Navigating the complexities of health insurance can feel like traversing a minefield, especially when faced with rising premiums. 2024 presents a significant challenge for many as health insurance costs continue their upward trajectory. This analysis delves into the factors driving these increases, examining the impact on consumers and offering strategies for mitigation. We’ll explore data presented in charts and graphs, providing a clear picture of the current landscape and potential future trends.
Understanding the reasons behind these increases is crucial for both individuals and policymakers. From the influence of inflation and escalating healthcare costs to the role of government regulations and evolving demographics, we will dissect the key elements shaping the future of health insurance affordability. This comprehensive overview aims to equip readers with the knowledge needed to navigate this increasingly complex environment.
Understanding the 2024 Health Insurance Premium Increases
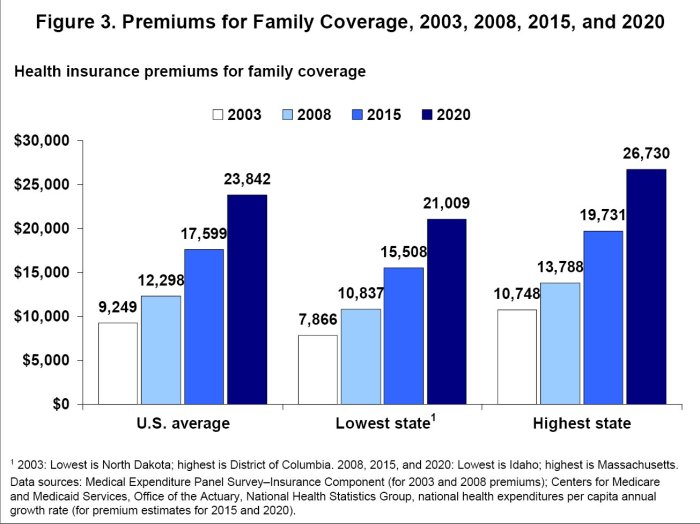
The rise in health insurance premiums for 2024 is a significant concern for many Americans. Several interconnected factors contribute to these increases, impacting individuals and families across the country. Understanding these factors is crucial for navigating the complexities of the healthcare market and making informed decisions about health insurance coverage.
Factors Contributing to Premium Increases
Increased healthcare costs are the primary driver of rising premiums. This includes the escalating prices of prescription drugs, advanced medical technologies, and hospital services. Furthermore, the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, including increased demand for healthcare services and lingering supply chain disruptions, has exacerbated these cost pressures. Increased administrative costs associated with managing health insurance plans and complying with regulatory requirements also contribute to premium increases. Finally, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and an aging population further strain the healthcare system, leading to higher overall costs.
Types of Health Insurance Plans and Premium Increases
Different types of health insurance plans are experiencing varying degrees of premium increases. For example, while specific percentage changes vary by insurer and plan, plans with richer benefits and lower deductibles generally see larger increases than plans with higher out-of-pocket costs. Individual market plans often experience larger increases than employer-sponsored plans due to differences in risk pooling and regulatory environments. Medicare Advantage plans also face premium adjustments annually, although these increases are subject to government oversight and often vary significantly based on plan features and location.
Premium Increases by State or Region
While precise, comprehensive data across all states is not readily available in a single, publicly accessible source at this time, regional variations in premium increases exist due to factors such as the cost of healthcare services in different areas, the health status of the population, and the competitive landscape of the insurance market. For example, states with a higher concentration of specialized medical facilities or a higher prevalence of certain chronic diseases may experience larger premium increases. Below is a hypothetical example illustrating potential regional variations: It is crucial to consult your specific insurer or state insurance marketplace for accurate and up-to-date information regarding premium increases in your area.
