Navigating the complexities of medical insurance can feel like deciphering a foreign language. Understanding your medical insurance monthly premium is crucial for budgeting and ensuring you receive the healthcare coverage you need. This guide unravels the mystery behind those monthly payments, exploring the factors that influence their cost, the components that make up the premium, and strategies to potentially reduce your expenses. We’ll delve into the intricacies of deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your healthcare plan.
From the impact of age and pre-existing conditions to the role of lifestyle choices and geographic location, we’ll examine the various elements that contribute to the final premium amount. We’ll also explore ways to find affordable plans, negotiate lower premiums, and ultimately, gain control over your healthcare costs. This guide serves as your roadmap to understanding and managing your medical insurance monthly premium effectively.
Factors Influencing Medical Insurance Monthly Premiums
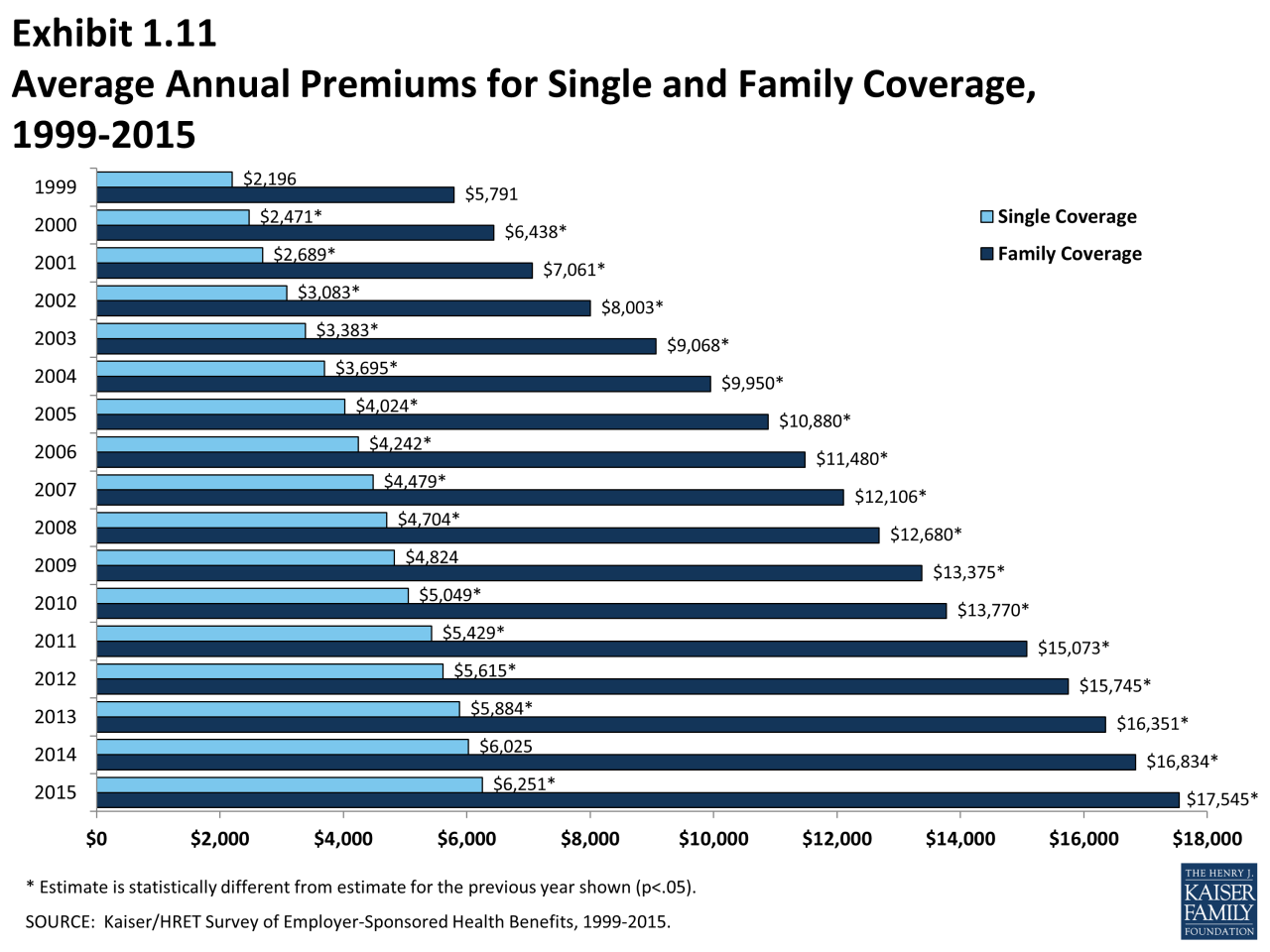
Understanding the factors that determine your monthly medical insurance premium is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. Several key elements contribute to the final cost, and it’s important to consider them when choosing a plan.
