Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code, especially for couples. Understanding the average cost of health insurance premiums is crucial for budgeting and planning. This guide unravels the intricacies of couple’s health insurance premiums, exploring the factors that influence costs and providing practical strategies for finding affordable coverage.
From the impact of age and location to the nuances of different plan types and the role of pre-existing conditions, we’ll delve into the key elements that shape your premium. We’ll also explore resources for obtaining accurate quotes and understanding government subsidies, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health insurance.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums for Couples
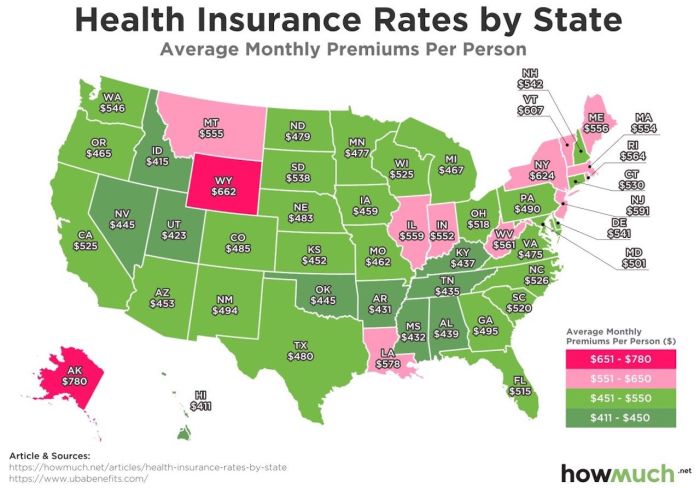
Several interconnected factors determine the cost of health insurance premiums for couples. Understanding these elements allows for more informed decision-making when selecting a plan. This section will explore the key demographic factors, plan types, cost-sharing mechanisms, and income’s influence on premium costs.
Demographic Factors and Premium Costs
Age, location, and health status are significant demographic factors impacting health insurance premiums. Older couples generally pay more due to a higher likelihood of needing medical care. Geographic location plays a crucial role; premiums are typically higher in areas with high healthcare costs and a higher concentration of specialists. Pre-existing health conditions or a family history of illness can also lead to increased premiums, as insurers assess the potential risk associated with covering the couple’s healthcare needs.
Plan Type and Premium Costs
The type of health insurance plan significantly influences premium costs. HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations) usually have lower premiums but restrict access to care to in-network providers. PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations) offer more flexibility in choosing doctors and hospitals, but generally come with higher premiums. Other plan types, such as POS (Point of Service) plans, offer a blend of HMO and PPO features with varying premium costs. The choice of plan type should align with the couple’s healthcare needs and preferences.
Deductibles, Out-of-Pocket Maximums, and Premiums
Deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums are crucial cost-sharing elements that influence premiums. A higher deductible (the amount you pay before insurance coverage begins) typically results in lower premiums. Conversely, a lower deductible usually translates to higher premiums. Similarly, a lower out-of-pocket maximum (the most you will pay out-of-pocket in a year) is often associated with higher premiums. Couples need to carefully weigh the trade-off between premium costs and out-of-pocket expenses.
Income Levels and Premium Costs
Income levels can indirectly influence premium costs through government subsidies or employer-sponsored plans. Couples with lower incomes may qualify for government subsidies that reduce their premium costs through programs like the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces. Employer-sponsored plans can also significantly impact premiums, with employers often contributing a portion of the cost, reducing the burden on the couple. However, the availability and generosity of employer-sponsored plans vary considerably.
Factors Impacting Health Insurance Premiums for Couples
| Factor | Impact on Premium | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Higher premiums with increasing age | A 60-year-old couple pays more than a 30-year-old couple. | Increased risk of health issues and higher healthcare utilization. |
| Location | Higher premiums in high-cost areas | A couple in New York City pays more than a similar couple in a rural area. | Variations in healthcare provider costs and market competition. |
| Health Status | Higher premiums with pre-existing conditions | A couple with diabetes pays more than a healthy couple. | Increased risk of needing extensive medical care. |
| Plan Type | PPOs generally cost more than HMOs | A PPO plan costs $1500/month while a comparable HMO costs $1200/month. | Trade-off between premium cost and flexibility in choosing providers. |
Obtaining Health Insurance Quotes for Couples
Securing affordable and comprehensive health insurance is a crucial step for couples. Understanding the process of obtaining accurate quotes and comparing plans is essential to finding the best coverage for your needs and budget. This section Artikels the steps involved in this process and highlights the resources available to assist you.
