Securing your financial legacy is a paramount concern, and understanding life insurance is a crucial step in that process. Single premium life insurance offers a unique approach to financial planning, providing a substantial death benefit with a single upfront payment. This guide delves into the intricacies of single premium life insurance, empowering you to navigate the complexities of planning for your future with confidence and clarity, using the invaluable tool: the single premium life insurance calculator.
This comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge to understand how these calculators function, the factors influencing premium costs, and how to effectively utilize them to make informed decisions. We’ll explore various scenarios, highlighting the benefits and potential pitfalls to ensure you’re well-prepared for this significant financial commitment.
How Single Premium Life Insurance Calculators Work
Single premium life insurance calculators are sophisticated tools that estimate the cost of a life insurance policy paid for with a single, upfront payment. They leverage actuarial science and complex mathematical models to determine the appropriate premium based on various individual factors. Understanding how these calculators work provides valuable insight into the process of securing life insurance.
Underlying Mathematical Models
These calculators primarily utilize life expectancy tables and mortality rates to assess the risk associated with insuring an individual. These tables, compiled by actuaries and insurance companies, provide statistical probabilities of death at various ages and health conditions. The calculator also incorporates interest rate assumptions, reflecting the anticipated return on the insurer’s investment of the premium. Essentially, the calculation balances the probability of the insurer having to pay a death benefit against the investment income generated from the premium. A key element is the present value calculation, discounting future payouts (death benefit) to their current worth. This accounts for the time value of money – a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. The formula is complex and varies slightly between insurers but generally involves calculating the present value of expected future payouts and adjusting this value for risk and profit margins.
Input Variables and Their Impact
Several key variables influence the premium calculation. These include:
- Age: Older applicants generally face higher premiums due to a statistically higher probability of death within the policy’s term.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions or unhealthy lifestyles typically pay higher premiums because they pose a greater risk to the insurer.
- Desired Death Benefit: A larger death benefit necessitates a larger premium, as the insurer needs to set aside more funds to cover the potential payout.
- Policy Type: Different policy types (e.g., whole life, term life) carry varying levels of risk and therefore impact the premium.
- Gender: Historically, actuarial tables have shown differences in life expectancy between genders, impacting premium calculations. However, this is becoming less significant due to evolving actuarial practices and legal considerations.
The interplay of these variables is complex. For instance, a 45-year-old male in excellent health seeking a $500,000 whole life policy will likely pay a significantly lower premium than a 60-year-old female with a pre-existing condition seeking the same coverage.
Step-by-Step Calculation Example
Let’s consider a hypothetical example: A 35-year-old male in good health wants a $1 million single premium whole life insurance policy.
1. Mortality Data: The calculator accesses mortality tables to determine the probability of death for a 35-year-old male in good health over various time periods.
2. Interest Rate Assumption: The calculator uses a projected interest rate (e.g., 4%) to calculate the future value of the premium.
3. Present Value Calculation: The calculator determines the present value of the potential future death benefit payout, discounted by the assumed interest rate.
4. Risk and Profit Margin: The insurer adds a margin to cover operational costs, potential unforeseen events, and profit. This margin is factored into the final premium.
5. Premium Calculation: The calculator sums the present value of the death benefit and the insurer’s margin, arriving at the single premium amount. This might be, for example, $250,000.
It is important to note that this is a simplified example; the actual calculations involve sophisticated actuarial models and numerous variables.
Data Flow in a Single Premium Life Insurance Calculator
A flowchart illustrating the data flow might look like this:
[Description of Flowchart: The flowchart begins with inputting the applicant’s details (age, gender, health, desired death benefit, policy type). This data feeds into a module that accesses actuarial tables and mortality data. Simultaneously, an interest rate is inputted. These data points are then processed through a present value calculation module. A separate module adds the insurer’s risk and profit margin. Finally, these results are combined to generate the single premium amount, which is then displayed to the user.]
Factors Affecting Single Premium Costs
Several key factors interact to determine the cost of a single premium life insurance policy. Understanding these factors allows for a more informed decision when purchasing this type of coverage. The price isn’t simply a fixed number; it’s a calculation based on your individual circumstances and the insurer’s risk assessment.
