Navigating the complexities of homeownership often involves understanding mortgage insurance premiums. For those considering an FHA loan in 2024, grasping the intricacies of FHA Mortgage Insurance Premiums (MIP) is crucial. This guide provides a clear and comprehensive overview of the 2024 FHA MIP chart, breaking down its components, influencing factors, and cost implications. We’ll explore the different types of MIP, how they’re calculated, and how they compare to other mortgage insurance options, empowering you to make informed decisions about your financial future.
Understanding FHA MIP is essential for budgeting accurately and comparing the overall cost of an FHA loan against other mortgage options. This guide will walk you through various scenarios, helping you visualize the impact of different loan amounts, down payments, and loan terms on your total MIP costs. We aim to demystify the process and provide you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the path to homeownership.
FHA Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP) Basics for 2024
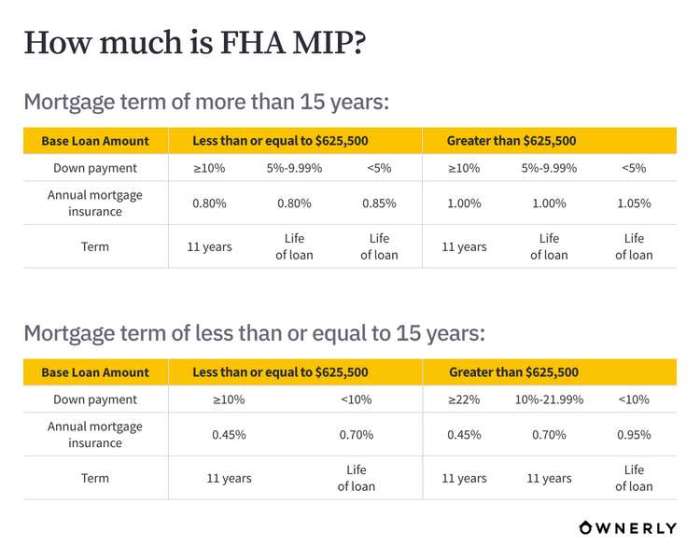
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) insures mortgages, reducing the risk for lenders and making homeownership more accessible. A key component of FHA loans is the Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP), a fee that protects the lender against potential losses if a borrower defaults. Understanding the different types and calculations of MIP is crucial for prospective homebuyers.
FHA MIP Purpose and Types
The purpose of FHA MIP is to mitigate the risk for lenders who provide FHA-insured mortgages. This protection allows lenders to offer more favorable terms and approve more borrowers. For 2024, FHA MIP consists of two main components: an upfront MIP and an annual MIP. The upfront MIP is a one-time fee paid at closing, while the annual MIP is an ongoing cost paid monthly as part of the mortgage payment.
Upfront MIP Calculation
The upfront MIP is calculated as a percentage of the base loan amount. In 2024, the standard upfront MIP rate is typically 1.75% of the base loan amount. This percentage can vary slightly depending on the loan term and other factors, but 1.75% serves as a good general estimate. This fee can be financed into the loan, increasing the total loan amount.
Annual MIP Calculation
The annual MIP is calculated as a percentage of the remaining loan balance and is paid monthly. The annual MIP rate varies based on the loan term and the type of loan. For example, for a 15-year loan, the annual MIP rate is generally lower than for a 30-year loan. The annual MIP is typically paid for the life of the loan, unless the borrower reaches a certain level of equity in their home.
MIP Calculation Examples
Let’s illustrate MIP calculation with examples. Assume a 1.75% upfront MIP rate and a variable annual MIP rate based on the loan term and other loan-specific factors. These rates are approximations and should be verified with current FHA guidelines.
Example 1: Loan amount of $200,000.
Upfront MIP: $200,000 x 0.0175 = $3,500
Annual MIP: This would depend on the loan term and the specific annual MIP rate for that term. It will be reflected as a monthly payment.
Example 2: Loan amount of $300,000.