Finding the right health insurance plan for a couple requires careful consideration and comparison. Several resources offer tools to simplify this process, allowing couples to explore various options and choose the most suitable plan.
Resources for Comparing Health Insurance Plans
Several avenues exist for comparing health insurance plans. Online marketplaces offer a centralized platform to browse plans from multiple insurers, often side-by-side. These marketplaces typically allow users to filter plans based on factors like premium cost, deductible, and network of doctors. Insurance brokers, independent professionals specializing in insurance, provide personalized guidance, assisting couples in navigating the complexities of plan selection and often providing access to plans not readily available through online marketplaces. Directly contacting insurance companies is another option, though it requires more individual research across various providers.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Couples Seeking Health Insurance
- Assess your needs: Consider your health history, current medications, and anticipated healthcare needs. Do you require specialized care? Do you frequently visit the doctor? Understanding these factors helps determine the level of coverage required.
- Determine your budget: Establish a realistic monthly premium budget. This will help narrow down the options available.
- Use online marketplaces: Utilize online health insurance marketplaces like Healthcare.gov (in the US) or your country’s equivalent to compare plans based on your needs and budget. These sites often provide tools to compare plans side-by-side.
- Consult an insurance broker: Consider engaging an insurance broker for personalized guidance. Brokers can help navigate complex plan details and find options that may not be readily available online.
- Review quotes carefully: Compare premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums across different plans. Pay close attention to the network of doctors and hospitals covered by each plan to ensure your preferred providers are included.
- Enroll in a plan: Once you’ve chosen a plan, complete the enrollment process through the chosen marketplace or insurance company.
Interpreting Key Information in a Health Insurance Quote
A health insurance quote presents crucial information that needs careful review. Key elements include the monthly premium (the amount you pay regularly), the deductible (the amount you pay out-of-pocket before the insurance begins to cover costs), co-pays (fixed fees for doctor visits), and the out-of-pocket maximum (the most you’ll pay out-of-pocket in a year). The quote should also specify the network of doctors and hospitals covered by the plan. For example, a quote might show a monthly premium of $500, a $5,000 deductible, a $50 co-pay for doctor visits, and a $10,000 out-of-pocket maximum. It’s vital to understand how these factors interact to determine your overall healthcare costs. The provider network is also critical; a quote listing a narrow network may limit your choice of doctors and hospitals.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions on Premiums
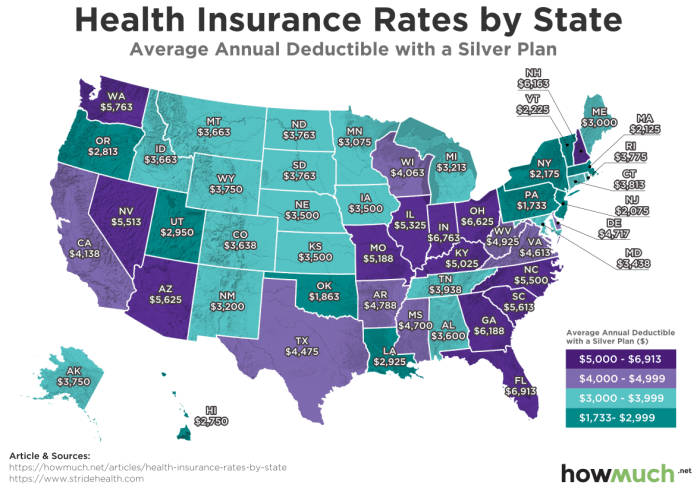
Pre-existing conditions, health issues present before obtaining health insurance, significantly influence the cost of health insurance for couples. The impact varies depending on the severity and type of condition, as well as the insurer and the specific plan chosen. Generally, couples with pre-existing conditions can expect to pay higher premiums than those without.
Pre-existing conditions can lead to higher premiums because they increase the likelihood of needing expensive medical care. Insurers assess risk when setting premiums, and individuals with pre-existing conditions are considered higher risk. This increased risk is reflected in higher premiums to offset the potential costs associated with treating those conditions. The difference in premiums between couples with and without pre-existing conditions can be substantial, depending on the specific conditions and the level of coverage desired.
