Navigating the complexities of tax season can be daunting, but understanding potential deductions like the health insurance premium tax deduction can significantly impact your financial well-being. This guide unravels the intricacies of this deduction, offering clarity on eligibility, documentation, and potential tax savings. We’ll explore various health insurance plans, common pitfalls to avoid, and recent updates to ensure you’re maximizing your return.
From understanding the eligibility criteria based on income levels and family structures to mastering the documentation process, we aim to equip you with the knowledge to confidently claim this valuable deduction. We’ll compare the tax benefits of different health insurance plans and highlight crucial steps to avoid common mistakes that could delay your refund or incur penalties.
Eligibility Criteria for Health Insurance Premium Tax Deduction
Claiming a tax deduction on health insurance premiums offers significant financial relief, but eligibility hinges on specific criteria. Understanding these rules is crucial for maximizing your tax benefits. This section details the eligibility requirements, providing clear examples to illustrate the process.
Income Limits and Age Restrictions
Eligibility for health insurance premium tax deductions often depends on factors such as your annual income and age. Income limits vary depending on the specific tax laws of your country or region. For example, in some jurisdictions, only individuals earning below a certain threshold might qualify. Similarly, age restrictions may apply; deductions might be available only to senior citizens or individuals with specific health conditions. These limitations are designed to target tax benefits to those most in need. It’s essential to consult the relevant tax authority’s guidelines for precise details.
Determining Eligibility Based on Income Brackets and Family Structures
To determine eligibility, you need to carefully consider your income and family structure. First, ascertain your adjusted gross income (AGI) for the tax year. This is your gross income minus certain deductions. Compare your AGI to the applicable income limits defined by your tax regulations. If your AGI falls below the limit, you may be eligible. Family structures also matter; some regulations allow for deductions based on the combined income of a family unit or offer higher limits for families with dependents. If you are part of a family, ensure you factor in the income of all family members to accurately assess your eligibility.
Examples of Qualifying and Non-Qualifying Individuals and Families
Consider a single individual, Sarah, earning $40,000 annually. If the income limit for her region is $50,000, she would likely qualify for the deduction. Conversely, John, who earns $75,000 annually, might not qualify if the same $50,000 limit applies. For families, consider the Miller family, with a combined annual income of $70,000 and two dependent children. Depending on the regulations, they might qualify for a higher deduction limit or a different set of eligibility criteria. Conversely, the Smith family, with a combined annual income of $120,000, may not qualify, regardless of the number of dependents.
Comparison of Eligibility Criteria Across Different Tax Regimes
| Country/Region | Income Limit | Age Restrictions | Other Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States (Example) | Varies by state and plan | May vary depending on the plan | Must be enrolled in a qualified health plan |
| Canada (Example) | Varies depending on province and plan | Typically none, but may have conditions based on the plan | Must meet the eligibility criteria for the plan |
| United Kingdom (Example) | Generally no income limit for basic health coverage | None for basic health coverage | Eligibility is based on residency and other factors |
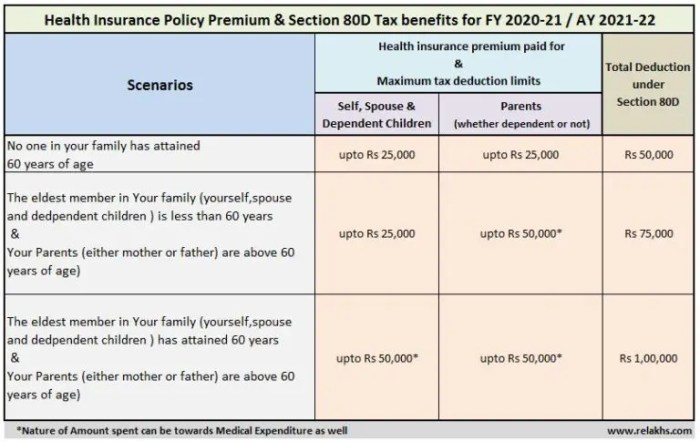
| India (Example) | Specified limits under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act | Specific age limits for senior citizens | Policy must be from an approved insurer |
Types of Health Insurance Plans Eligible for Deduction

Understanding which health insurance plans qualify for premium tax deductions is crucial for maximizing your tax savings. This section details the eligible plans, compares their tax benefits, and Artikels the necessary documentation for claiming deductions. Different plans offer varying levels of coverage and, consequently, different tax advantages.
Individual Health Insurance Plans
Individual health insurance plans cover the medical expenses of a single person. The tax benefits are straightforward: the premium paid can be claimed as a deduction under the relevant section of the income tax act. The documentation required typically includes a copy of the health insurance policy, premium payment receipts, and proof of identity. For example, a self-employed individual purchasing an individual plan can deduct the premiums paid from their taxable income.
Family Floater Health Insurance Plans
Family floater plans cover multiple family members under a single policy. This offers cost-effectiveness and broader coverage. The tax benefits are similar to individual plans; the total premium paid is deductible. However, it’s important to note that the entire premium is considered a single deduction, not separate deductions for each family member. Required documentation mirrors that of individual plans: policy copy, premium receipts, and proof of family relationship. A family of four, for example, could significantly reduce their taxable income by claiming the premium paid for their family floater plan.
