Capital premium finance insurance offers businesses a unique pathway to manage large insurance premiums, transforming a potential financial burden into a strategic advantage. This guide delves into the intricacies of this specialized financing solution, exploring its mechanics, benefits, and potential drawbacks to provide a clear understanding of its role in modern business strategy. We will examine how this insurance works, the legal landscape surrounding it, and real-world examples of its successful implementation.
Understanding capital premium finance insurance requires navigating the complex interplay between lenders, insurers, and businesses. This involves careful consideration of various factors, including the specific insurance needs of the business, the terms of the financing agreement, and the potential financial implications. This guide aims to demystify this process, providing a clear and concise overview for businesses seeking to leverage this powerful financial tool.
Definition and Scope of Capital Premium Finance Insurance
Capital premium finance insurance is a specialized form of financing that allows businesses to pay their insurance premiums over time, rather than in a single lump sum. This financing is secured by the insurance policy itself, acting as collateral. Essentially, it’s a loan specifically designed to cover the cost of insurance premiums, offering businesses greater flexibility in managing their cash flow.
This type of financing differs significantly from other forms of business loans as it is directly tied to the insurance policy. The lender’s risk is mitigated by the policy’s value, making it an attractive option for both the lender and the borrower.
Businesses Utilizing Capital Premium Finance Insurance
Businesses that frequently benefit from capital premium finance insurance are those with significant insurance premium costs and fluctuating cash flows. These often include businesses with large commercial property insurance policies, significant liability coverage, or extensive fleets of vehicles requiring comprehensive insurance. The need for this type of financing often arises when a company faces unexpected expenses or seasonal fluctuations in revenue. For example, a construction company might require substantial insurance coverage for its projects and equipment, making premium financing a practical solution to manage cash flow during periods of low project activity.
Situations Where Capital Premium Finance Insurance is Most Beneficial
Capital premium finance insurance proves particularly beneficial in scenarios where immediate access to substantial capital for premium payments is unavailable. This might be due to a business experiencing temporary financial constraints, or when large, unexpected insurance premiums become due. For instance, a sudden increase in liability insurance premiums following an incident could be easily managed through this financing option. Another example would be a small business experiencing a period of slow sales; instead of dipping into operating capital, premium financing can ensure insurance coverage remains uninterrupted.
Comparison to Other Financing Options
Compared to other financing options like traditional business loans or lines of credit, capital premium finance insurance offers a more specialized and often simpler application process. Traditional loans may require extensive financial documentation and a more rigorous credit assessment. In contrast, premium finance is often approved more quickly, with the insurance policy itself providing a substantial level of security for the lender. Furthermore, unlike general business loans which can be used for any purpose, this type of financing is solely dedicated to insurance premium payments, providing a clear and focused use of funds. This specificity often translates to more favorable interest rates compared to general purpose loans, particularly for businesses with strong credit profiles and valuable insurance policies.
How Capital Premium Finance Insurance Works
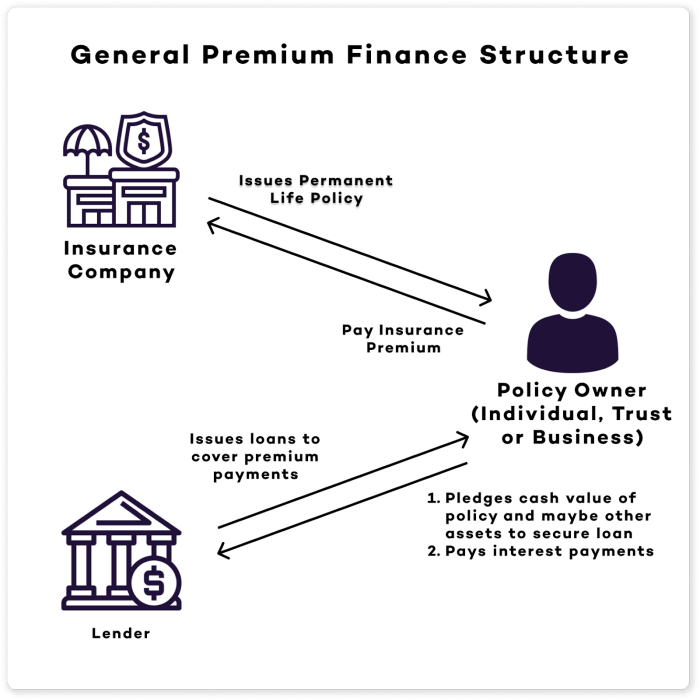
Capital premium finance insurance provides a crucial financial mechanism for businesses and individuals needing to pay large insurance premiums upfront. It essentially allows the insured to spread the cost of their premium payments over time, often through a loan agreement, while mitigating the risk for the lender. This process involves a carefully structured arrangement between the insured, a lender specializing in premium finance, and the insurance provider.