The Affordable Care Act and Pre-existing Conditions
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) significantly altered the landscape of health insurance in the United States, particularly regarding pre-existing conditions. Prior to the ACA, insurers could deny coverage or charge exorbitant premiums to individuals with pre-existing conditions. The ACA prohibits this discriminatory practice, ensuring that individuals with pre-existing conditions can obtain health insurance without facing discriminatory pricing or denial of coverage. However, it’s important to note that while the ACA prevents insurers from denying coverage based on pre-existing conditions, it doesn’t eliminate the potential impact on premium costs entirely.
Premium Differences Based on Pre-existing Conditions
The following table illustrates potential premium differences for couples with various pre-existing conditions. These are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary based on numerous factors including location, insurer, plan type, and the specific details of the pre-existing conditions. Remember that these are hypothetical examples for illustrative purposes only and should not be taken as definitive pricing.
| Couple | Pre-existing Conditions | Approximate Monthly Premium (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Couple A | None | $1200 |
| Couple B | Type 1 Diabetes (one partner) | $1500 |
| Couple C | Heart Disease (one partner), Asthma (both partners) | $2000 |
| Couple D | Cancer (one partner), requiring ongoing treatment | $2800 |
Government Subsidies and Tax Credits
Finding affordable health insurance can be a challenge for many couples, but government assistance programs can significantly alleviate the financial burden. These programs offer subsidies and tax credits to help individuals and families purchase health insurance through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces. Understanding these programs and their eligibility requirements is crucial for couples seeking to lower their premium costs.
Government subsidies and tax credits are designed to make health insurance more accessible and affordable. These programs reduce the monthly premium a couple pays, making coverage attainable for those who otherwise might struggle to afford it. The amount of assistance received depends on several factors, including income, family size, and the cost of insurance in the individual’s area.
Eligibility Requirements for Subsidies and Tax Credits
Eligibility for subsidies and tax credits is primarily determined by income. Generally, couples must have an income between 100% and 400% of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL). The exact percentages can vary slightly from year to year. Additionally, couples must obtain health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace (also known as the ACA marketplace) rather than through an employer or other means. They cannot be eligible for Medicare or Medicaid. Citizenship or legal immigration status is also a requirement.
Examples of Subsidy Impact on Premium Costs
Let’s consider a hypothetical example. Suppose a couple’s annual income is $60,000, placing them within the eligible range for subsidies. Without a subsidy, their monthly premium for a suitable health plan might be $1,200. With a subsidy, this cost could be reduced to $400 per month, representing a significant savings of $800 monthly or $9,600 annually. The specific subsidy amount depends on the plan chosen and the couple’s income level. Another example: a couple earning $45,000 annually might see their monthly premium reduced from $800 to $200 with the help of a tax credit, resulting in a substantial yearly saving. These are illustrative examples; actual savings will vary based on individual circumstances and the plan selected.
Key Features of Government Assistance Programs
- Income-Based Subsidies: The amount of the subsidy is directly tied to the couple’s income. Lower incomes generally receive larger subsidies.
- Tax Credits: These are non-refundable tax credits, meaning they can reduce a couple’s tax liability but not result in a direct refund if the credit exceeds their tax liability.
- Marketplace Enrollment: Subsidies and tax credits are only available through the official Health Insurance Marketplace.
- Annual Adjustments: Eligibility and subsidy amounts are reviewed annually based on updated income information.
Final Conclusion
Securing affordable and comprehensive health insurance is a vital step in financial planning for couples. By understanding the factors influencing premiums, utilizing available resources for quote comparisons, and exploring potential government assistance, couples can confidently navigate the health insurance landscape and choose a plan that best suits their needs and budget. Remember, proactive planning and informed decision-making are key to securing the right coverage.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO plan?
HMOs typically require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who manages your care and referrals to specialists. PPOs offer more flexibility, allowing you to see any in-network doctor without a referral, but usually at a higher cost.
Can I get a health insurance quote without providing personal information?
While some websites offer general estimates, obtaining an accurate quote usually requires providing personal information such as age, location, and health status. This information allows insurers to accurately assess your risk.
What if one spouse has a pre-existing condition?
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurers from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions. However, the specific impact on premiums may vary depending on the condition and the plan.
Where can I find information on government subsidies and tax credits?
You can find information on government subsidies and tax credits through the HealthCare.gov website or by contacting a healthcare insurance broker or navigator.