The year 2024 is shaping up to be another challenging year for individuals and families navigating the complexities of health insurance. Across the nation, health insurance premiums are projected to rise significantly, impacting millions and raising concerns about healthcare accessibility and affordability. This increase is a multifaceted issue stemming from a confluence of factors, including escalating healthcare costs, pharmaceutical pricing, and increased utilization of services. Understanding these contributing elements is crucial for individuals to effectively manage their healthcare expenses and advocate for policy changes that address this growing concern.
This comprehensive analysis delves into the key drivers behind the 2024 health insurance premium surge, exploring their impact on various demographic groups and offering practical strategies for mitigating the financial burden. We’ll examine the influence of government regulations, the role of insurance company profits, and the potential long-term trends impacting future premium costs. By understanding these factors, we can work towards a more sustainable and equitable healthcare system.
Factors Contributing to 2024 Health Insurance Premium Increases
The increase in health insurance premiums for 2024 is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of factors, all contributing to a higher cost of healthcare. Understanding these factors is crucial for both consumers and policymakers.
Rising Healthcare Costs
The fundamental driver of premium increases is the overall escalating cost of healthcare services. This includes expenses related to hospital stays, physician visits, diagnostic tests, and other medical procedures. Inflation, advancements in medical technology (often expensive), and an aging population placing greater demands on the healthcare system all contribute to this upward trend. For example, the cost of advanced cancer treatments has risen significantly in recent years, directly impacting insurance payouts and, consequently, premiums.
Prescription Drug Prices
Prescription drug costs represent a significant and rapidly growing portion of healthcare expenditures. The high prices of brand-name drugs, coupled with limited generic alternatives, place substantial pressure on insurance companies. The lack of price controls in some areas and the complex pricing structures of pharmaceutical companies exacerbate this issue. For instance, the rising cost of insulin has disproportionately affected individuals with diabetes, driving up claims and influencing premium increases.
Increased Utilization of Healthcare Services
Higher utilization of healthcare services, meaning more people seeking medical care, also contributes to premium increases. This can be attributed to various factors, including improved access to care (leading to more preventative visits), an aging population with increased healthcare needs, and a greater awareness of health issues. Increased utilization translates to higher claims payouts for insurers, necessitating higher premiums to maintain profitability and solvency. For example, an increase in elective procedures after the COVID-19 pandemic contributed to higher healthcare utilization rates.
Administrative Costs and Insurer Profits
Administrative costs associated with managing health insurance plans, including billing, claims processing, and marketing, represent a considerable expense. While efforts to streamline these processes are ongoing, administrative costs remain a factor influencing premium levels. Additionally, insurer profits, while regulated, contribute to the overall cost structure. The balance between ensuring insurer solvency and keeping premiums affordable remains a persistent challenge. Examples include the cost of maintaining extensive IT infrastructure for managing large databases of patient information and claims.
Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies significantly impact health insurance premiums. Changes in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) regulations, state-level mandates for coverage (such as mental health parity), and reimbursement rates negotiated between insurers and healthcare providers all play a role. For example, state-level mandates requiring coverage for specific conditions can increase the cost of insurance plans, ultimately leading to higher premiums.
| State | Average Premium Increase (%) | Contributing Factors | State-Specific Policies |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 8 | Rising prescription drug costs, increased hospital utilization | Increased emphasis on preventative care programs |
| Texas | 6 | Higher administrative costs, increased utilization of emergency services | Focus on market competition among insurers |
| Florida | 7 | Rising hospital costs, increased demand for specialized care | Emphasis on cost-containment measures |
| New York | 9 | High prescription drug prices, aging population | Stronger regulations on insurer pricing practices |
Impact of Premium Increases on Different Demographics

The rising cost of health insurance premiums in 2024 will disproportionately affect various demographic groups, exacerbating existing health disparities and creating new challenges for access to care. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and ensuring equitable access to healthcare for all.
Premium Increases and Low-Income Families
For low-income families, even a modest premium increase can represent a significant financial burden. This often leads to difficult choices between paying for healthcare and meeting other essential needs like housing, food, and transportation. Many may forgo necessary medical care, leading to worse health outcomes in the long run. The increased financial strain can also push families into medical debt, further hindering their financial stability.