Upfront MIP: $300,000 x 0.0175 = $5,250
Annual MIP: Again, this is dependent on the loan term and the specific annual MIP rate for that term, appearing as a monthly payment.
Sample FHA MIP Calculation Table
| Loan Amount | Upfront MIP (1.75%) | Estimated Annual MIP (Example – 0.8% for 30-year loan) | Estimated Monthly Annual MIP (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $200,000 | $3,500 | $2,400 (Annual) | $200 (Monthly) |
| $250,000 | $4,375 | $3,000 (Annual) | $250 (Monthly) |
| $300,000 | $5,250 | $3,600 (Annual) | $300 (Monthly) |
*Note: Annual and Monthly MIP amounts are estimates and will vary depending on the loan term and specific FHA guidelines.*
Factors Affecting 2024 FHA MIP Rates
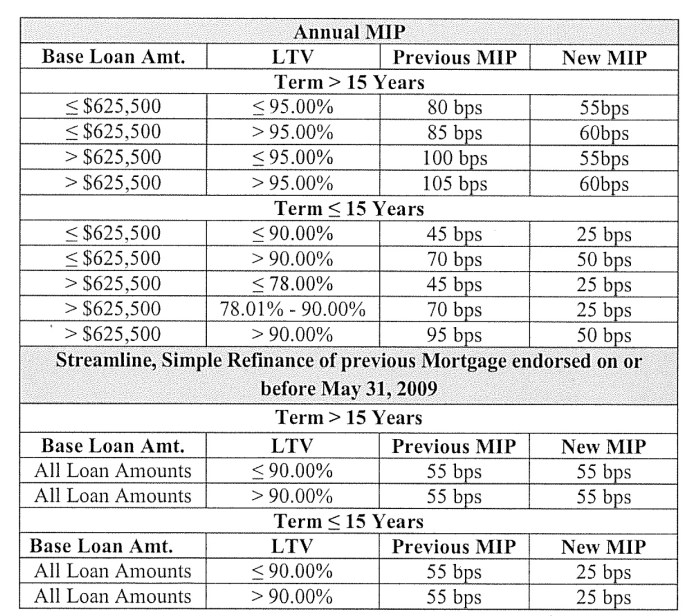
Several key factors influence the FHA Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP) rates you’ll pay in 2024. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately budgeting for your home purchase. These factors interact to determine your specific MIP cost, making it essential to consider them holistically.
Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV) Impact on MIP
The loan-to-value ratio (LTV) is a significant determinant of your MIP. The LTV is calculated by dividing the loan amount by the appraised value of the property. A lower LTV generally translates to a lower MIP, reflecting the reduced risk to the FHA. For example, a borrower with a 20% down payment will have a lower LTV (80%) and consequently a lower MIP compared to a borrower with a 5% down payment (95% LTV). The higher the LTV, the greater the risk for the FHA, leading to a higher MIP to compensate for that increased risk.
Down Payment Amount’s Effect on MIP
The down payment amount directly affects the LTV and, therefore, the MIP. A larger down payment results in a lower LTV, leading to a lower MIP. Conversely, a smaller down payment increases the LTV and consequently the MIP. This is because a larger down payment signifies less risk for the lender and the FHA. Borrowers should carefully consider the trade-off between a smaller down payment and potentially higher MIP costs.
MIP Rates for Different Loan Terms
MIP rates can also vary depending on the loan term. Generally, 15-year mortgages have lower MIP rates than 30-year mortgages. This is because shorter-term loans present less risk to the FHA due to the faster repayment schedule. The shorter repayment period minimizes the length of time the FHA is exposed to potential default. While the monthly payment is higher for a 15-year loan, the overall MIP paid will likely be less.
MIP Scenarios Based on LTV
The following scenarios illustrate how different LTVs impact MIP rates. Note that these are examples and actual rates may vary slightly based on other factors and the specific FHA guidelines in effect. It’s always recommended to consult with a lender for the most up-to-date and accurate information.
- Scenario 1: 10% Down Payment (90% LTV): Higher MIP rate due to higher risk.
