The rising cost of healthcare is a significant concern for millions, and 2024 promises to be no exception. Health insurance premiums are projected to increase, impacting individuals, families, and employers alike. This increase isn’t a singular event but a complex interplay of factors, from inflation and pharmaceutical prices to healthcare utilization and government policy. Understanding these drivers is crucial for navigating the challenges and making informed decisions about healthcare coverage.
This analysis delves into the multifaceted reasons behind the anticipated health insurance premium hikes in 2024. We’ll explore the various contributing factors, examine their impact on different demographics, and offer practical strategies for managing these rising costs. We’ll also look ahead to future trends and potential legislative changes that could further shape the landscape of health insurance in the years to come.
Factors Contributing to Premium Increases in 2024

Several interconnected factors contribute to the rise in health insurance premiums for 2024. Understanding these elements is crucial for both insurers and consumers to navigate the changing landscape of healthcare financing. This section will delve into the key drivers behind these increases.
Inflation’s Impact on Healthcare Costs
Inflation significantly impacts healthcare costs, directly influencing premium increases. Rising prices for medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and labor all contribute to higher overall healthcare spending. For example, the cost of hospital beds, medical equipment, and even administrative staff salaries have seen substantial increases, necessitating higher premiums to maintain adequate coverage. This inflationary pressure cascades through the entire healthcare system, making it more expensive to provide and consequently to insure.
Rising Prescription Drug Prices
The escalating cost of prescription drugs is a major driver of premium increases. The prices of many brand-name medications, along with the increasing demand for specialty drugs to treat complex conditions, contribute substantially to overall healthcare expenditures. For instance, the cost of certain cancer therapies or biologics has risen dramatically in recent years, placing significant pressure on insurance plans. Negotiating lower drug prices remains a challenge, impacting the affordability of comprehensive health insurance.
Increased Utilization of Healthcare Services
Higher utilization of healthcare services also contributes to premium increases. This can stem from various factors, including an aging population requiring more care, advancements in medical technology leading to more complex and expensive treatments, and improved access to care leading to increased demand. For example, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease results in increased demand for ongoing medical care, tests, and medications, directly influencing premium costs.
Impact of New Medical Technologies
The introduction of innovative medical technologies, while often beneficial for patient outcomes, frequently increases healthcare costs. New treatments, sophisticated diagnostic tools, and advanced surgical procedures often carry high price tags. For example, the adoption of advanced imaging techniques like PET scans or robotic surgery adds to the overall cost of care, influencing the premiums needed to cover these services. While these technologies improve treatment options, their cost must be factored into insurance plans.
Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies play a significant role in shaping health insurance premiums. Changes in reimbursement rates for medical services, mandates for specific coverage (such as mental health services), and regulations surrounding insurer practices all affect the cost of providing and purchasing insurance. For example, changes in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or state-level regulations can lead to adjustments in premium pricing to comply with new mandates or requirements.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Premiums | Potential Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflation | Increased prices for medical supplies, labor, and other healthcare resources. | Directly increases the cost of providing healthcare, leading to higher premiums. | Government intervention to control inflation, increased efficiency in healthcare delivery. |
| Rising Prescription Drug Prices | High cost of brand-name and specialty drugs. | Significant increase in overall healthcare spending, necessitating higher premiums. | Drug price negotiation, increased generic drug utilization, focus on preventative care. |
| Increased Healthcare Utilization | Higher demand for healthcare services due to aging population, chronic diseases, and advanced treatments. | Increased costs associated with providing more services. | Emphasis on preventative care, promoting healthy lifestyles, improving chronic disease management. |
| New Medical Technologies | High cost of advanced treatments, diagnostic tools, and procedures. | Increases the cost of providing advanced healthcare, resulting in higher premiums. | Careful evaluation of cost-effectiveness of new technologies, exploring alternative treatment options. |
| Government Regulations | Changes in reimbursement rates, mandates for specific coverage, and regulations affecting insurers. | Can either increase or decrease premiums depending on the nature of the regulations. | Careful consideration of the cost implications of new regulations, transparent and efficient regulatory processes. |
Impact on Different Demographics
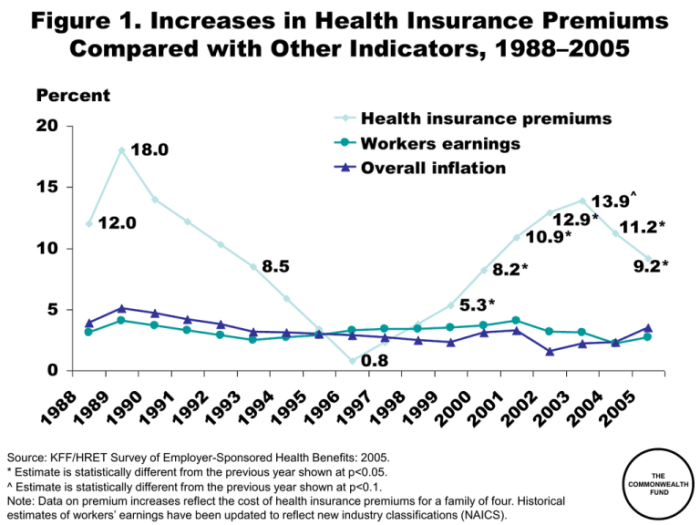
The rising cost of health insurance premiums in 2024 disproportionately affects various demographic groups, creating significant challenges for many individuals and families. Understanding these disparities is crucial for developing effective policy solutions and ensuring equitable access to healthcare.
