Navigating the world of insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. Understanding how much you’ll pay in insurance premiums is crucial for effective financial planning. This guide delves into the various factors influencing insurance costs, from your age and driving history to your location and credit score. We’ll explore different insurance types, compare average premiums, and provide actionable strategies to help you secure the best possible rates.
From car insurance and homeowners’ insurance to health and life insurance, the cost of premiums varies widely depending on a multitude of factors. This guide aims to demystify the process, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and potentially save money on your insurance costs. We’ll examine the intricacies of policy components, coverage options, and the impact of personal choices on your premium amounts.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums

Insurance premiums, the amount you pay for coverage, are determined by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance choices and potentially save money. This section will explore some key influences on premium costs across various insurance types.
Age and Insurance Premiums
Age significantly impacts insurance premiums across various sectors. For car insurance, younger drivers (typically under 25) generally pay higher premiums due to statistically higher accident rates. As drivers age and gain experience, their premiums usually decrease, reaching a minimum point in middle age before potentially rising again in later years due to increased health risks. Health insurance premiums also reflect age, with older individuals typically facing higher costs due to a greater likelihood of needing medical care. Life insurance premiums are lowest for young, healthy individuals and increase with age as the risk of death increases.
Driving History and Car Insurance
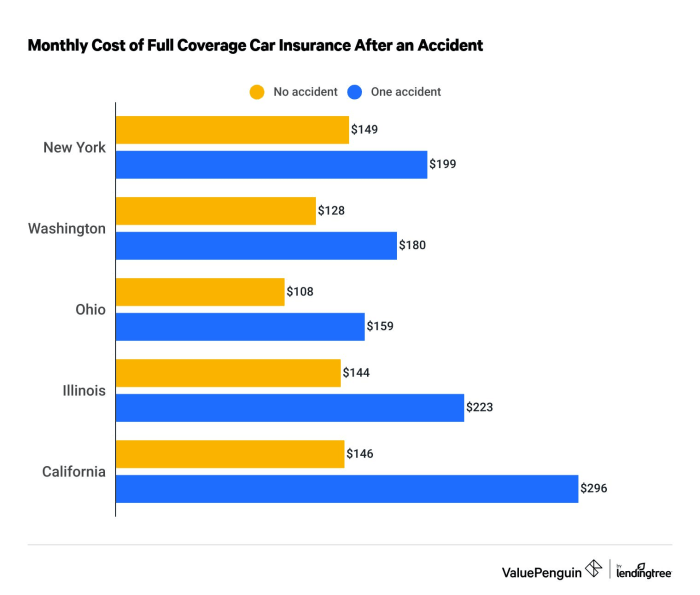
Driving history is a crucial factor in determining car insurance premiums. A clean driving record leads to lower premiums, while violations and accidents increase costs. For example, a speeding ticket might result in a 10-20% premium increase, while a DUI could lead to a much more substantial rise, sometimes even resulting in policy cancellation. At-fault accidents significantly impact premiums, potentially doubling or tripling the cost depending on the severity of the accident and the insurer. Multiple violations within a short period will further increase premiums.
Health Insurance Coverage Levels
Health insurance plans offer various coverage levels, each impacting premiums. Bronze plans have the lowest premiums but the highest out-of-pocket costs. Silver, Gold, and Platinum plans offer progressively higher levels of coverage and lower out-of-pocket costs, but with correspondingly higher premiums. The choice depends on individual risk tolerance and financial capacity. A healthy individual might opt for a bronze plan, while someone with pre-existing conditions might prefer a gold or platinum plan to minimize out-of-pocket expenses.
Credit Score and Insurance Premiums
In many states, credit score plays a role in determining insurance premiums for auto, home, and even some renters insurance. Insurers use credit scores as an indicator of risk, believing that individuals with poor credit are more likely to file claims. A higher credit score generally leads to lower premiums, while a lower score can result in significantly higher costs. This practice is controversial, with some arguing it unfairly penalizes individuals with poor credit histories who may not be higher risk.
Location and Insurance Premiums
Geographic location significantly influences both home and auto insurance premiums. Areas with high crime rates typically have higher home insurance premiums due to increased risk of theft and vandalism. Similarly, areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or wildfires, command higher premiums for both home and auto insurance. Rural areas may have lower premiums than urban areas due to lower crime rates and less traffic congestion.
| Location | Insurance Type | Average Premium | Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Miami, FL | Home Insurance | $3000 | Hurricane risk, high property values |
| San Francisco, CA | Auto Insurance | $2000 | High cost of living, traffic congestion |
| Rural Nebraska | Home Insurance | $800 | Low crime rates, low property values |
| Chicago, IL | Auto Insurance | $1500 | High crime rates, traffic congestion |
Types of Insurance and Premium Costs

Understanding the cost of insurance premiums is crucial for effective financial planning. Premiums vary significantly based on the type of insurance, individual circumstances, and the level of coverage selected. This section will explore the average premium costs for several common insurance types and the factors that influence them.
