The cost of healthcare is a significant concern for many, and understanding medical insurance premiums is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and financial well-being. This guide delves into the complexities of HMO and PPO premiums, providing a clear and concise overview of the factors that influence costs, the various options available, and strategies for managing your insurance expenses effectively. Whether you’re navigating the world of individual plans or employer-sponsored coverage, understanding premiums is key to securing the right level of healthcare protection.
From exploring the differences between individual and family plans to deciphering the often-confusing details of Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC) documents, we’ll break down the essential aspects of medical insurance premiums in a straightforward manner. We will also address common concerns regarding payment methods, late payments, and accessing available financial assistance programs.
Understanding Medical Insurance Premiums

Choosing a health insurance plan involves understanding the costs involved, primarily the premiums. Premiums are the regular payments you make to maintain your health insurance coverage. Understanding the factors that influence these costs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Factors Influencing HMO and PPO Premium Costs
Several factors contribute to the variation in HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) and PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) premium costs. These include the plan’s benefits and coverage, your location, your age, your health status (pre-existing conditions can influence premiums), and the insurer’s administrative costs. Generally, plans with broader networks of providers and more comprehensive benefits tend to have higher premiums. Geographic location plays a significant role; premiums in areas with high healthcare costs are typically higher. The insurer’s administrative overhead, including marketing and claims processing, also impacts premiums. PPO plans often have higher premiums than HMO plans due to their greater flexibility in choosing providers.
Individual vs. Family Premiums
The cost difference between individual and family premiums is substantial. Individual premiums cover only the policyholder, while family premiums cover the policyholder and their eligible dependents (spouse and children). Family premiums are significantly higher than individual premiums because they cover a larger pool of individuals, increasing the potential for healthcare utilization and claims. For example, a family plan may cost two to three times more than an individual plan, depending on the number of dependents and the specific plan details.
Common Premium Payment Methods
Several methods exist for paying health insurance premiums. Most insurers offer a variety of options for convenience. Common methods include automatic bank withdrawals (electronic funds transfer), mailing a check or money order, paying online through the insurer’s website, and paying in person at designated locations. Some employers may also facilitate premium payments through payroll deductions. Choosing a convenient payment method ensures timely premium payments and avoids potential penalties for late payments.
Premium Costs Across Different Age Groups
The table below illustrates how premiums can vary across different age groups. These are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary depending on the insurer, plan type, location, and health status.
| Age Group | Individual HMO Premium (Monthly) | Individual PPO Premium (Monthly) | Family PPO Premium (Monthly) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | $250 | $300 | $750 |
| 26-35 | $300 | $375 | $900 |
| 36-45 | $400 | $500 | $1200 |
| 46-55 | $550 | $650 | $1500 |
Factors Affecting Premium Costs
Understanding the cost of your medical insurance premium involves recognizing several key factors that influence the final price. These factors interact in complex ways, resulting in significant variations in premiums between individuals and groups. This section will detail the most important elements affecting your premium.
Key Health Factors Impacting Premium Rates
Pre-existing conditions, age, and lifestyle choices significantly impact premium costs. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, generally pay higher premiums because they represent a greater risk to the insurance provider. Age is another crucial factor; older individuals typically pay more due to the increased likelihood of needing medical care. Lifestyle choices, including smoking, obesity, and lack of exercise, can also elevate premiums, reflecting the higher risk of developing health problems. For example, a smoker might pay significantly more than a non-smoker of the same age and with a similar medical history. Insurance companies use actuarial data to assess these risks and adjust premiums accordingly.
Geographic Location and Premium Costs
The location where you reside plays a significant role in determining your premium. Areas with high costs of living, specialized medical facilities, and a higher concentration of medical specialists often have higher premiums. For instance, premiums in urban centers with advanced medical technology tend to be higher than those in rural areas with fewer resources. This is because healthcare providers in high-cost areas often charge more for their services, directly impacting insurance costs. Competition among insurance providers within a geographic area can also influence premiums, but the underlying cost of healthcare services remains a major driver.
Employer-Sponsored vs. Individual Plans
The cost of insurance varies dramatically between employer-sponsored and individually purchased plans. Employer-sponsored plans often offer lower premiums due to economies of scale and group purchasing power. Employers negotiate rates with insurance providers on behalf of their employees, resulting in lower costs compared to individuals purchasing coverage on their own. Furthermore, employers frequently contribute a portion of the premium, further reducing the employee’s out-of-pocket expense. Conversely, individuals purchasing plans directly from insurance companies typically face higher premiums because they lack the bargaining power of a large employer group. The availability of subsidies and tax credits can mitigate this cost difference for some individuals, but the fundamental disparity often remains.