Premium increases are not uniform across all segments of the population. Several factors, including age, location, health status, and income, contribute to the varying impact of these increases.
Age-Based Premium Variations
Older individuals generally face significantly higher premiums than younger adults. This is primarily due to the increased likelihood of needing more extensive healthcare services as people age. For example, a 65-year-old might see a premium increase of 15%, while a 25-year-old might experience a 5% increase, reflecting the higher healthcare costs associated with aging. This difference underscores the need for policies that address the specific affordability challenges faced by seniors.
Geographic Disparities in Premium Costs
Premiums also vary considerably based on geographic location. Rural areas often have higher premiums due to factors like limited healthcare provider availability, higher transportation costs to access care, and a smaller pool of insured individuals to spread the risk. Conversely, densely populated urban areas may see lower premiums due to economies of scale and greater competition among insurance providers. For instance, premiums in a rural county in the Midwest might be 20% higher than in a major metropolitan area on the East Coast.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing conditions are particularly vulnerable to high premium costs. While the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurers from denying coverage based on pre-existing conditions, these individuals often face higher premiums than those without such conditions. This is because insurers assess the likelihood of incurring higher healthcare expenses for individuals with chronic illnesses or other health concerns. Someone with diabetes, for example, might pay significantly more than someone without the condition.
Affordability Challenges for Low-Income Families
Rising premiums pose significant affordability challenges for low-income families. For many, the cost of health insurance represents a substantial portion of their household budget, leaving them with limited resources for other essential needs. A family struggling to make ends meet might face a difficult choice between paying for healthcare or meeting basic needs like food and housing. This situation highlights the urgent need for government subsidies and affordable care options for low-income populations.
Visual Representation of Disproportionate Impact
Imagine a bar graph. The horizontal axis represents different demographic groups (young adults, seniors, rural residents, urban residents, individuals with pre-existing conditions, low-income families). The vertical axis represents the percentage increase in premiums. The bars representing seniors, rural residents, individuals with pre-existing conditions, and low-income families would be significantly taller than the bars representing younger adults and urban residents without pre-existing conditions, visually illustrating the disproportionate impact of premium increases on vulnerable populations.
Wrap-Up

Navigating the complexities of rising health insurance premiums requires proactive planning and informed decision-making. While the outlook for 2024 and beyond presents challenges, understanding the underlying factors and available resources empowers individuals and families to take control of their healthcare costs. By carefully considering the information presented, readers can better prepare for the changes ahead and implement strategies to mitigate the impact of increasing premiums on their financial well-being.
FAQ Summary
What are the main reasons behind the projected increase in health insurance premiums for 2024?
Several factors contribute, including inflation impacting healthcare costs, rising prescription drug prices, increased healthcare utilization, the introduction of new medical technologies, and government regulations.
Can I switch health insurance plans to avoid the premium increase?
Yes, you can typically switch plans during open enrollment periods. Comparing plans from different insurers is crucial to finding a more affordable option that meets your needs.
What if I can’t afford the increased premiums?
Explore options like high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) with health savings accounts (HSAs), government subsidies (if eligible), and negotiating payment plans with your insurer.
Are there any government programs to help with rising healthcare costs?
Yes, depending on your income and location, you may be eligible for programs like Medicaid or subsidies through the Affordable Care Act marketplaces.