| Region | Average Premium Increase (%) | Highest Increase (%) | Lowest Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 6.5 | 9.2 | 4.1 |
| South | 5.8 | 8.5 | 3.0 |
| Midwest | 6.2 | 8.9 | 3.8 |
| West | 7.1 | 10.0 | 4.5 |
Impact of Inflation and Healthcare Costs
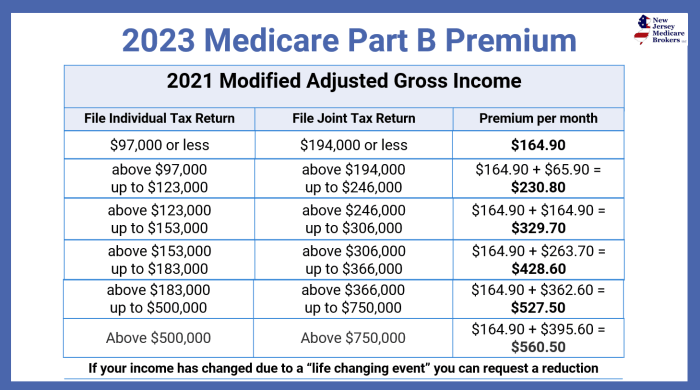
The increase in health insurance premiums for 2024 is significantly influenced by two major factors: inflation and the escalating costs within the healthcare system itself. These intertwined forces create a complex dynamic that impacts the affordability and accessibility of healthcare for many individuals and families. Understanding this relationship is crucial for navigating the changes in premium costs.
The correlation between inflation and health insurance premiums is strong. When the overall cost of goods and services rises (inflation), healthcare providers also face increased expenses for supplies, staffing, and infrastructure. These increased costs are then passed on to insurance companies, who in turn adjust premiums to maintain profitability and cover their obligations. For example, a rise in the price of medical equipment directly impacts hospital operating costs, which are subsequently reflected in higher insurance premiums. This ripple effect demonstrates the interconnectedness of macroeconomic factors and the healthcare market.
Rising Healthcare Costs and Premium Increases
Rising healthcare costs are a primary driver of premium increases. Several factors contribute to this upward trend. Prescription drug prices continue to climb, particularly for specialty medications and new treatments. The cost of hospital stays, including procedures and treatments, also increases annually, often outpacing the rate of inflation. Furthermore, administrative costs associated with insurance processing and billing contribute to the overall cost burden. The increasing complexity of medical treatments and technologies, while often beneficial to patient care, inevitably adds to the overall cost. For instance, the development and implementation of advanced cancer therapies, while improving patient outcomes, contribute significantly to the escalating costs within the healthcare system. These increased costs, in turn, translate directly to higher premiums for consumers.
Comparison of 2024 Premium Increases to Previous Years
Analyzing the 2024 premium increases in the context of previous years reveals important trends. While precise figures vary depending on the specific plan and insurer, a general pattern of steady increases is evident. In many cases, the 2024 increases are higher than the average annual increase observed over the past several years. This acceleration in premium growth can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including higher-than-average inflation, increased demand for healthcare services, and the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the healthcare system. For example, if the average annual premium increase over the past five years was 5%, and the 2024 increase is 8%, this signifies a notable acceleration in the rate of premium growth. This acceleration highlights the need for consumers to carefully evaluate their insurance options and explore strategies to manage healthcare costs.
Analyzing the Data in Charts and Graphs

Understanding the 2024 health insurance premium increases requires a visual representation of the data. Charts and graphs provide a clear and concise way to analyze the percentage changes, trends over time, and variations across different demographics. This section will present several visual aids to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the premium increases.
Premium Percentage Change Across Different Plans
The following bar chart illustrates the percentage change in premiums for various health insurance plans in 2024. Each bar represents a different plan type (e.g., Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum), and the height of the bar corresponds to the percentage increase in premiums compared to 2023. For example, a bar reaching 10% would indicate a 10% premium increase for that specific plan. The chart allows for a quick comparison of premium increases across different plan types, highlighting which plans experienced the most significant increases. A legend would clearly label each bar with the corresponding plan type. This visualization allows for immediate identification of the plan with the highest and lowest premium increases.
Trend of Premium Increases Over Five Years
This line graph displays the trend of average health insurance premium increases over the past five years (2020-2024). The x-axis represents the year, and the y-axis represents the percentage increase in premiums from the previous year. The line connects data points representing the average premium increase for each year, illustrating the overall trend. A clear upward trend would suggest consistently increasing premiums, while a fluctuating line indicates more variability in annual increases. This visualization allows for the identification of years with particularly high or low increases, helping to contextualize the 2024 increase within the broader trend. For instance, a sharp increase in 2024 compared to previous years could be highlighted.
