Planning for long-term care is a crucial aspect of financial security, and understanding the associated costs is paramount. This guide delves into the intricacies of long-term care insurance premium calculators, empowering you to navigate the complexities of this often-overlooked, yet vital, financial planning tool. We’ll explore the various factors influencing premium calculations, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your future well-being.
From deciphering policy types and coverage levels to understanding the impact of age and health status on premiums, we’ll equip you with the tools and insights necessary to confidently estimate your long-term care insurance costs. We’ll also guide you through the process of using a premium calculator effectively, comparing quotes, and selecting a policy that aligns with your individual needs and financial capabilities.
Understanding Long-Term Care Insurance Premiums
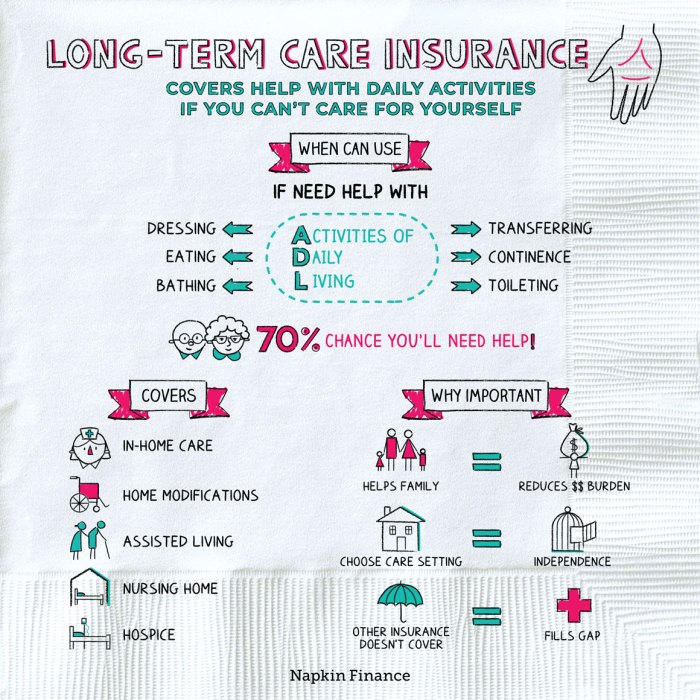
Long-term care insurance premiums can seem complex, but understanding the factors that influence their calculation is key to making an informed decision. Several interconnected elements determine the cost of your policy, impacting your monthly or annual payments. This section will clarify these factors and help you navigate the various policy options available.
Factors Influencing Long-Term Care Insurance Premium Calculations
Numerous factors contribute to the final premium amount. Age is a significant factor; younger individuals generally receive lower premiums due to a longer projected period before needing care. Health status plays a crucial role, with pre-existing conditions potentially leading to higher premiums or even policy denial. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, can also increase premiums. The chosen policy’s benefit amount, daily or monthly payout, and benefit period (length of coverage) directly influence premium costs; higher benefits naturally result in higher premiums. Finally, the type of policy selected (e.g., traditional, hybrid) and the insurer’s financial stability and risk assessment contribute to the overall premium. Location also impacts premiums, reflecting regional variations in healthcare costs.
Types of Long-Term Care Insurance Policies and Premium Structures
Several policy types offer varying premium structures. Traditional long-term care insurance policies typically involve fixed premiums that remain constant throughout the policy’s duration, although some insurers may offer limited premium adjustments over time. These policies offer comprehensive coverage for a range of care services. Hybrid policies, combining long-term care benefits with life insurance or other financial products, often feature more complex premium structures, sometimes with a combination of fixed and variable components. These structures might involve a level premium for the life insurance component and an increasing premium for the long-term care benefit. The premium structure will also be influenced by the chosen payment options, such as single-pay, periodic payments, or even financing options offered by some insurers.
Comparison of Premium Costs Between Various Policy Types and Coverage Levels
The following table illustrates a simplified comparison of premium costs. Remember that these are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary significantly based on the factors discussed previously. Always obtain personalized quotes from multiple insurers.
| Policy Type | Coverage Level (Daily Benefit) | Premium (Annual) | Premium (Monthly) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | $150 | $2,500 | $208.33 |
| Traditional | $300 | $4,000 | $333.33 |
| Hybrid (Life Insurance + LTC) | $150 | $3,200 | $266.67 |
| Hybrid (Annuities + LTC) | $200 | $4,500 | $375.00 |
Using a Long-Term Care Insurance Premium Calculator
Long-term care insurance premium calculators are invaluable tools for prospective buyers. They provide a quick and easy way to estimate the cost of a policy based on individual circumstances, allowing for informed decision-making before committing to a potentially significant financial investment. Understanding how these calculators work is key to effectively planning for future long-term care needs.
These calculators typically function by taking various personal details and policy preferences as input and then generating a projected premium. The output will show you a monthly, quarterly, or annual cost depending on the calculator’s design. It’s important to remember that these are estimates, and the final premium offered by an insurance company may vary slightly.
Calculator Features and Functionalities
Long-term care insurance premium calculators typically include several key features. These usually involve input fields for personal information like age, gender, and health status. They also require details about the desired policy benefits, such as the daily benefit amount, benefit period, and inflation protection options. Advanced calculators might even incorporate options for spousal coverage or include various rider options. The calculator then processes this data using actuarial tables and algorithms to produce a premium estimate. Some calculators may also provide comparison tools, allowing users to see how different policy choices impact the cost.
