Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. Understanding what constitutes a monthly premium, and how it impacts your healthcare access, is crucial for making informed decisions. This guide demystifies monthly premium health insurance, exploring its components, variations, and the factors that influence its cost. We’ll delve into different plan types, helping you choose the best fit for your needs and budget.
From understanding your policy document to effectively utilizing your coverage and navigating the healthcare system, we aim to provide a clear and concise understanding of monthly premium health insurance. We’ll also compare providers and address common questions to empower you with the knowledge needed to confidently manage your healthcare expenses.
Defining Monthly Premium Health Insurance
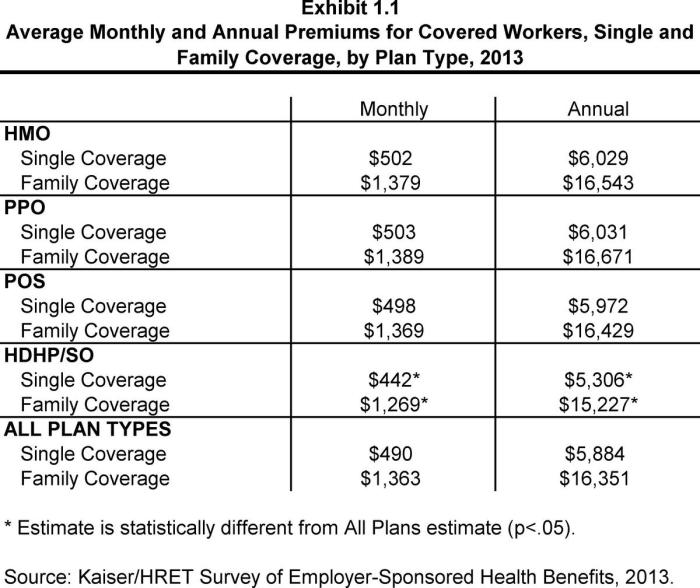
Monthly premium health insurance is a type of health insurance plan where you pay a fixed amount each month in exchange for coverage of medical expenses. This regular payment ensures access to a wide range of healthcare services, reducing the financial burden of unexpected medical costs. Understanding the components and factors that influence these monthly payments is crucial for choosing a suitable plan.
Components of a Monthly Premium
Several factors contribute to the calculation of your monthly health insurance premium. These components are often intertwined and influence each other. The insurer considers a variety of aspects to determine the final cost.
The insurer uses actuarial data to determine the likelihood of claims based on demographics, health history, and location. Administrative costs, including salaries, technology, and marketing, are also factored into the premium. The level of coverage offered (e.g., basic, comprehensive) significantly affects the premium; more extensive coverage generally leads to higher monthly payments. Finally, the insurer’s profit margin is incorporated to ensure the financial viability of the company.
Factors Influencing Monthly Premium Costs
Numerous factors influence the cost of monthly health insurance premiums. Individual characteristics play a significant role, such as age, health status, and lifestyle choices. Geographic location also matters, as healthcare costs vary significantly across different regions. The type of plan selected, such as HMO, PPO, or POS, will also impact the premium amount. Finally, the deductible, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximum all influence the overall cost, although not directly reflected in the monthly premium itself. A higher deductible, for instance, often translates to a lower monthly premium.
Premium Comparison Across Age Groups
The following table illustrates how age can significantly influence monthly premiums. These figures are hypothetical and serve only as an example; actual premiums vary widely based on the factors mentioned previously.
| Age Range | Individual Plan (Hypothetical) | Family Plan (Hypothetical) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | $250 | $600 | Lower premiums due to generally lower healthcare utilization. |
| 26-35 | $350 | $800 | Premiums increase as the likelihood of needing healthcare rises. |
| 36-45 | $450 | $1000 | Further increase due to potential for chronic conditions and family growth. |
| 46-55 | $600 | $1300 | Premiums rise considerably as the risk of major health issues increases. |
Navigating the Healthcare System with Monthly Premiums
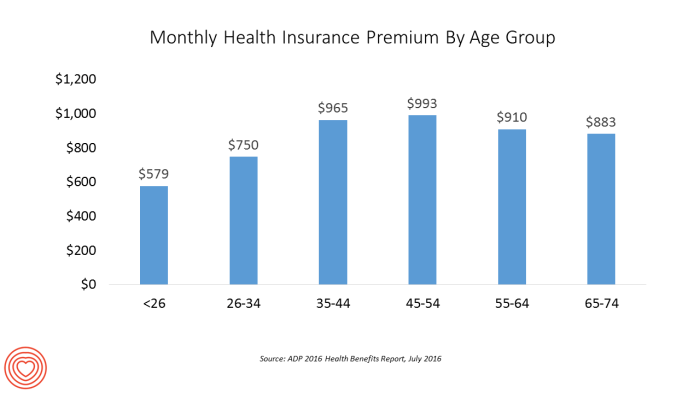
Having health insurance with monthly premiums provides access to a complex yet vital system. Understanding how to effectively utilize your plan is key to maximizing its benefits and minimizing out-of-pocket expenses. This section will guide you through the process of navigating the healthcare system with your monthly premium health insurance.