Age and Health
Your age and health status significantly impact the premium. Older applicants generally pay more because they have a statistically higher likelihood of claiming benefits within the policy’s term. Similarly, individuals with pre-existing health conditions or a family history of certain illnesses will usually face higher premiums due to the increased risk the insurer assumes. For example, a 30-year-old in excellent health will receive a substantially lower premium than a 60-year-old with a history of heart disease. The insurer uses actuarial tables and sophisticated risk models to assess these factors.
Insurance Provider Variations
Premiums vary considerably between insurance providers. Each company uses its own proprietary risk assessment models and pricing strategies. Some insurers might specialize in specific demographics or risk profiles, leading to price differences. Competitive market forces also play a role, with some companies offering more aggressive pricing to attract customers. It’s crucial to compare quotes from multiple insurers to find the most competitive option. For instance, one insurer might prioritize low premiums for younger, healthier individuals, while another may focus on providing competitive rates for older applicants.
Policy Type and Features
The type of single premium life insurance policy and its included features also influence the cost. A whole life policy, providing lifelong coverage, will naturally be more expensive than a term life policy, which offers coverage for a specific period. Additional features, such as riders offering accelerated death benefits or long-term care coverage, will increase the overall premium. A policy with a higher death benefit will also command a higher premium.
Prioritized List of Factors
The following list prioritizes the factors influencing single premium costs based on their typical impact:
- Age: Age is generally the most significant factor, with premiums increasing exponentially as the applicant ages.
- Health Status: Pre-existing conditions and family medical history significantly affect the risk assessment and, consequently, the premium.
- Policy Type and Features: The type of policy (whole life vs. term) and the inclusion of riders directly impact the premium amount.
- Insurance Provider: Variations in pricing strategies between different insurance providers can lead to noticeable differences in premiums.
Using a Single Premium Life Insurance Calculator Effectively
A single premium life insurance calculator is a powerful tool, but its effectiveness hinges on understanding how to use it correctly. Choosing the right calculator and interpreting its results accurately are crucial steps in making an informed financial decision. This section details how to maximize the benefits of these calculators and avoid potential pitfalls.
Selecting the Appropriate Calculator
The market offers various single premium life insurance calculators, each with its own features and limitations. The ideal calculator will depend on individual needs and the complexity of the desired calculation. Simpler calculators might suffice for straightforward estimations, while more sophisticated tools may be necessary for scenarios involving complex financial situations or specific insurance product features. Consider factors such as the type of policy (term, whole, universal life etc.), the inclusion of riders (additional benefits), and the level of customization offered. For instance, a calculator that only considers age and death benefit might be insufficient for someone planning for estate taxes or wanting to incorporate investment growth projections. A calculator offering greater flexibility and detail would be more suitable in such cases.
Interpreting Calculator Results and Understanding Implications
Calculator results typically provide an estimated premium amount based on the input parameters. It’s vital to understand that these are estimates, not guarantees. The quoted premium reflects the insurer’s assessment of risk based on the information provided. Variations in underwriting criteria across different companies might lead to slightly different premiums for the same individual. The results should be seen as a starting point for further investigation, not a final decision. Consider reviewing the policy’s terms and conditions carefully before making a purchase. For example, a calculator might show a premium of $50,000 for a $1 million death benefit. However, the actual premium offered by an insurer could vary based on their specific underwriting guidelines and current market conditions. Factors such as health status, lifestyle, and occupation can all influence the final premium.
Utilizing Calculator Features: Benefit Adjustments
Many calculators allow for adjustments to the death benefit amount. This feature is useful for exploring the relationship between the premium and the desired coverage. By increasing or decreasing the death benefit, users can observe the corresponding impact on the premium. This iterative process helps determine the optimal balance between coverage and cost. For example, reducing the death benefit by 10% might significantly lower the premium, while still providing substantial financial protection for beneficiaries. Similarly, exploring the impact of adding riders, such as accelerated death benefits or long-term care riders, will allow for a more comprehensive understanding of the overall cost and value proposition. Note that adding riders typically increases the premium.