Premium Calculation Process
The following flowchart illustrates the typical process used to calculate insurance premiums:
[Start] --> [Assess Applicant's Health Profile (Age, Pre-existing Conditions, Lifestyle)] --> [Determine Geographic Location] --> [Consider Plan Type (Individual vs. Employer-Sponsored)] --> [Apply Actuarial Data & Risk Assessment] --> [Calculate Base Premium] --> [Add Applicable Fees & Taxes] --> [Final Premium Determined] --> [End]
Illustrative Examples of Premium Costs
Understanding the cost of medical insurance premiums can be complex, but looking at specific examples helps clarify the factors involved. The following illustrations demonstrate how various factors influence premium costs, providing a clearer picture of what you might expect to pay.
Premium Differences Between Two HMO Plans
Let’s compare two hypothetical HMO plans, “Plan A” and “Plan B,” offered by the same insurance provider in the same geographic area. Plan A is a basic plan with a lower monthly premium of $300, but it has a higher copay ($50) for doctor visits and a higher deductible ($2,000) before significant insurance coverage begins. Plan B offers a higher monthly premium of $450, but it features lower copays ($25) and a lower deductible ($1,000). The choice between these plans depends on individual risk tolerance and anticipated healthcare needs. Someone expecting frequent doctor visits might find Plan B more cost-effective in the long run, despite the higher premium, while someone expecting fewer visits might prefer the lower premium of Plan A.
Sample Insurance Policy and Premiums
Consider a sample family health insurance policy from a hypothetical provider, “HealthyLife Insurance.” This policy covers two adults and one child. The policy includes comprehensive coverage, including hospitalization, surgery, and prescription drugs. The monthly premium for this policy is $1,200. This premium includes a $500 annual deductible per person, a 20% co-insurance rate after the deductible is met, and a maximum out-of-pocket expense of $6,000 per year per person. The policy also covers preventative care, such as annual checkups and vaccinations, with no additional cost. This example showcases a higher premium due to the family coverage and the comprehensive benefits included.
Impact of Adding Dependents on Premiums
Adding dependents significantly increases the overall premium. For instance, if the HealthyLife Insurance policy described above only covered one adult, the monthly premium might be $600. Adding a spouse increases the cost to $900, and adding a child increases it further to $1,200. This demonstrates the substantial cost increase associated with family coverage, reflecting the increased risk the insurance company assumes.
Cost Difference Between High-Deductible and Low-Deductible Plans
Let’s compare a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) with a low-deductible plan. A hypothetical HDHP might have a monthly premium of $200 and an annual deductible of $5,000. A low-deductible plan from the same provider might have a monthly premium of $400 and an annual deductible of $1,000. The HDHP offers significant cost savings upfront, but the individual bears a higher financial risk if significant healthcare is required before the deductible is met. The low-deductible plan offers greater protection against high medical bills but comes with a considerably higher monthly premium. The best choice depends on individual financial circumstances and risk tolerance.
Ultimate Conclusion
Securing affordable and comprehensive healthcare coverage is a vital step in safeguarding your health and financial future. By understanding the intricacies of medical insurance premiums, including the factors that influence costs and the available options, you can make informed choices that best suit your needs and budget. Remember to carefully review your policy details, utilize available resources, and don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance when needed. Taking control of your healthcare costs empowers you to prioritize your well-being with confidence.
Expert Answers
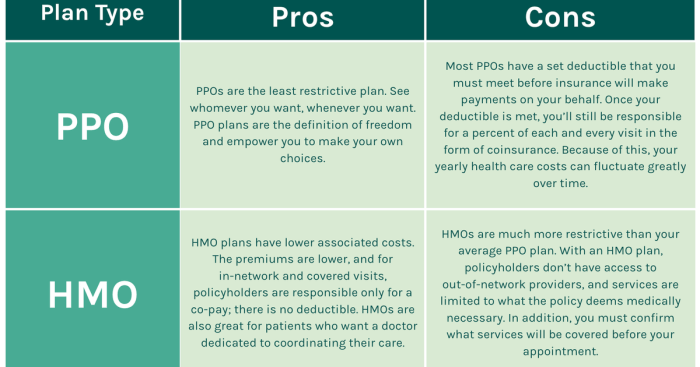
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO?
HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations) typically require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who manages your care and refers you to specialists. PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations) offer more flexibility, allowing you to see specialists without a referral, but often at a higher cost.
Can I change my medical insurance plan during the year?
Generally, you can only change your plan during open enrollment periods, unless you experience a qualifying life event (like marriage, birth, or job loss) that allows for a special enrollment period. Check with your insurance provider for specific details.
What happens if I miss a premium payment?
Missing premium payments can lead to your coverage being cancelled or suspended. Late fees may also apply. Contact your insurance provider immediately if you anticipate difficulties making a payment to explore options for avoiding cancellation.
Where can I find financial assistance for health insurance?
Government programs like the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace offer subsidies and tax credits to help individuals and families afford health insurance. You can also explore assistance programs offered by your state or local government.