Car Insurance Premiums
Car insurance premiums are highly variable, depending on factors like driving history, location, vehicle type, and coverage level. Three primary types of car insurance coverage are liability, collision, and comprehensive. Liability insurance covers damages caused to others; collision covers damage to your vehicle in an accident; and comprehensive covers damage from events like theft or weather. Average premiums can range widely. For example, a young driver with a poor driving record in a high-risk area might pay significantly more than an older driver with a clean record in a low-risk area. A general estimate for liability-only coverage might start around $500 annually, while adding collision and comprehensive could easily double or triple that cost, depending on the aforementioned factors. Precise figures are difficult to state definitively without specifying all relevant variables.
Homeowner’s Insurance Premiums
Homeowner’s insurance premiums are largely determined by the value of the home, its location, and the coverage level selected. A larger, more expensive home in a high-risk area (e.g., prone to hurricanes or wildfires) will typically command higher premiums than a smaller, less expensive home in a low-risk area. For instance, a $300,000 home in a low-risk area might have an annual premium around $1,000, while a similar home in a high-risk area could cost $2,000 or more. The age and condition of the home, security systems installed, and the homeowner’s claims history also influence the premium.
Health Insurance Premiums
Several key factors influence individual and family health insurance premiums. Age, health status (pre-existing conditions), location, and the chosen plan (e.g., HMO, PPO) all play significant roles. Generally, older individuals and those with pre-existing conditions tend to pay more. Plans with lower deductibles and copays usually have higher premiums. Family plans naturally cost more than individual plans. Geographic location also impacts premiums, as healthcare costs vary across regions. The specific benefits included in the plan, such as prescription drug coverage, also impact the cost. It is not uncommon to see annual premiums ranging from a few thousand dollars for a basic individual plan to tens of thousands for a comprehensive family plan.
Life Insurance Premiums
Life insurance premiums are determined by several factors including the policyholder’s age, health, lifestyle (smoking, etc.), the death benefit amount, and the policy term (length of coverage). A younger, healthier individual will typically pay less than an older, less healthy person for the same death benefit. Longer-term policies (e.g., whole life) generally have higher premiums than shorter-term policies (e.g., term life).
| Death Benefit | 10-Year Term | 20-Year Term | Whole Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| $250,000 | $200 – $300 | $300 – $500 | $500 – $1000+ |
| $500,000 | $400 – $600 | $600 – $1000 | $1000 – $2000+ |
| $1,000,000 | $800 – $1200 | $1200 – $2000 | $2000 – $4000+ |
*Note: These are illustrative examples only and actual premiums will vary significantly based on individual circumstances.
Renters Insurance Premiums
The cost of renters insurance is influenced by several factors, including the value of the renter’s possessions, the location of the rental property, and the level of coverage selected. Renters in high-crime areas or areas prone to natural disasters typically pay more. The amount of liability coverage chosen also impacts the premium. Adding coverage for specific items, such as expensive electronics, will also increase the cost. A basic renters insurance policy might cost between $10 and $30 per month, but comprehensive coverage can cost significantly more.
Getting Lower Insurance Premiums
Securing affordable insurance is a significant financial consideration for most individuals and families. Fortunately, several strategies can help lower your premiums across various insurance types. By understanding these methods and proactively implementing them, you can significantly reduce your overall insurance costs.
Car Insurance Premium Discounts
Several avenues exist for reducing your car insurance premiums. Many insurance companies offer discounts for completing defensive driving courses, demonstrating a commitment to safe driving practices. Bundling your car insurance with other policies, such as homeowners or renters insurance, frequently results in substantial savings due to the combined risk assessment. Furthermore, opting for higher deductibles can lower your monthly premiums, although this means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim. Finally, maintaining a clean driving record is crucial; insurers reward drivers with a history of safe driving with lower premiums. A single accident or traffic violation can significantly impact your rates.
Lowering Homeowner’s Insurance Premiums
Home improvements focused on safety and security can lead to lower homeowner’s insurance premiums. Installing security systems, smoke detectors, and fire-resistant roofing materials demonstrates a proactive approach to risk mitigation, making your property less risky to insure. Regular maintenance, including updates to plumbing and electrical systems, also reduces the likelihood of costly claims. Properly documented upgrades and renovations can further support lower premiums by showcasing improvements in your home’s overall condition and safety. For example, replacing an older, less efficient heating system with a modern one might qualify for a discount.
Affordable Health Insurance Options
Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be challenging, but several strategies exist to find affordable plans. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace offers subsidies to individuals and families based on income, making health insurance more accessible. Comparing plans from different providers is crucial to identifying the best coverage at the most affordable price. Factors such as deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums significantly influence the overall cost. Understanding these factors allows for a more informed decision based on your individual needs and financial capabilities. For example, a high-deductible plan might be more affordable upfront but could lead to substantial out-of-pocket expenses if significant medical care is needed.
Benefits of a Good Driving Record
Maintaining a clean driving record is arguably the most impactful factor in reducing auto insurance premiums. Insurance companies assess risk based on driving history, and a history of accidents or traffic violations indicates a higher risk profile, resulting in higher premiums. Conversely, a driver with a spotless record is considered low-risk, leading to significantly lower premiums. This underscores the importance of safe driving practices, adherence to traffic laws, and defensive driving techniques. The financial benefits of safe driving extend far beyond avoiding accidents; they translate directly into lower insurance costs.