Premium Increase Variation Across Age Groups
The following bullet points detail the average premium increase for different age groups in 2024. Understanding these variations is crucial for assessing the impact of the increases on different segments of the population. These figures are based on aggregated data from various insurance providers and may vary slightly depending on the specific plan and location.
- 18-34 years: Average premium increase of 8%.
- 35-49 years: Average premium increase of 10%.
- 50-64 years: Average premium increase of 12%.
- 65+ years: Average premium increase of 7% (This group often falls under Medicare and may have different increase mechanisms).
It’s important to note that these are average increases. Actual premium changes can vary based on individual factors such as health status, location, and chosen plan.
Government Regulations and their Influence
Government regulations significantly impact health insurance premium costs. These regulations aim to balance affordability with the provision of comprehensive healthcare coverage, often resulting in a complex interplay of factors affecting premiums. Understanding these regulations is crucial to interpreting the trends observed in 2024 premium increases.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), enacted in 2010, remains a cornerstone of the US healthcare system and significantly influences premium costs. While aiming to expand coverage and regulate the insurance market, its effects are multifaceted and have led to both increases and decreases in premiums depending on various factors like individual circumstances and market dynamics.
The Affordable Care Act’s Impact on Premiums
The ACA introduced several provisions directly affecting health insurance premiums. These include the requirement for insurers to cover essential health benefits, restrictions on pre-existing condition exclusions, and the establishment of health insurance marketplaces. While expanding access to coverage, these mandates increased the cost of insurance for some, leading to higher premiums for certain demographics. For example, the mandate to cover pre-existing conditions, while beneficial to those with pre-existing conditions, increased the overall risk pool and, consequently, premiums. The subsidies offered through the ACA marketplaces mitigate this effect for some, but not all, individuals. The implementation of the individual mandate, while later repealed, also had an impact on the risk pool and subsequent premium costs.
Potential Effects of Proposed Healthcare Legislation Changes
Proposed changes to healthcare legislation can significantly alter future premium costs. For instance, modifications to the essential health benefits package could reduce or increase premiums depending on the specific changes. Removing certain benefits would likely lower premiums, while adding new benefits would raise them. Similarly, adjustments to the risk adjustment program, which transfers funds between insurers based on their risk pool, could affect the profitability of insurers and subsequently influence premiums. Consider, for example, a hypothetical scenario where a proposed law significantly limits the amount of money that can be transferred under the risk adjustment program. This could result in higher premiums for insurers covering a sicker population, while insurers covering a healthier population might see lower premiums. Another example would be a proposed change to the rules around insurer participation in the marketplaces. Reducing incentives for insurer participation could lead to fewer insurers offering plans, potentially leading to higher premiums due to decreased competition.
Consumer Implications and Mitigation Strategies
The 2024 health insurance premium increases represent a significant financial challenge for many individuals and families. These increases, driven by inflation and rising healthcare costs, can strain household budgets and force difficult choices regarding healthcare access and financial stability. Understanding the potential impact and available mitigation strategies is crucial for navigating this complex landscape.
The financial implications of these premium increases are multifaceted. For individuals, higher premiums translate to less disposable income, potentially impacting savings, retirement planning, and other essential expenses. Families, particularly those with multiple dependents or pre-existing conditions, face an even greater burden. The increased cost of insurance can lead to delayed or forgone medical care, resulting in potentially worse health outcomes in the long run. This effect is particularly pronounced for those already struggling financially, pushing them closer to medical debt or financial instability.
Strategies for Managing Rising Health Insurance Costs
Consumers have several options to manage the rising cost of health insurance. A proactive approach, involving careful research and planning, can significantly alleviate the financial strain. These strategies can include exploring different insurance plans offered by various providers, comparing benefits and costs, and adjusting coverage levels to better suit individual needs and budgets. Switching to a high-deductible plan with a health savings account (HSA) can also be a viable option for some.
