Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. At the heart of this system lies the health insurance premium – the monthly payment you make for your coverage. Understanding what constitutes this cost, the factors influencing it, and strategies to manage it is crucial for securing affordable and effective healthcare. This guide unravels the intricacies of health insurance premiums, providing clarity and empowering you to make informed decisions.
From defining the core components of a premium to exploring the impact of individual factors like age and health status, we’ll examine how different plan types and government assistance programs affect the final cost. We’ll also delve into practical strategies for reducing your premiums and interpreting your monthly bill, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the healthcare landscape.
Definition of Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums are essentially the regular payments you make to your insurance company in exchange for the coverage they provide. Think of it like a membership fee – you pay consistently to access the benefits of the plan when you need them. These payments help the insurance company cover the costs of providing healthcare services to all its members.
Health insurance premiums are calculated based on a number of factors, and represent the cost of your health insurance plan. They are the monthly, quarterly, or annual payments you make to maintain your coverage. The amount you pay depends on several interconnected components, making each premium unique to the individual and the plan. These components contribute to the overall cost of the insurance and are factored into your premium calculation.
Premium Calculation Components
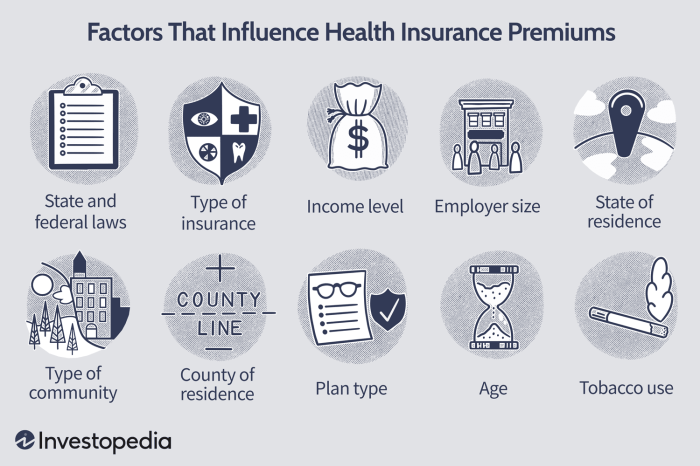
Several key factors influence the calculation of your health insurance premium. These factors are analyzed and weighted by the insurance company to determine your individual premium amount. A higher risk profile generally translates to a higher premium.
These factors include, but are not limited to: your age, your location (cost of healthcare varies geographically), your health status (pre-existing conditions can significantly impact premiums), your chosen plan (a comprehensive plan will be more expensive than a basic plan), your tobacco use (smokers often pay more), your family size (family plans usually cost more than individual plans), and the deductible and out-of-pocket maximum you choose (higher deductibles generally mean lower premiums, but you pay more out-of-pocket before insurance kicks in).
Hypothetical Premium Calculation Scenarios
Let’s illustrate premium calculation with some simplified examples. Keep in mind that real-world calculations are far more complex and involve sophisticated actuarial models.
Scenario 1: Imagine two individuals, both 30 years old, living in the same city. Person A is a non-smoker with no pre-existing conditions and chooses a plan with a $2,000 deductible. Person B is a smoker with a pre-existing condition (high blood pressure) and chooses the same plan. Person B’s premium will likely be significantly higher than Person A’s due to the increased risk associated with smoking and the pre-existing condition. The difference could be several hundred dollars per month.
Scenario 2: Consider two families, both with two adults and two children. Family A lives in a rural area with lower healthcare costs, while Family B lives in a major metropolitan area with higher healthcare costs. Even if they choose the same plan, Family B will likely pay higher premiums due to the higher cost of healthcare in their location. The difference could be a few hundred dollars per year.
Scenario 3: Two individuals, both 45 years old, non-smokers, and living in the same area, choose different plans. Person C selects a basic plan with a high deductible and a low monthly premium, while Person D chooses a comprehensive plan with a low deductible and a high monthly premium. Person D will pay more each month but will have lower out-of-pocket expenses when they need care.
It is important to note that these are simplified examples. Actual premium calculations involve numerous factors and sophisticated statistical models used by insurance companies.
Factors Affecting Premium Costs
Several interconnected factors influence the cost of health insurance premiums. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions when choosing a plan. This section will explore the key elements that contribute to premium variations.
Age’s Impact on Premium Costs
Age is a significant factor in determining health insurance premiums. Older individuals generally have higher premiums than younger individuals. This is because the risk of developing health issues increases with age, leading to potentially higher healthcare utilization and costs. Insurance companies use actuarial data to assess the likelihood of claims for different age groups, reflecting this increased risk in premium calculations. For example, a 60-year-old might pay significantly more than a 30-year-old for the same coverage due to the higher probability of needing more extensive medical care.