Checklist Before Purchasing Single Premium Life Insurance
Before finalizing a purchase based on calculator results, a thorough review is essential. This checklist will help ensure you’ve considered all relevant factors:
- Verify the calculator’s accuracy: Compare results from multiple calculators to ensure consistency.
- Consult a financial advisor: Seek professional advice to tailor the policy to your specific financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Review policy documents: Carefully examine the policy’s terms and conditions, including exclusions and limitations.
- Compare quotes from multiple insurers: Don’t rely on a single quote; shop around for the best rates and coverage.
- Assess your long-term financial goals: Ensure the policy aligns with your overall financial plan and objectives.
- Consider tax implications: Understand the tax implications of owning and potentially cashing out the policy.
Illustrative Examples and Scenarios
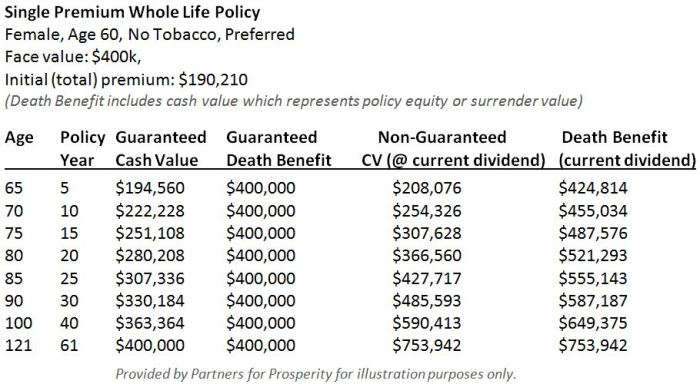
Understanding how a single premium life insurance calculator works is best illustrated through real-world examples. The following scenarios demonstrate how different individuals might utilize the calculator and the potential outcomes. Remember, these are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary based on individual circumstances and the insurer’s specific underwriting guidelines.
The following scenarios highlight the diverse applications of single premium life insurance, emphasizing the varying needs and financial situations of different individuals. Each example will detail the input parameters used in a hypothetical calculator and the resulting premium, followed by an analysis of the long-term financial implications.
Young Professional Scenario
This scenario focuses on a 30-year-old young professional, aiming to secure their financial future and protect their family in case of unexpected events.
- Input Parameters: Age: 30; Desired Death Benefit: $500,000; Policy Term: 20 years; Health Status: Excellent.
- Resulting Premium: Approximately $60,000 (This is a hypothetical example and actual premiums will vary).
- Financial Implications and Long-Term Benefits: A single premium payment provides peace of mind knowing a substantial death benefit is in place to protect loved ones or settle debts. The investment aspect provides a potentially higher return than alternative savings methods. The young professional’s risk tolerance is high and they are comfortable with the one-time, substantial investment.
Descriptive Image: A vibrant image depicting a young professional, perhaps in a modern office setting, confidently working on their laptop. A subtle visual element, like a graph showing upward financial trajectory, could represent the long-term growth potential. The overall tone is optimistic and forward-looking.
Retiree Scenario
This scenario illustrates how a retiree might use a single premium life insurance calculator to leave a legacy and ensure financial security for their heirs.
- Input Parameters: Age: 65; Desired Death Benefit: $250,000; Policy Term: Until death; Health Status: Good.
- Resulting Premium: Approximately $80,000 (This is a hypothetical example and actual premiums will vary).
- Financial Implications and Long-Term Benefits: The retiree secures a death benefit to cover estate taxes, funeral expenses, and provide an inheritance for their family without impacting their current retirement income. This offers peace of mind knowing their loved ones are financially protected.
Descriptive Image: A serene image depicting a retired couple enjoying their golden years. Perhaps they are sitting on a porch, surrounded by flowers, with a gentle sun setting in the background. A subtle visual element, like a photograph of their family, could represent the legacy they are leaving behind.
Family with Young Children Scenario
This scenario highlights the use of single premium life insurance by a family with young children to provide financial security in case of the untimely death of a parent.
- Input Parameters: Age: 35 (primary insured); Desired Death Benefit: $1,000,000; Policy Term: Until death; Health Status: Average.
- Resulting Premium: Approximately $120,000 (This is a hypothetical example and actual premiums will vary).