Critical Illness Health Insurance Plans
Critical illness plans offer a lump-sum payout upon diagnosis of specified critical illnesses like cancer, heart attack, or stroke. While these plans don’t cover routine medical expenses, the premiums are still eligible for tax deductions under the applicable tax laws. The documentation needed is the same as for other plans: policy details, premium payment proofs, and identity verification. A person anticipating higher risk of critical illness might find this plan advantageous both for coverage and tax benefits.
Key Features of Eligible and Ineligible Health Insurance Plans
Understanding the key differentiators between eligible and ineligible plans is essential for successful tax planning.
- Eligible Plans: These plans are generally issued by registered insurers and comply with all applicable regulations. They explicitly cover medical expenses and/or critical illnesses.
- Ineligible Plans: Plans that primarily focus on personal accident coverage, travel insurance, or other non-medical benefits are typically not eligible for premium tax deductions. Similarly, plans from unregistered insurers or those that don’t meet regulatory compliance standards would be ineligible.
Tax Benefits and Implications
The health insurance premium tax deduction offers significant tax advantages, potentially reducing your overall tax liability and boosting your savings. Understanding these benefits is crucial for maximizing your tax efficiency. This section will detail how this deduction works, its impact on your tax bill, and how it compares to other tax-saving investment options.
The deduction directly reduces your taxable income. This means that the amount you spend on eligible health insurance premiums is subtracted from your gross income before your tax is calculated. The lower your taxable income, the lower your tax liability. The actual tax savings depend on your tax bracket; those in higher tax brackets will see a more substantial reduction in their tax burden.
Impact on Overall Tax Liability
The health insurance premium deduction’s effect on your overall tax liability is directly proportional to your tax bracket and the amount of your eligible premiums. For example, an individual in the 30% tax bracket who deducts $10,000 in premiums will see a tax saving of $3,000 ($10,000 x 30%). This reduction directly lowers the amount of tax owed. The higher your income and therefore your tax bracket, the greater the potential savings.
Comparison with Other Tax-Saving Investment Options
Several other investment options offer tax benefits, but the health insurance premium deduction stands out due to its direct impact on reducing your tax liability, rather than deferring or reducing tax on investment gains. While options like Public Provident Fund (PPF) or Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) offer tax benefits on investments and returns, the health insurance premium deduction provides immediate tax relief on an essential expense. The choice between these options depends on individual financial goals and risk tolerance. The health insurance deduction is particularly attractive for those prioritizing immediate tax savings and securing health coverage.
Potential Tax Savings at Different Income Levels
The following table illustrates potential tax savings at different income levels, assuming a standard deduction of eligible premiums. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual savings may vary based on individual circumstances, applicable tax laws, and the specific amount of eligible premiums. Tax rates and laws are subject to change.
| Annual Income (₹) | Tax Bracket (%) | Assumed Eligible Premium (₹) | Potential Tax Savings (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500,000 | 20 | 10,000 | 2,000 |
| 1,000,000 | 30 | 20,000 | 6,000 |
| 1,500,000 | 30 | 30,000 | 9,000 |
| 2,000,000 | 30 | 40,000 | 12,000 |
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls to Avoid
Claiming the health insurance premium tax deduction can be straightforward, but overlooking certain details can lead to delays or penalties. Understanding common errors and implementing preventative measures ensures a smooth and successful tax filing process. This section Artikels frequent mistakes and provides practical advice to avoid them.
Incorrect Documentation
Submitting incomplete or inaccurate documentation is a primary reason for claim rejections. This includes missing policy details, incorrect PAN numbers, or discrepancies between the policy and the claim form. Consequences can range from delays in processing to complete rejection of the deduction claim. To avoid this, meticulously verify all information on the claim form against your policy documents. Double-check all numbers, dates, and names for accuracy before submission. Keep copies of all submitted documents for your records.
Claiming Deduction for Ineligible Dependents
Taxpayers sometimes incorrectly claim deductions for dependents who do not meet the eligibility criteria defined by the Income Tax Act. This could involve including dependents who are not financially dependent or those who have their own health insurance coverage. The result is an inaccurate claim, potentially leading to a notice from the tax authorities and the need to amend the return. Always verify your dependents’ eligibility based on the specific rules and regulations. Ensure that each dependent meets the criteria for financial dependence and lacks their own comprehensive health insurance.
Missing the Deadline
Filing the tax return after the deadline is a common mistake that can result in penalties. The tax authorities have specific deadlines for filing tax returns, and missing these deadlines can lead to interest charges and late filing penalties. These penalties can significantly impact your tax refund amount. To avoid this, plan ahead and file your return well before the deadline. Set reminders to ensure you don’t miss the important dates. If you anticipate needing an extension, apply for one well in advance of the original deadline.