Age and Premium Costs
Age is a significant factor influencing premium costs. Generally, older individuals pay more for insurance than younger individuals. This is because the risk of needing more extensive medical care increases with age. Insurance companies base their premiums on actuarial data, which reflects the statistically higher healthcare utilization among older populations. For example, a 60-year-old might pay significantly more than a 30-year-old for the same coverage level, even if both are in excellent health.
Pre-existing Conditions and Premiums
Pre-existing conditions, or health issues you had before obtaining insurance, can significantly impact your premium. Insurers assess the potential cost of treating these conditions when calculating your premium. Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, often face higher premiums because these conditions statistically lead to greater healthcare expenses. However, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in many countries helps mitigate this impact by prohibiting insurers from denying coverage or charging exorbitant rates solely based on pre-existing conditions. The extent of this protection varies depending on the specific regulations in your region.
Geographic Location and Premium Variation
Geographic location plays a crucial role in determining premium costs. Premiums vary widely across different states and even within regions of a state. Areas with higher costs of living, higher healthcare provider salaries, and greater demand for medical services typically have higher premiums. For instance, someone living in a major metropolitan area with a high concentration of specialists might pay considerably more than someone living in a rural area with limited access to specialized care.
Lifestyle Choices and Premium Impact
Lifestyle choices such as smoking and lack of exercise can influence your premiums. Smokers, for instance, often face higher premiums than non-smokers due to the increased risk of smoking-related illnesses. Similarly, individuals who lead sedentary lifestyles and have poor health habits may pay more because of the higher probability of developing health problems requiring medical attention. Conversely, individuals who maintain a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise and a balanced diet may qualify for discounts or lower premiums with some insurers.
Coverage Levels and Monthly Costs
Different coverage levels, often categorized as bronze, silver, gold, and platinum, directly impact your monthly premiums. Bronze plans typically have the lowest monthly premiums but the highest out-of-pocket costs. As you move up the scale to silver, gold, and platinum, monthly premiums increase, but your out-of-pocket expenses decrease. The choice depends on your risk tolerance and financial situation. For example, a bronze plan might have a monthly premium of $200 but a high deductible of $6,000, while a gold plan might have a monthly premium of $500 but a much lower deductible of $1,000.
Individual vs. Family Plan Premiums
The following table compares average monthly premiums for individual and family plans, highlighting the differences based on coverage level and age range. These are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary based on location, insurer, and specific plan details.
| Plan Type | Coverage Level | Age Range | Average Monthly Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual | Bronze | 25-34 | $350 |
| Individual | Gold | 45-54 | $600 |
| Family | Silver | 35-44 | $1200 |
| Family | Platinum | 55-64 | $1800 |
The Role of Deductibles, Co-pays, and Out-of-Pocket Maximums

Understanding deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums is crucial for navigating the complexities of medical insurance and making informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. These three elements significantly impact your overall healthcare costs and your financial responsibility for medical expenses.