The process of securing capital premium finance insurance involves several key steps. First, the insured applies for the insurance policy with their chosen provider. Simultaneously, or shortly thereafter, they apply for premium financing with a lender. The lender will assess the insured’s creditworthiness and the terms of the insurance policy. If approved, the lender pays the insurance premium in full to the insurer, and the insured repays the loan to the lender, typically in installments over a predetermined period.
The Roles of the Lender and the Insurance Provider
The lender acts as the financial intermediary, providing the capital to pay the insurance premium upfront. They evaluate the risk involved in lending to the insured, considering factors like credit history, income, and the type of insurance policy. The insurance provider, on the other hand, receives the premium payment in full and provides the insurance coverage as agreed upon in the policy. Both parties have a vested interest in the successful completion of the transaction; the lender wants repayment of the loan, and the insurer wants to ensure the policy remains in force.
Key Terms and Conditions in Capital Premium Finance Agreements
Several key terms and conditions are typically included in capital premium finance agreements. These commonly involve the loan amount (equal to the insurance premium), the interest rate charged by the lender, the repayment schedule (often monthly installments), the loan term (duration of the repayment period), and any associated fees or charges. The agreement will also specify the consequences of default, including potential penalties or the cancellation of the insurance policy. It’s crucial for the insured to carefully review and understand all terms before signing the agreement.
A Step-by-Step Guide to a Typical Transaction
A typical capital premium finance insurance transaction unfolds as follows:
- Application for Insurance: The insured applies for and is approved for an insurance policy.
- Application for Premium Finance: The insured applies for premium financing with a lender, providing necessary financial information.
- Credit Assessment: The lender assesses the insured’s creditworthiness and the risk associated with the loan.
- Loan Approval: If approved, the lender provides a loan agreement outlining the terms and conditions.
- Premium Payment: The lender pays the insurance premium directly to the insurance provider.
- Policy Activation: The insurance policy is activated, providing coverage to the insured.
- Repayment: The insured makes regular installment payments to the lender according to the agreed-upon schedule.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Capital Premium Finance Insurance

Capital Premium Finance Insurance offers a unique approach to managing insurance premiums, particularly for businesses with substantial coverage needs. Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages is crucial for making an informed decision about whether this financing method is right for your situation. This section will Artikel the key benefits and drawbacks, providing a balanced perspective to aid in your evaluation.
Advantages of Capital Premium Finance Insurance
Using capital premium finance insurance presents several compelling advantages for businesses. Primarily, it allows businesses to manage cash flow more effectively by spreading the cost of large insurance premiums over a period, rather than paying a lump sum. This can be particularly beneficial for smaller businesses or those experiencing temporary cash flow constraints. Furthermore, it can improve a company’s credit rating by demonstrating responsible financial management and freeing up capital for other operational needs. Finally, it offers a predictable and manageable payment schedule, providing budgeting certainty and reducing the risk of unexpected financial burdens.
Disadvantages and Risks of Capital Premium Finance Insurance
While capital premium finance insurance offers significant benefits, it’s important to acknowledge potential drawbacks. The primary concern is the added cost associated with the financing. Interest charges and fees will increase the overall cost of the insurance premium. Additionally, the financing agreement itself carries risks. Failure to make timely payments can result in penalties and potentially the cancellation of the insurance policy, leaving the business exposed. Moreover, the terms of the agreement, including interest rates and repayment schedules, need careful consideration to ensure they align with the business’s financial capabilities. Finally, the complexity of the financing process may require professional financial advice to fully understand the implications.
Comparison of Pros and Cons
| Benefit | Drawback |
|---|---|
| Improved cash flow management | Increased overall cost of insurance due to interest and fees |
| Frees up capital for other investments | Risk of penalties or policy cancellation for missed payments |
| Predictable and manageable payment schedule | Complexity of the financing agreement and potential need for professional advice |
| Potential improvement in credit rating | Potential negative impact on financial ratios if not managed carefully |
Financial Implications
The financial implications of capital premium finance insurance are multifaceted. On the positive side, improved cash flow can lead to increased profitability and investment opportunities. The freed-up capital can be used for expansion, equipment upgrades, or other strategic initiatives. However, the added cost of interest and fees needs to be carefully factored into the overall financial planning. Failure to account for these costs accurately can negatively impact profitability and potentially strain the business’s finances. A thorough cost-benefit analysis, considering both the short-term and long-term financial effects, is crucial before entering into such an agreement. For example, a small business might find that the improved cash flow allows them to secure a larger contract, ultimately offsetting the financing costs. Conversely, a business already struggling with cash flow might find the additional interest burden unsustainable.