- Scenario 2: 15% Down Payment (85% LTV): Moderately lower MIP rate compared to Scenario 1.
- Scenario 3: 20% Down Payment (80% LTV): Lower MIP rate due to lower risk.
Comparing FHA MIP with Other Mortgage Insurance
Choosing between an FHA loan with its associated MIP and a conventional loan requiring PMI involves careful consideration of several factors. Both are mortgage insurance designed to protect lenders from losses if a borrower defaults, but they differ significantly in their structure, cost, and eligibility requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
FHA MIP versus PMI: A Direct Comparison
FHA MIP and PMI serve similar purposes, but their application and cost structures differ. PMI, or Private Mortgage Insurance, is required on conventional loans when the down payment is less than 20% of the home’s purchase price. FHA MIP, on the other hand, is required on all FHA-insured loans, regardless of the down payment. This means that even with a substantial down payment on an FHA loan, you’ll still pay MIP. The key difference lies in who provides the insurance: a private company for PMI and the Federal Housing Administration for MIP.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FHA MIP Compared to PMI
FHA MIP offers several advantages, primarily its accessibility to borrowers with lower credit scores and smaller down payments. However, it also comes with some drawbacks. PMI, while potentially less expensive in some scenarios, generally requires a higher credit score and a larger down payment for eligibility.
| Feature | FHA MIP | PMI |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Score Requirements | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Down Payment Requirements | Can be as low as 3.5% | Typically requires at least 10% |
| Insurance Cost | Usually higher upfront and ongoing, but can be lower in certain situations compared to PMI | Potentially lower than FHA MIP depending on the loan-to-value ratio and credit score |
| Cancellation | Can be cancelled after reaching a certain loan-to-value ratio (LTV) | Can be cancelled once the loan-to-value ratio reaches 80% |
Situations Where FHA MIP Might Be More Beneficial
FHA MIP proves advantageous for first-time homebuyers, individuals with lower credit scores, or those with limited savings for a down payment. For example, a borrower with a 600 credit score and a 3.5% down payment might find FHA MIP more accessible than securing a conventional loan requiring PMI. The lower credit score and down payment requirement make FHA loans more attainable for this borrower, despite the added cost of MIP.
Examples Illustrating Cost Comparison
Let’s consider two scenarios involving a $300,000 home.
Scenario 1: A borrower secures an FHA loan with a 3.5% down payment ($10,500). The annual MIP might be approximately 1% of the loan amount, resulting in an annual cost of around $2,850.
Scenario 2: A borrower secures a conventional loan with a 10% down payment ($30,000). The annual PMI might be around 0.5% of the loan amount, resulting in an annual cost of approximately $1,350. However, if the borrower had only a 5% down payment, the annual PMI could be significantly higher.
These are illustrative examples; the actual costs vary based on several factors including loan terms, interest rates, and individual borrower profiles. The potential savings from a lower down payment with an FHA loan might outweigh the higher MIP costs for some borrowers.
Wrap-Up
Securing a mortgage can feel overwhelming, but understanding the details of FHA MIP is a significant step towards informed decision-making. This guide has provided a detailed look at the 2024 FHA MIP chart, clarifying the calculation methods, influencing factors, and cost implications. By considering the various scenarios presented and comparing FHA MIP to other mortgage insurance options, you are better equipped to evaluate the true cost of your FHA loan and make a confident choice that aligns with your financial goals. Remember to consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
FAQ Section
What happens to my MIP if I pay off my FHA loan early?
Your annual MIP payments cease upon full loan payoff. The upfront MIP is a one-time cost and is not refundable.
Can I refinance my FHA loan to eliminate MIP?
Yes, refinancing to a conventional loan with at least 20% equity can eliminate MIP. However, refinancing involves new closing costs.
Is the upfront MIP included in my loan amount?
Yes, the upfront MIP is typically financed as part of your overall loan amount.
Are there any exceptions to the standard FHA MIP rates?
While the rates are generally standard, some exceptions may exist for certain loan programs or specific borrower situations. Consult with a lender for details.