Utilizing Health Insurance Effectively
Effective utilization of your health insurance involves proactive engagement with your plan. This includes understanding your coverage details, choosing in-network providers whenever possible, and actively participating in preventative care. Preventive care, such as annual checkups and screenings, often has little to no cost-sharing under most plans, significantly contributing to long-term health and cost savings. Choosing in-network providers ensures you benefit from negotiated rates and avoid higher out-of-pocket expenses. Regularly reviewing your Explanation of Benefits (EOB) statements will help you understand the billing process and identify any discrepancies.
Filing Claims and Understanding Reimbursements
The claims process typically involves submitting documentation of your medical services to your insurance provider. This documentation usually includes a claim form completed by your healthcare provider and any supporting medical records. Upon receipt, your insurer processes the claim, verifying coverage and applying any applicable deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. The reimbursement amount is then calculated and sent to you or directly to your provider, depending on your plan’s structure. Understanding your plan’s specific claim procedures is essential for timely reimbursement. Many insurers offer online portals and mobile apps that simplify claim submission and tracking. For example, a common scenario involves submitting a claim for a doctor’s visit. The provider will provide a superbill, which is then submitted to the insurance company. The insurance company processes this, applying the appropriate cost-sharing, and sends a remittance to the provider or the insured.
Crucial Scenarios for Health Insurance
Health insurance is vital in numerous situations, significantly reducing financial burden during unexpected health crises. Major illnesses, accidents, and chronic conditions can generate substantial medical expenses. For example, a serious car accident resulting in hospitalization and rehabilitation could easily incur hundreds of thousands of dollars in medical bills. Health insurance dramatically mitigates this risk. Similarly, unexpected pregnancies and childbirth, or the diagnosis and treatment of a chronic disease like diabetes, are scenarios where the financial protection offered by insurance is invaluable. Preventative care, while seemingly less urgent, is also crucial. Early detection of diseases like cancer through screenings can lead to more effective and less costly treatment, highlighting the importance of comprehensive coverage.
Accessing Essential Coverage Information
Your insurance policy documents, often available online, contain comprehensive details of your coverage. This includes your plan’s deductible, copay amounts, coinsurance percentage, and the list of covered services. Your insurer’s website typically offers a member portal, allowing access to your plan summary, claims history, and provider directory. The member services phone number provides direct access to customer support for addressing specific queries or resolving issues related to your coverage. Understanding your policy’s terms and conditions is vital to making informed healthcare decisions and avoiding unexpected costs. Regularly checking your policy information ensures you remain aware of any changes or updates to your coverage.
Final Summary

Securing affordable and comprehensive health insurance is a cornerstone of financial well-being. This guide has provided a framework for understanding monthly premium health insurance, from defining the core concepts to navigating the complexities of choosing a plan and utilizing your coverage effectively. Remember, proactive engagement with your policy and a clear understanding of your provider’s services are key to maximizing your healthcare benefits and minimizing unexpected costs. By being informed and prepared, you can confidently navigate the healthcare system and prioritize your health.
Questions and Answers
What happens if I miss a monthly premium payment?
Missing a payment can lead to a lapse in coverage, meaning you’ll be responsible for all medical expenses until your payment is reinstated. Late fees may also apply. Contact your provider immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment.
Can I change my health insurance plan during the year?
Generally, you can only change plans during the annual open enrollment period, unless you experience a qualifying life event (e.g., marriage, job loss). Check with your provider for specific details.
What is a deductible and how does it work?
A deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance begins to pay. Once you meet your deductible, your co-pays and coinsurance will apply.
What is the difference between co-pay and coinsurance?
A co-pay is a fixed amount you pay for a doctor’s visit or other service. Coinsurance is a percentage of the cost you pay after meeting your deductible.