Incorrect Calculation of Deductible Amount
Miscalculating the deductible amount is another prevalent error. This might involve exceeding the maximum permissible deduction or misinterpreting the rules about the type of insurance plan eligible for deduction. This can result in a claim being partially or completely rejected. Carefully review the relevant sections of the Income Tax Act and the guidelines provided by the tax authorities to understand the maximum deductible amount. Use a tax calculator or consult a tax professional if you’re unsure about the calculations.
Best Practices for Accurate and Efficient Claiming
Proper planning and careful execution are key to a successful claim. Following these best practices will minimize the risk of errors and ensure a smooth process.
- Maintain accurate records of your health insurance premiums throughout the year.
- Verify the eligibility of all dependents before including them in your claim.
- Double-check all information on the claim form against your policy documents.
- File your tax return well before the deadline to avoid penalties.
- Consult a tax professional if you have any doubts or complexities in your tax situation.
- Keep copies of all submitted documents for your records.
Changes and Updates to the Health Insurance Premium Tax Deduction
Tax laws concerning health insurance premium deductions are not static; they evolve to reflect economic conditions, healthcare policy shifts, and government priorities. Understanding these changes is crucial for taxpayers to maximize their tax benefits and avoid potential penalties. Staying informed about updates is essential for accurate tax filing and financial planning.
Recent changes and anticipated future modifications to the health insurance premium tax deduction significantly impact taxpayers’ ability to reduce their tax burden. These alterations often involve adjustments to eligibility criteria, the types of plans covered, and the overall amount deductible. Analyzing these modifications helps individuals and families plan effectively for their healthcare expenses and tax obligations.
Recent Changes in Health Insurance Premium Tax Deduction Rules
The specific details of recent changes vary depending on the country and its tax system. For example, in some jurisdictions, there might have been adjustments to the maximum amount deductible, or changes to the definition of a “qualifying” health insurance plan. These changes might include stricter requirements for pre-existing conditions or a shift in the types of plans eligible for the deduction (e.g., a preference for plans that promote preventative care). To provide concrete examples, one might cite a specific tax law change in a given country – such as a hypothetical increase in the maximum deductible amount from $2,000 to $2,500 in a specific year. This change directly impacts the amount taxpayers can deduct, leading to potential tax savings. Another example might be the addition of a new category of qualifying health plans, leading to a broader range of options for taxpayers.
Impact of Changes on Taxpayers
The impact of these changes varies depending on individual circumstances. Higher maximum deduction limits, for example, directly benefit taxpayers with higher healthcare expenses. Conversely, stricter eligibility requirements might exclude some individuals from claiming the deduction altogether, leading to a higher tax burden. For instance, if a previously eligible plan is no longer considered qualifying due to a regulatory change, taxpayers enrolled in that plan will lose the tax benefit. This would directly increase their tax liability, highlighting the importance of staying updated on changes. Furthermore, the complexity of these changes might necessitate professional tax advice for many taxpayers.
Anticipated Future Changes
Predicting future changes with certainty is impossible. However, based on current trends, one could anticipate potential changes related to the integration of telehealth services into qualifying health plans. Governments might incentivize the use of telehealth by expanding the tax deduction to include premiums for telehealth-focused plans. Another potential change could involve adjustments based on the affordability and accessibility of health insurance. This might include changes to the eligibility criteria to better support low-income individuals or families. These are hypothetical scenarios, illustrating the potential directions future changes might take, but their occurrence is subject to legislative processes and policy decisions.
Timeline of Significant Changes
Illustrating changes with a timeline requires specific country-based tax law information. A hypothetical example might be:
| Year | Significant Change | Impact on Taxpayers |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Increased maximum deductible amount | Reduced tax burden for eligible taxpayers |
| 2022 | Modified eligibility criteria for pre-existing conditions | Some taxpayers previously eligible became ineligible |
| 2024 (Projected) | Inclusion of telehealth plans in qualifying plans | Expanded tax benefits for taxpayers using telehealth |
This table provides a simplified hypothetical example. Actual timelines and changes will vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction.
Concluding Remarks
Successfully claiming the health insurance premium tax deduction requires careful planning and attention to detail. By understanding the eligibility requirements, gathering the necessary documentation, and avoiding common pitfalls, taxpayers can significantly reduce their tax liability and enjoy substantial financial savings. This guide provides a roadmap to navigate this process effectively, empowering you to take control of your tax obligations and maximize your financial resources.
FAQ Compilation
Can I claim a deduction for my parents’ health insurance premium?
Yes, under certain conditions. Eligibility often depends on your parents’ age and income, and you may need to meet specific dependency requirements. Check the relevant tax laws for your jurisdiction.
What if my health insurance policy was purchased mid-year?
You can still claim a deduction for the premiums paid during the tax year, but the amount will be pro-rated based on the period of coverage within the tax year.
Are premiums paid through a salary deduction eligible for the tax deduction?
Yes, premiums paid through salary deductions are generally eligible, provided you have the necessary documentation from your employer showing the deduction.
What happens if I submit incorrect information?
Submitting incorrect information may lead to delays in processing your return, potential penalties, and even disallowance of the deduction. Ensure accuracy before submitting your claim.
Where can I find the most up-to-date information on the health insurance premium tax deduction?
Consult the official website of your country’s tax authority for the most current rules and regulations.