Input Parameters
The accuracy of a premium estimate depends heavily on the input parameters. Let’s examine some examples. Age is a crucial factor, with younger individuals generally paying lower premiums than older individuals due to a longer time horizon before potential claims. Health status is another critical element; individuals with pre-existing conditions or poor health might face higher premiums or even be ineligible for coverage. Policy benefits also significantly impact the cost. A higher daily benefit amount, a longer benefit period, and the inclusion of inflation protection will all lead to higher premiums. For instance, a 60-year-old in good health seeking a $150 daily benefit for five years might see a significantly lower premium than a 70-year-old with a pre-existing condition seeking a $300 daily benefit for ten years with inflation protection.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Long-Term Care Insurance Premium Calculator
Effectively using a long-term care insurance premium calculator involves a systematic approach.
- Gather Necessary Information: Before starting, collect all relevant personal information, including your age, gender, health status (including any pre-existing conditions), and smoking status. Also, decide on your desired policy features such as the daily benefit amount, benefit period, and whether you want inflation protection.
- Find a Reputable Calculator: Many insurance companies and independent websites offer long-term care insurance premium calculators. Choose a reputable source to ensure the accuracy of the estimates. Look for calculators that clearly explain their methodology and limitations.
- Enter Your Information Accurately: Carefully and accurately enter all the required information into the calculator’s input fields. Double-check for any errors before proceeding.
- Review the Results: Once you’ve entered all the information, the calculator will generate a premium estimate. Carefully review the results and ensure you understand all the components of the cost. Pay close attention to any assumptions made by the calculator.
- Compare Different Scenarios: Experiment with different policy options to see how they impact the premium. For example, try varying the daily benefit amount, benefit period, or inflation protection to see how these changes affect the cost. This allows you to find a balance between affordability and adequate coverage.
- Consult with an Insurance Agent: While calculators provide valuable estimates, they are not a replacement for professional advice. Contact a licensed insurance agent to discuss your specific needs and get personalized recommendations.
Illustrative Examples

Understanding long-term care insurance premiums can be challenging. These examples illustrate how various factors influence premium calculations and provide a clearer picture of what you might expect. Remember that these are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary based on individual circumstances and the specific insurance provider.
Premium Calculation for a 55-Year-Old
Let’s consider a 55-year-old non-smoker, female, with a clean bill of health, seeking a long-term care policy with a $150 daily benefit, a 3-year benefit period, and a 5% inflation rider. Using a hypothetical premium calculator (specific numbers are for illustrative purposes only and do not reflect any particular insurer’s rates), the annual premium might be calculated as follows:
| Component | Cost |
|---|---|
| Base Premium (Daily Benefit & Benefit Period) | $2,500 |
| Inflation Rider (5%) | $125 |
| Total Annual Premium | $2,625 |
This breakdown shows the core premium cost and the additional cost associated with the inflation rider, which protects against rising healthcare costs over time. Remember that other factors such as health status, occupation, and the insurer’s specific underwriting guidelines will also impact the final premium.
Impact of Different Benefit Periods on Premium Cost
The length of the benefit period significantly affects the premium. Let’s compare the same 55-year-old individual’s premium with the same daily benefit and inflation rider, but varying benefit periods:
| Benefit Period | Annual Premium (Illustrative) |
|---|---|
| 2 Years | $2,200 |
| 3 Years | $2,625 |
| 5 Years | $3,500 |
As the table demonstrates, a longer benefit period (covering a longer duration of potential care) results in a substantially higher annual premium. This reflects the increased risk the insurance company assumes.
Relationship Between Age and Premium Cost
The relationship between age and premium cost is directly proportional: premiums generally increase significantly with age. Imagine a graph where the x-axis represents age (from 50 to 70) and the y-axis represents the annual premium. The line would show a steep upward trend. For example, a 55-year-old might pay $2,625 annually, while a 65-year-old with the same coverage might pay $4,500 or more. This increase reflects the higher probability of needing long-term care at older ages. The increase isn’t linear; it accelerates as age increases. This is because the risk of needing long-term care increases exponentially with age. Therefore, purchasing a policy at a younger age generally results in lower premiums over the long term.
Summary
Securing your future with appropriate long-term care insurance is a significant step towards peace of mind. By understanding the factors influencing premium costs and effectively utilizing a long-term care insurance premium calculator, you can make informed choices that protect both your financial stability and your quality of life in the years to come. Remember, proactive planning is key to mitigating potential financial burdens and ensuring a comfortable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a guaranteed and non-guaranteed premium?
A guaranteed premium remains fixed throughout the policy’s duration, while a non-guaranteed premium may increase over time based on factors like the insurer’s experience and claims.
Can I use a calculator if I have pre-existing health conditions?
Yes, most calculators allow you to input pre-existing conditions, which will affect the premium estimate. Be sure to accurately disclose all relevant health information.
How often should I review my long-term care insurance policy?
It’s recommended to review your policy annually or at least every few years to ensure it still aligns with your needs and financial situation. Life circumstances change, and so might your insurance requirements.
What happens if I can’t afford my premiums later on?
Policies offer various options to manage this, such as reducing benefits, extending the payment period, or even surrendering the policy (with potential penalties). Review your policy’s specifics for details.