurance premium through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces.
Where can I find more information about health insurance plans in my area?
You can find information on the HealthCare.gov website, your state insurance marketplace, or directly from insurance providers.