- Increased risk of delaying or forgoing necessary medical care due to cost.
- Higher likelihood of accumulating medical debt, impacting credit scores and overall financial well-being.
- Potential for increased reliance on emergency rooms for care, which are often more expensive.
Premium Increases and Individuals with Pre-existing Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing conditions are particularly vulnerable to premium increases. They often face higher premiums even before any increase, and a further rise can make coverage unaffordable, leaving them without necessary healthcare. This can lead to a deterioration of their health and increased healthcare costs in the long term. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has protections, but even with these protections, increases can still create substantial challenges.
- Increased difficulty in affording necessary medications and treatments.
- Higher risk of health complications due to delayed or forgone care.
- Potential for increased reliance on charity care or other safety net programs.
Premium Increases: Young Adults vs. Older Adults
The impact of premium increases differs between young adults and older adults. Young adults, often facing higher deductibles and out-of-pocket costs, may be more likely to delay or forgo care due to affordability concerns. Older adults, on the other hand, may have higher healthcare needs and are more vulnerable to the consequences of reduced access to care. While older adults may have Medicare, supplemental plans can still see significant increases in premiums, impacting their ability to cover out-of-pocket costs.
- Young adults: Increased likelihood of delaying preventative care, leading to more serious health issues later.
- Older adults: Greater financial strain in affording necessary medications and treatments, even with Medicare.
Geographic Disparities in Premium Increases
Premium increases are not uniform across geographic locations. Rural areas often face higher premiums due to factors such as limited provider networks and higher transportation costs. Similarly, areas with higher concentrations of individuals with chronic illnesses may experience larger increases. This creates significant health equity challenges. For example, a rural resident in Montana might experience a larger percentage increase than a city-dweller in New York City, even if the raw dollar amount is similar.
- Rural populations may face greater challenges accessing affordable healthcare due to limited provider networks and higher transportation costs.
- Urban areas with high concentrations of individuals with pre-existing conditions may experience higher premium increases.
Premium Increases and Access to Healthcare
The cumulative effect of these premium increases is reduced access to healthcare for many demographics. This includes delayed or forgone preventative care, reduced adherence to medication regimens, and increased reliance on emergency care. These consequences ultimately lead to worse health outcomes and higher overall healthcare costs. For example, delaying preventative screenings for cancer could lead to later diagnosis and more expensive, less effective treatment.
- Increased health disparities based on socioeconomic status, geographic location, and pre-existing conditions.
- Potential for worsening health outcomes due to delayed or forgone care.
- Increased strain on the healthcare system due to higher utilization of emergency services.
Potential Future Trends in Health Insurance Premiums

Predicting the future of health insurance premiums requires considering a complex interplay of technological advancements, shifts in the healthcare landscape, policy changes, and broader economic factors. While precise forecasting is impossible, analyzing current trends and likely developments allows us to paint a plausible picture of potential premium trajectories over the next five years.
Technological Advancements and Premium Costs
Technological advancements hold the potential to both increase and decrease health insurance premiums. On one hand, advancements in personalized medicine, gene editing, and sophisticated diagnostic tools could lead to higher initial costs, driving up premiums in the short term. However, in the long run, these technologies may lead to more effective treatments and preventative measures, potentially reducing overall healthcare spending and, consequently, premiums. For example, the widespread adoption of telehealth has already demonstrated the potential to lower costs associated with routine check-ups and consultations. The continued development and integration of AI in diagnostics and treatment planning could further streamline processes and improve efficiency, potentially mitigating premium increases.
Impact of Healthcare Landscape Changes on Premiums
The aging population, coupled with the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease, will likely continue to exert upward pressure on healthcare costs. This demographic shift necessitates increased healthcare resources and services, ultimately affecting premium rates. Furthermore, changes in provider reimbursement models, such as the shift towards value-based care, could impact premiums. While value-based care aims to improve efficiency and quality, its initial implementation might involve adjustments that temporarily influence premium costs before yielding long-term savings. The consolidation of healthcare systems, potentially leading to less competition and higher negotiated prices, could also contribute to premium increases.