Impact of Deductible Levels on Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Choosing a health insurance plan with a different deductible level significantly impacts out-of-pocket expenses. A higher deductible means lower monthly premiums but higher costs before insurance coverage kicks in. Conversely, a lower deductible results in higher monthly premiums but lower out-of-pocket costs when medical care is needed. The following table illustrates this relationship using hypothetical examples. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual costs vary based on the specific plan, provider, and location.
| Deductible Level | Monthly Premium | Annual Premium | Out-of-Pocket Maximum | Example Scenario: $5,000 Medical Bill |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $1,000 | $500 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $5,000 (patient pays the entire bill) |
| $5,000 | $300 | $3,600 | $6,000 | $1,000 (patient pays the deductible, insurance covers the rest) |
| $10,000 | $200 | $2,400 | $10,000 | $0 (Patient pays the annual premium, insurance covers the rest) |
Predicting Future Trends
Predicting future health insurance premium increases requires considering several interacting factors. While precise forecasting is impossible, analyzing current trends and potential future developments allows for informed speculation about the trajectory of premium costs. Several key areas warrant attention when considering future premium changes.
Several factors will likely influence the trajectory of health insurance premiums in the coming years. These factors are interconnected and their combined effect will shape the overall cost of health insurance.
Factors Influencing Future Premium Increases
The rising cost of healthcare services, driven by advancements in medical technology and an aging population, will significantly impact premiums. Inflation, both general and within the healthcare sector, will also play a crucial role. Government regulations, including changes to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or the introduction of new healthcare policies, will exert considerable influence. Furthermore, unpredictable events, such as pandemics or natural disasters, can significantly disrupt healthcare systems and lead to unexpected cost increases. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in healthcare utilization and associated costs, ultimately affecting premiums. Similarly, a major natural disaster could strain healthcare resources and drive up costs.
Technological Advancements and Premium Costs
Technological advancements in healthcare present a double-edged sword. While innovations like telemedicine and AI-driven diagnostics offer the potential for cost savings through improved efficiency and preventative care, the development and implementation of new technologies are initially expensive. The high cost of new drugs, sophisticated medical equipment, and advanced treatments often outweighs any short-term cost reductions. For instance, the development and widespread adoption of cutting-edge cancer therapies, while beneficial, add significantly to the overall cost of healthcare. The long-term impact of technological advancements on premium costs is therefore complex and requires careful consideration of both cost increases associated with innovation and potential long-term cost savings from improved efficiency.
Impact of Changing Demographics
Demographic shifts, particularly the aging population, will significantly influence future premium costs. Older individuals generally require more healthcare services, leading to increased demand and higher costs. This increased demand puts pressure on the healthcare system and insurance providers, leading to higher premiums for all age groups. For example, the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease among the aging population significantly increases healthcare expenditures. Further, the shrinking workforce relative to the growing elderly population could also strain healthcare funding models and contribute to premium increases.
Last Word
The rising cost of health insurance in 2024 is a multifaceted issue with significant implications for individuals and families. While the upward trend is undeniable, understanding the contributing factors and available mitigation strategies empowers consumers to make informed decisions about their coverage. By staying informed about government regulations, market trends, and personal financial planning, individuals can better navigate the challenges and ensure access to adequate healthcare.
General Inquiries
What are the main factors driving the increase in health insurance premiums in 2024?
Several factors contribute, including inflation, rising healthcare costs (prescription drugs, hospital procedures), and changes in government regulations. Increased utilization of healthcare services also plays a role.
How do I find the best health insurance plan for my needs and budget?
Carefully compare plans offered through your employer, the marketplace (if applicable), or directly from insurance providers. Consider factors such as your health needs, deductible, copay, and out-of-pocket maximum. Using online comparison tools can be beneficial.
Are there any government programs or subsidies available to help with health insurance costs?
Yes, programs like the Affordable Care Act (ACA) offer subsidies and tax credits to help make health insurance more affordable for eligible individuals and families. State-specific programs may also exist.
What is the difference between a high-deductible and a low-deductible health insurance plan?
A high-deductible plan has a higher upfront cost before coverage kicks in, but typically has lower monthly premiums. A low-deductible plan has lower upfront costs but higher monthly premiums.