- Financial Implications and Long-Term Benefits: The large death benefit ensures the family’s financial stability, covering mortgage payments, children’s education, and living expenses. The one-time payment simplifies financial planning and eliminates the need for future premium payments.
Descriptive Image: A heartwarming image of a family with young children, possibly at a park or playing together at home. The image should convey a sense of family unity and security. A subtle visual element, like a house or a school, could represent the long-term financial security provided by the insurance.
Potential Pitfalls and Considerations

While online single premium life insurance calculators offer a convenient way to estimate costs, it’s crucial to understand their limitations and potential drawbacks. Relying solely on these tools without professional guidance can lead to suboptimal decisions and potentially significant financial consequences. Understanding these limitations is key to making informed choices.
Using a calculator alone presents several potential pitfalls. These tools typically provide estimates based on the data you input, and inaccuracies in this data will directly affect the result. Furthermore, calculators may not account for all relevant factors influencing premiums, such as your health status beyond basic information or specific policy features. They also generally lack the ability to provide personalized financial advice tailored to your unique circumstances.
Limitations of Online Calculators
Online calculators offer a simplified view of a complex financial product. They often rely on generalized assumptions and may not reflect the nuances of individual situations. For example, a calculator might not accurately predict the impact of pre-existing health conditions or specific lifestyle factors on premium calculations. Moreover, the range of policy options available can be vast, and a calculator may not encompass the full spectrum of choices. It’s essential to remember that these tools are designed for estimation purposes only, and the actual premium may differ from the calculated amount.
Importance of Consulting a Financial Advisor
A financial advisor brings a wealth of experience and expertise to the process. They can assess your individual financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals to recommend the most suitable life insurance policy. This personalized approach goes beyond the limitations of an online calculator, ensuring that the chosen policy aligns with your overall financial strategy. A financial advisor can also explain complex policy features and help you navigate the often-confusing world of insurance options. They can help you understand the implications of various policy choices, compare different insurers, and ensure you are getting the best value for your investment.
Avoiding Common Mistakes When Using Calculators
Several common mistakes can significantly impact the accuracy of the results obtained from single premium life insurance calculators. Inputting inaccurate or incomplete information is a major pitfall. For instance, failing to accurately reflect your age, health status, or smoking habits can lead to a misleading estimate. Another common mistake is overlooking the impact of various policy riders or additional features, which can influence the final premium. Finally, relying solely on the calculator’s output without considering your individual financial goals and circumstances can result in a poor decision.
Warnings and Cautions Regarding Online Calculators
- Online calculators provide estimates only; actual premiums may vary.
- Inputting inaccurate information can lead to significantly flawed results.
- Calculators may not account for all relevant factors influencing premiums.
- They cannot provide personalized financial advice or consider individual circumstances.
- Do not make critical financial decisions based solely on calculator outputs.
- Always consult with a qualified financial advisor before purchasing a single premium life insurance policy.
Closing Summary
Ultimately, utilizing a single premium life insurance calculator is a powerful tool for proactive financial planning. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, considering all relevant factors, and seeking professional advice when needed, you can confidently navigate the process of securing your family’s financial future. Remember, careful consideration and informed decision-making are key to maximizing the benefits of single premium life insurance.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between a single premium and a regular premium life insurance policy?
A single premium policy requires one lump-sum payment, while a regular premium policy involves recurring payments over time. The single premium offers immediate coverage, while regular premium policies build cash value over time.
Can I adjust the death benefit after purchasing a single premium life insurance policy?
The ability to adjust the death benefit after purchase varies depending on the policy and insurer. Some policies allow for increases, while others may not offer any adjustments.
Are there tax implications associated with single premium life insurance?
Yes, there can be tax implications. Consult a tax professional to understand the potential tax consequences in your specific situation.
What happens if my health changes after purchasing a single premium life insurance policy?
Your policy remains in effect, but your health status is generally not reevaluated. Pre-existing conditions are typically covered.
How accurate are online single premium life insurance calculators?
Online calculators provide estimates based on the input data. They are helpful tools, but it’s crucial to remember they are not a substitute for professional financial advice. Individual circumstances can significantly impact the final premium.