Actionable Steps to Reduce Insurance Premiums
Implementing the following steps can contribute to lower premiums across various insurance types:
- Shop around and compare quotes from multiple insurance providers.
- Maintain a good credit score (this impacts many insurance types).
- Bundle multiple insurance policies with the same provider.
- Increase deductibles (where financially feasible).
- Take defensive driving courses.
- Make home improvements that enhance safety and security.
- Regularly maintain your home and vehicles.
- Explore available government subsidies or discounts.
- Review your insurance coverage annually to ensure you have the right level of protection at the best price.
Understanding Insurance Policies and Costs
Understanding the intricacies of your insurance policy is crucial for maximizing its benefits and managing your financial responsibilities. This section will delve into the components of various insurance policies, outlining how different factors influence their costs. A clear grasp of these details allows for informed decision-making regarding coverage and premium payments.
Car Insurance Policy Components and Premium Impact
Several factors within a car insurance policy directly affect the premium. Liability coverage, which protects you against claims for bodily injury or property damage you cause to others, is a significant factor. Higher liability limits generally result in higher premiums, but offer greater protection. Collision coverage, which pays for damage to your vehicle regardless of fault, and comprehensive coverage, which covers damage from events like theft or weather, also influence premiums. The cost of these coverages depends on factors such as the vehicle’s make, model, year, and safety features. Your driving record, location (affecting risk of accidents and theft), and age also significantly impact your premium. A history of accidents or traffic violations leads to higher premiums, while a clean driving record may qualify you for discounts.
Homeowner’s Insurance Coverage Options and Costs
Homeowner’s insurance policies offer various coverage options, each affecting the overall premium. Dwelling coverage protects the physical structure of your home, while personal property coverage protects your belongings inside. Liability coverage protects you against claims if someone is injured on your property. Additional living expenses coverage helps cover temporary housing costs if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered event. The cost of these coverages is determined by factors like the location of your home (risk of natural disasters), the value of your home and belongings, and the level of coverage you choose. Higher coverage limits generally result in higher premiums, but provide greater financial security. Including features like a security system or smoke detectors might qualify you for discounts.
Factors Determining Health Insurance Plan Costs
The cost of health insurance plans varies widely depending on several key factors. Deductibles, which are the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in, are a significant factor. Higher deductibles typically result in lower monthly premiums but higher upfront costs. Co-pays, which are fixed amounts you pay for doctor visits or other services, also influence the overall cost. Out-of-pocket maximums represent the most you’ll pay in a year for covered services. Once this limit is reached, your insurance covers 100% of eligible expenses. The type of plan (e.g., HMO, PPO) significantly impacts cost and access to care. Your age, location, and health status also influence your premium, with higher-risk individuals generally paying more. Employer-sponsored plans often offer lower premiums than individual plans.
Interpreting an Insurance Policy Document
Insurance policies are legally binding contracts, and understanding their terms is essential. The policy’s declarations page summarizes key information such as the insured, coverage limits, and premium amounts. The insuring agreement Artikels the insurer’s promise to provide coverage. Exclusions detail specific situations or events not covered by the policy. Conditions Artikel the responsibilities of both the insured and the insurer. Carefully reading and understanding these sections ensures you are aware of your coverage and obligations. If any aspect is unclear, seeking clarification from your insurer or an independent insurance professional is recommended.
Sample Insurance Premium Breakdown
Let’s imagine a sample car insurance premium breakdown for a 30-year-old driver with a clean driving record living in a suburban area. The total premium is $1200 annually. This is comprised of: Liability Coverage ($400), Collision Coverage ($300), Comprehensive Coverage ($200), and Uninsured Motorist Coverage ($300). These individual components illustrate how different aspects of coverage influence the overall cost. Discounts for safe driving habits, bundling policies, or choosing a higher deductible could potentially lower this total cost. For example, opting for a higher deductible on collision coverage could reduce the collision portion of the premium, leading to an overall lower annual cost.
Final Summary
Ultimately, understanding how much your insurance premiums will be is a journey of self-education. By carefully considering the factors influencing costs, comparing different policies and providers, and proactively taking steps to mitigate risk, you can significantly reduce your expenses and secure the coverage you need. Remember, informed decisions lead to better financial outcomes. This guide provides a solid foundation for navigating the often-complex landscape of insurance premiums, enabling you to make choices that best suit your individual needs and budget.
FAQ Compilation
What is a deductible?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in.
How often are insurance premiums reviewed?
Premiums are typically reviewed annually, and adjustments are made based on various factors like claims history and market conditions.
Can I get insurance even with a poor credit score?
Yes, but a poor credit score will likely result in higher premiums. Some insurers may specialize in high-risk individuals.
What is bundling insurance policies?
Bundling involves combining multiple insurance policies (e.g., car and home insurance) with the same provider, often resulting in discounts.
How do I compare different insurance plans?
Use online comparison tools or contact multiple insurance providers directly to obtain quotes and compare coverage options and prices.