Health Status and Premium Costs
An individual’s health status plays a crucial role in premium determination. People with pre-existing conditions or a history of significant health issues typically face higher premiums. This is because they represent a higher risk to the insurance company, as they are more likely to require medical treatment and incur substantial healthcare expenses. Insurance companies assess medical history, including current conditions and past treatments, to gauge the potential cost associated with insuring an individual. Someone with a history of heart disease, for instance, will likely have a higher premium than someone with a clean bill of health.
Geographic Location and Premium Costs
The cost of healthcare varies considerably depending on geographic location. Premiums tend to be higher in areas with a higher cost of living and higher healthcare provider rates. Areas with a shortage of healthcare professionals or a high concentration of specialized medical facilities may also see elevated premiums. For instance, premiums in major metropolitan areas often exceed those in rural communities due to the higher cost of medical services and higher administrative expenses.
Premium Variations Across Different Health Insurance Plans
Different types of health insurance plans, such as HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations) and PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), offer varying levels of coverage and cost structures, resulting in different premium amounts. HMOs typically have lower premiums but restrict access to care to a specific network of providers. PPOs generally offer higher premiums but provide more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, including those outside the network, although at a higher cost. The trade-off between cost and flexibility is a key consideration when selecting a plan.
The Role of Deductibles, Co-pays, and Out-of-Pocket Maximums
Deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums significantly impact premium costs. A higher deductible (the amount you pay before your insurance coverage kicks in) usually translates to a lower premium. Conversely, a lower deductible often results in a higher premium. Co-pays (fixed fees paid at the time of service) and out-of-pocket maximums (the most you will pay out-of-pocket in a year) also influence premium calculations. Plans with lower co-pays and out-of-pocket maximums typically come with higher premiums. These cost-sharing mechanisms are designed to balance affordability and cost control.
Illustrative Table of Factors Influencing Premium Costs
| Factor | Low Cost Scenario | Medium Cost Scenario | High Cost Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 25 years | 40 years | 60 years |
| Health Status | Excellent health, no pre-existing conditions | Minor health issues, well-managed | Significant pre-existing conditions requiring ongoing treatment |
| Location | Rural area | Suburban area | Major metropolitan area |
| Plan Type | HMO with high deductible | PPO with moderate deductible | PPO with low deductible and comprehensive coverage |
| Estimated Monthly Premium | $200 | $400 | $800 |
Types of Health Insurance Plans and Their Premiums

Understanding the different types of health insurance plans is crucial because the type of plan you choose significantly impacts your monthly premium. Premiums vary widely based on factors like the plan’s coverage, your age, location, and health status. This section will explore these variations and provide a clearer picture of what you can expect to pay.
Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and cost-sharing. Generally, plans with lower monthly premiums often have higher out-of-pocket costs, such as deductibles and co-pays, while plans with higher premiums typically offer lower out-of-pocket expenses. The best plan for you will depend on your individual needs and risk tolerance.
Premium Cost Differences Between Various Health Insurance Plans
The cost of health insurance premiums varies considerably depending on the type of plan. Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) often have lower premiums than Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) because they typically restrict your choice of doctors and hospitals to a specific network. Point-of-Service (POS) plans fall somewhere in between, offering more flexibility than HMOs but less than PPOs, reflecting their premium costs. High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) usually have the lowest premiums but require you to pay a substantial amount out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Catastrophic plans, designed for young adults, have very low premiums but cover only catastrophic events.
Individual vs. Family Health Insurance Premiums
Family health insurance plans generally cost significantly more than individual plans. The added cost reflects the increased risk of needing healthcare services for multiple individuals. While the exact difference varies based on factors like the number of family members and their ages, it’s common to see family premiums exceeding individual premiums by a substantial margin – often double or even triple the cost. For example, an individual plan might cost $500 per month, while a family plan covering a spouse and two children could easily reach $1500 or more.
Common Health Insurance Plans and Their Premium Structures
The following table summarizes common health insurance plans and their typical premium structures. Keep in mind that these are generalizations, and actual premiums vary significantly based on location, insurer, and individual circumstances.
| Plan Type | Premium Structure | Typical Cost (Example – varies widely) |
|---|---|---|
| HMO | Generally lower premiums, limited network | $300 – $600 per month (individual) |
| PPO | Higher premiums, broader network | $500 – $1000 per month (individual) |
| POS | Moderate premiums, some network restrictions | $400 – $800 per month (individual) |
| HDHP | Lowest premiums, high deductible | $200 – $400 per month (individual) |
| Catastrophic | Very low premiums, limited coverage | Under $100 per month (individual) |
Employer-Sponsored vs. Individual Market Health Insurance Premiums
Employer-sponsored plans often have lower premiums than plans purchased on the individual market. This is because employers often negotiate group rates with insurance companies, leading to lower costs for employees. Additionally, employers may contribute a portion of the premium cost, further reducing the employee’s financial burden. Individual market plans, on the other hand, are purchased directly by individuals and are subject to the individual’s age, health status, and location, leading to higher premiums compared to group plans.