The Relationship Between Deductibles and Monthly Premiums
Deductibles and monthly premiums have an inverse relationship. A higher deductible generally results in a lower monthly premium, and vice versa. This is because a higher deductible means the insurance company pays out less frequently, allowing them to offer a lower monthly cost. Conversely, a lower deductible, meaning you pay less out-of-pocket before the insurance kicks in, results in a higher monthly premium as the insurer anticipates more frequent payouts. The choice depends on your risk tolerance and financial situation; someone who rarely needs medical care might opt for a high deductible and low premium, while someone with frequent health concerns might prefer a lower deductible and higher premium.
The Effect of Co-pays on Overall Healthcare Spending
Co-pays are fixed amounts you pay for specific medical services, such as doctor visits or prescription drugs. While seemingly small individually, co-pays contribute to your overall healthcare spending throughout the year. The frequency of your healthcare needs directly impacts the total cost of your co-pays. For example, someone with chronic conditions requiring regular doctor visits will pay significantly more in co-pays annually than someone who rarely seeks medical attention. The cumulative effect of co-pays can be substantial, especially for individuals or families with multiple members requiring regular healthcare.
The Function of an Out-of-Pocket Maximum in Protecting Against High Medical Costs
The out-of-pocket maximum is the most you will pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare expenses in a given plan year. Once this limit is reached, your insurance company covers 100% of the remaining eligible expenses. This acts as a crucial financial safety net, preventing catastrophic medical bills from bankrupting individuals or families. The out-of-pocket maximum is particularly important for individuals facing expensive treatments or unexpected illnesses.
Impact of Different Combinations of Deductibles, Co-pays, and Out-of-Pocket Maximums on Total Annual Healthcare Expenses
The interplay between deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums significantly influences total annual healthcare expenses. A high deductible plan with low co-pays might seem attractive initially, but a significant illness could lead to substantial out-of-pocket expenses before the out-of-pocket maximum is reached. Conversely, a low deductible plan with high co-pays might result in lower upfront costs but higher ongoing expenses due to the frequent co-pay payments. The optimal combination depends on individual circumstances and risk assessment.
Examples of Financial Implications Under Various Scenarios
Let’s consider three hypothetical scenarios for a single individual:
| Scenario | Deductible | Co-pay (Doctor Visit) | Out-of-Pocket Maximum | Annual Healthcare Expenses (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Deductible Plan | $5,000 | $30 | $6,000 | $6,000 (Assuming expenses exceed deductible but remain below OOM) |
| Moderate Deductible Plan | $2,000 | $50 | $4,000 | $3,500 (Assuming 10 doctor visits and expenses below OOM) |
| Low Deductible Plan | $500 | $75 | $2,500 | $2,000 (Assuming 15 doctor visits and expenses below OOM) |
These examples demonstrate how different plan structures can result in vastly different annual costs, even with similar levels of healthcare utilization. It is crucial to carefully consider your individual needs and financial situation when selecting a plan.
Ultimate Conclusion

Ultimately, understanding your medical insurance monthly premium is key to responsible healthcare planning. By understanding the factors that influence its cost, the components that comprise it, and the strategies for managing expenses, you can make informed decisions that align with your budget and healthcare needs. Remember to regularly review your plan and explore options to optimize your coverage and minimize your out-of-pocket expenses. Proactive planning empowers you to navigate the healthcare system confidently and ensures you receive the care you deserve without unnecessary financial strain.
Detailed FAQs
What happens if I miss a medical insurance monthly premium payment?
Missing a payment can lead to your coverage being canceled or suspended. Contact your insurer immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment; they may offer payment plans or other solutions.
Can I change my medical insurance plan during the year?
Generally, you can only change plans during the annual open enrollment period, unless you experience a qualifying life event (e.g., marriage, job loss). Check with your insurer or the marketplace for specific rules.
How often are medical insurance monthly premiums adjusted?
Premiums are typically adjusted annually, often reflecting changes in healthcare costs and utilization patterns. You’ll receive notification of any changes before they take effect.
What if my income changes significantly? Will my premium change?
Significant income changes may affect your eligibility for government subsidies or tax credits that help reduce your premium. Contact your insurer or the marketplace to update your information.