Future Trends and Developments

The capital premium finance insurance market is poised for significant change, driven by technological advancements, evolving regulatory landscapes, and shifting consumer demands. Understanding these trends is crucial for insurers, brokers, and businesses utilizing this financing method to adapt and thrive in a dynamic market. The coming years will likely witness a convergence of factors that reshape the landscape of capital premium finance.
Technological advancements will play a pivotal role in the evolution of capital premium finance insurance. Increased automation, improved data analytics, and the expansion of digital platforms will streamline processes, enhance risk assessment, and improve customer experiences. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will likely lead to more accurate underwriting, personalized pricing, and more efficient claims handling.
Increased Use of Insurtech and Fintech Solutions
The integration of Insurtech and Fintech solutions is expected to significantly impact the efficiency and accessibility of capital premium finance. Insurtech companies are developing innovative platforms that automate underwriting processes, simplify application procedures, and provide real-time policy management tools. Fintech solutions, meanwhile, offer streamlined payment processing and improved risk assessment capabilities through sophisticated algorithms and data analysis. For example, a hypothetical Insurtech platform could automatically assess the creditworthiness of applicants and provide instant approval for premium financing, reducing processing times from days to minutes. This increased speed and efficiency would make capital premium finance more attractive to a wider range of businesses.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Changes in regulatory environments, both at national and international levels, will influence the capital premium finance market. Increased scrutiny of financial products and a focus on consumer protection may lead to stricter regulations regarding transparency, disclosure, and responsible lending practices. For instance, stricter regulations might require more detailed disclosures of interest rates and fees associated with premium finance, ensuring greater transparency for consumers. Conversely, regulatory changes could also aim to stimulate the market by simplifying compliance requirements or encouraging the use of innovative technologies. These changes could necessitate adjustments in business models and operational procedures for insurers and brokers involved in capital premium finance.
Expansion of Product Offerings and Customization
The future of capital premium finance insurance will likely see an expansion of product offerings and a greater focus on customization. Insurers may develop more tailored premium finance plans to cater to the specific needs of different business segments and risk profiles. This might include specialized products for specific industries or those with unique risk characteristics. For example, a premium finance plan could be designed specifically for businesses in the construction industry, taking into account the inherent risks associated with that sector. Moreover, we can expect to see more flexible repayment options and innovative financing structures to accommodate diverse customer preferences and financial situations.
Enhanced Customer Experience through Digitalization
Digitalization will play a key role in improving the customer experience within capital premium finance. Online portals, mobile apps, and automated communication tools will streamline interactions between insurers, brokers, and customers. This will lead to increased transparency, quicker response times, and improved accessibility. For example, a customer could use a mobile app to track their payments, view their policy details, and communicate directly with their insurer or broker. This improved customer experience is crucial for building trust and loyalty, particularly in a competitive market.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, capital premium finance insurance presents a valuable tool for businesses seeking to effectively manage significant insurance premium payments. By carefully weighing the benefits and drawbacks, understanding the regulatory landscape, and selecting a reputable lender and insurer, businesses can harness the potential of this financing option to achieve their financial goals. A thorough understanding of the process and associated risks is crucial for successful implementation and long-term financial health. The future of capital premium finance insurance is likely to be shaped by technological advancements and evolving regulatory environments, demanding continued vigilance and adaptation from businesses utilizing this financial strategy.
Helpful Answers
What types of insurance premiums are typically financed through capital premium finance insurance?
A wide range of insurance premiums can be financed, including commercial property insurance, liability insurance, workers’ compensation insurance, and professional liability insurance, among others. The specific types depend on the lender’s policies and the borrower’s needs.
What are the typical interest rates for capital premium finance insurance?
Interest rates vary depending on factors like creditworthiness, the amount financed, and prevailing market conditions. It’s crucial to compare rates from multiple lenders before committing to a loan.
What happens if a business fails to make payments on a capital premium finance insurance loan?
Failure to make payments can result in penalties, late fees, and potentially even default, leading to legal action by the lender. The lender may also take action to recover the outstanding debt, which could include seizing assets or pursuing legal action.
Are there any hidden fees associated with capital premium finance insurance?
It’s essential to carefully review all loan documents to understand all fees involved, including origination fees, processing fees, and any other charges. Transparency is crucial, and any unclear aspects should be clarified with the lender before proceeding.