Comparison of Premium Structures for Various Plans
The following bullet points highlight key differences in premium structures across various plan types:
- HMOs: Typically offer the lowest premiums but restrict your choice of doctors and hospitals.
- PPOs: Offer higher premiums but provide greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- POS plans: Represent a middle ground between HMOs and PPOs in terms of both premiums and network restrictions.
- HDHPs: Feature the lowest premiums but have high deductibles, meaning you pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage begins.
- Family plans: Consistently cost more than individual plans, reflecting the increased risk associated with covering multiple individuals.
- Employer-sponsored plans: Generally offer lower premiums than individual market plans due to group discounts and potential employer contributions.
Understanding Your Health Insurance Premium Bill
Your health insurance premium bill, received monthly or annually, details the cost of your health insurance coverage. Understanding its components is crucial for managing your healthcare finances effectively. This section will break down the typical elements of a premium bill, offer strategies for cost management, and guide you in identifying potential errors.
Components of a Health Insurance Premium Bill
A typical health insurance premium bill includes several key components. These components vary slightly depending on your insurance provider and plan type, but generally include the premium amount itself, any applicable taxes, and potentially additional fees. Understanding each component allows for better budgeting and proactive management of your healthcare expenses.
Common Charges and Fees
Many factors contribute to the overall premium cost. Common charges and fees included in your premium may include the base premium, which reflects the cost of your chosen plan’s coverage level. Additional fees might encompass administrative costs incurred by the insurance company, state-mandated taxes, and possibly a surcharge if you are using tobacco products. Some plans might also include a monthly fee for dependent coverage. For instance, a family plan would naturally have a higher premium than an individual plan due to the increased coverage provided.
Strategies for Understanding and Managing Health Insurance Costs
Effective management of health insurance costs involves several key strategies. Firstly, carefully review your plan’s summary of benefits and coverage (SBC) to understand what’s included and excluded. Secondly, actively compare different plans available to you to find the best value for your needs. Thirdly, consider enrolling in a Health Savings Account (HSA) or Flexible Spending Account (FSA) to set aside pre-tax dollars for medical expenses. Finally, maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce potential healthcare needs and therefore, lower overall costs. For example, choosing a plan with a higher deductible but lower premium can be a cost-effective strategy if you are generally healthy and anticipate few medical expenses.
Identifying Potential Errors or Discrepancies
Regularly reviewing your health insurance premium bill is essential for identifying potential errors or discrepancies. Check that the amount billed matches your plan’s stated premium. Verify that any additional fees or taxes are accurately reflected and are in line with your plan’s terms. If you find any inconsistencies, immediately contact your insurance provider to clarify and resolve the issue. Discrepancies might include incorrect application of discounts, inaccurate calculation of taxes, or misreporting of dependent coverage.
Sample Health Insurance Premium Bill
| Description | Amount | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Premium | $300 | October 26, 2024 | Covers individual plan |
| State Tax | $15 | October 26, 2024 | Standard state tax |
| Administrative Fee | $5 | October 26, 2024 | Insurance company fee |
| Total Premium | $320 | October 26, 2024 | Due by November 15, 2024 |
Strategies for Lowering Health Insurance Premiums
High health insurance premiums can be a significant financial burden. Fortunately, several strategies can help individuals and families reduce their costs. Understanding these options and taking proactive steps can lead to considerable savings over time.
Negotiating Lower Premiums with Insurance Providers
Directly contacting your insurance provider to discuss your premium is a viable option. Many insurers are willing to work with their customers, especially those with a history of consistent payments and a clean claims record. Highlighting your commitment to responsible healthcare utilization and exploring options like increasing your deductible or opting for a higher copay can demonstrate your willingness to share the cost. Be prepared to discuss your specific circumstances and explore alternative plan options they may offer. Some insurers may offer discounts for enrolling in automatic payments or bundling insurance products.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle to Influence Premiums
A healthy lifestyle can significantly impact your health insurance premiums. Insurers often reward individuals who actively manage their health through wellness programs and discounts. These programs frequently include incentives for preventative care like annual checkups, vaccinations, and screenings. By participating in such programs and maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and engaging in regular physical activity, you demonstrate a reduced risk profile, which can lead to lower premiums. Some insurers even offer wearable device integration to track fitness goals and reward healthy habits. For instance, an insurer might offer a discount for consistently meeting step goals or maintaining a healthy weight range.