Potential Policy Changes Affecting Premium Costs
Government regulations and policy decisions significantly influence health insurance premiums. For instance, changes to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or the introduction of new healthcare legislation could substantially alter premium structures. Policies aimed at increasing transparency in healthcare pricing, controlling pharmaceutical costs, or expanding access to preventative care could moderate premium growth. Conversely, policies that reduce government subsidies or weaken regulations could lead to higher premiums. The impact of these policy shifts is often complex and varies based on specific provisions and their implementation.
Factors Contributing to Premium Stabilization or Decrease
Several factors could contribute to a stabilization or even a decrease in premium increases. Increased consumer engagement in healthcare decision-making, driven by greater access to information and tools for cost comparison, could foster price competition among providers. Furthermore, a greater focus on preventative care and wellness programs, along with initiatives promoting healthier lifestyles, could lead to a reduction in the incidence of chronic diseases, lowering overall healthcare expenditures. Finally, improvements in healthcare efficiency and technology, as discussed earlier, could result in cost savings that are passed on to consumers in the form of lower premiums.
Projected Future Trends in Health Insurance Premiums (5-Year Outlook)
The following visual representation depicts a possible trend line for average annual health insurance premiums over the next five years. Imagine a graph with “Year” on the horizontal axis (Years 2024-2028) and “Average Annual Premium” on the vertical axis. The line starts at a point representing the 2024 average premium, showing a moderate upward trend in the first two years (2024-2025). This initial increase reflects the continuing impact of inflation and rising healthcare costs. However, from 2026 onwards, the upward trend slows considerably, flattening out into a less steep incline by 2028. This moderation reflects the gradual influence of technological advancements, policy changes promoting cost containment, and a greater emphasis on preventative care. While the premium will still be higher in 2028 than in 2024, the rate of increase will have significantly decreased, suggesting a potential future stabilization or even a slowing of premium growth. This illustrates a scenario where initial cost increases are gradually offset by longer-term efficiencies and preventative measures.
Ultimate Conclusion
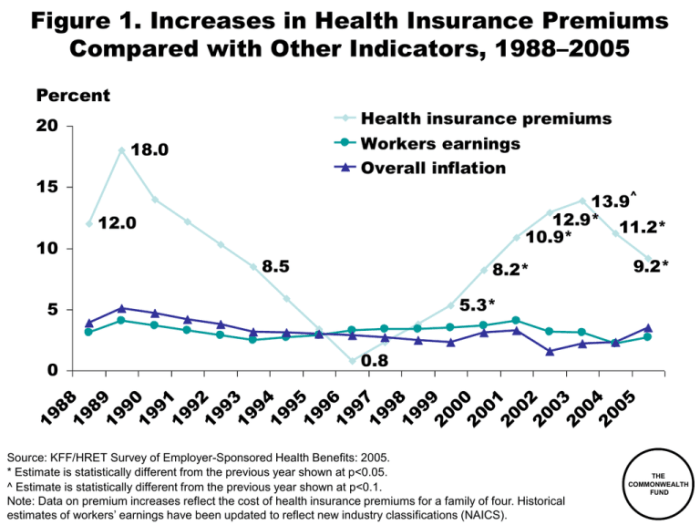
The rise in health insurance premiums for 2024 presents a significant challenge, demanding proactive strategies from both individuals and policymakers. While the factors contributing to these increases are complex and interconnected, understanding the key drivers—from rising healthcare costs and pharmaceutical prices to administrative expenses and utilization patterns—is crucial for effective mitigation. By employing cost-saving strategies, actively engaging in plan selection, and advocating for policy reforms, we can navigate these challenges and ensure continued access to quality healthcare for all. The future of affordable healthcare requires a collaborative effort, and informed action is the first step toward a more sustainable and equitable system.
Clarifying Questions
What are the main reasons behind the increase in health insurance premiums in 2024?
Several factors contribute, including rising healthcare costs (hospital stays, procedures), increased prescription drug prices, higher utilization of healthcare services, administrative costs, and insurer profits.
Can I do anything to lower my health insurance premiums?
Yes. Consider a high-deductible plan with an HSA, shop around for different plans, negotiate medical bills, and utilize preventative care to reduce future costs.
How do rising premiums affect access to healthcare?
Higher premiums can limit access for low-income individuals and families, forcing some to forgo necessary care due to unaffordability. This disproportionately affects vulnerable populations.
What are Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)?
HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts used to pay for qualified medical expenses. They are often paired with high-deductible health plans.