Choosing a Cost-Effective Health Insurance Plan
Selecting the right health insurance plan is crucial for managing premium costs. Understanding the differences between HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), and EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations) is essential. HMOs generally offer lower premiums but restrict access to care within a network of providers. PPOs provide more flexibility in choosing providers but usually come with higher premiums. EPOs are a hybrid offering some flexibility but with a stricter network than PPOs. Carefully comparing the deductible, copay, and out-of-pocket maximum for each plan is critical. A higher deductible typically translates to lower premiums, but you’ll pay more upfront before insurance coverage kicks in. Conversely, a lower deductible will mean higher premiums.
Comparing Health Insurance Plans for Affordability: A Step-by-Step Guide
Finding the most affordable health insurance plan requires a systematic approach.
- Assess your needs: Determine your healthcare needs and usage patterns. Consider factors like pre-existing conditions, frequency of doctor visits, and potential need for specialized care.
- Use online comparison tools: Many websites, including those run by state insurance marketplaces, allow you to compare plans side-by-side based on factors such as premium, deductible, copay, and network coverage. Healthcare.gov is a prime example for those eligible for subsidies.
- Review plan details carefully: Don’t just focus on the premium. Thoroughly examine the deductible, out-of-pocket maximum, copay amounts, and the provider network to ensure the plan aligns with your healthcare needs and budget. Pay close attention to what services are covered and any limitations.
- Consider your employer’s plan: If you have employer-sponsored insurance, carefully compare the options available through your employer’s plan with those available on the open market. You may find that your employer’s plan offers better coverage or lower premiums.
- Factor in potential tax credits and subsidies: If you qualify, explore government subsidies and tax credits that can significantly reduce your premium costs. These are often available through state and federal marketplaces.
The Role of Government Subsidies and Tax Credits
Government subsidies and tax credits play a crucial role in making health insurance more accessible and affordable for many individuals and families. These programs, often administered at the federal and state levels, reduce the out-of-pocket costs associated with health insurance premiums, making coverage attainable for those who might otherwise struggle to afford it. The specifics of these programs vary depending on location and eligibility criteria.
Eligibility Requirements for Government Assistance Programs
These programs are designed to assist individuals and families with limited incomes. Eligibility is generally determined by factors such as income, household size, and citizenship status. Specific income thresholds vary depending on the program and location. For instance, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplace offers subsidies based on a sliding scale tied to the Federal Poverty Level (FPL). Those with incomes below a certain percentage of the FPL may qualify for substantial premium assistance, while those with higher incomes might receive smaller subsidies or none at all. State-specific programs may have additional eligibility criteria, such as residency requirements or specific health conditions.
Impact of Subsidies and Credits on Premium Costs
Government subsidies directly reduce the amount an individual or family pays for their monthly health insurance premium. Tax credits, on the other hand, reduce the amount of income tax owed, effectively lowering the overall cost of insurance. The amount of the subsidy or credit depends on the individual’s income and the cost of the chosen health insurance plan. For example, an individual with an income of $30,000 might receive a $200 monthly subsidy, reducing their premium from $400 to $200. A family earning $50,000 might receive a $300 monthly subsidy and a $1,000 annual tax credit, significantly decreasing their total health insurance expenses for the year. It’s important to note that these amounts are illustrative examples; actual subsidies and credits vary widely.
Examples of Premium Reduction Through Government Programs
Consider a single mother with two children earning $25,000 annually. Without government assistance, a suitable health insurance plan might cost $800 per month, making it financially unattainable. Through the ACA Marketplace, she might qualify for a $500 monthly subsidy, reducing her monthly premium to $300. This makes health insurance affordable and allows her to access necessary medical care for herself and her children. Another example could involve a self-employed individual with a fluctuating income. During a period of lower income, they might qualify for a significant premium subsidy, ensuring they maintain continuous health coverage even during financial hardship. These programs help bridge the gap between the cost of insurance and the individual’s ability to pay, fostering better health outcomes by ensuring access to necessary care.
Outcome Summary

Ultimately, understanding health insurance premiums is key to securing affordable and appropriate healthcare coverage. By grasping the factors that influence premium costs, exploring various plan options, and implementing cost-saving strategies, you can take control of your healthcare expenses. This guide serves as a foundational resource, empowering you to make informed decisions and confidently navigate the complexities of health insurance.
FAQ Summary
What happens if I miss a premium payment?
Missing a premium payment may result in your coverage being suspended or cancelled. Contact your insurance provider immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment to explore options like payment plans or hardship waivers.
Can I change my health insurance plan during the year?
Generally, you can only change your health insurance plan during open enrollment periods, unless you experience a qualifying life event (like marriage, divorce, or job loss) that allows for a special enrollment period.
What is a pre-existing condition, and how does it affect my premiums?
A pre-existing condition is a health issue you had before starting your health insurance coverage. Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), insurance companies cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions.
How are my premiums affected if I use my health insurance frequently?
While frequent use of your health insurance might not directly increase your premiums in the short term, it could influence your future premiums if your claims history reflects higher healthcare utilization.