Navigating the world of insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. One key element is understanding the “average insurance premium,” a figure that significantly impacts individual budgets and the overall insurance market. This guide unravels the mysteries behind this seemingly simple number, exploring its calculation, influencing factors, regional variations, and future trends. We’ll delve into the diverse landscape of insurance types – from auto and home to health – examining how average premiums are determined and what factors drive their fluctuations.
From demographic influences to the impact of claims history and technological advancements, we will dissect the various components that shape the cost of insurance. This exploration will equip you with the knowledge to better understand your own insurance premiums and make informed decisions.
Factors Affecting Average Premiums
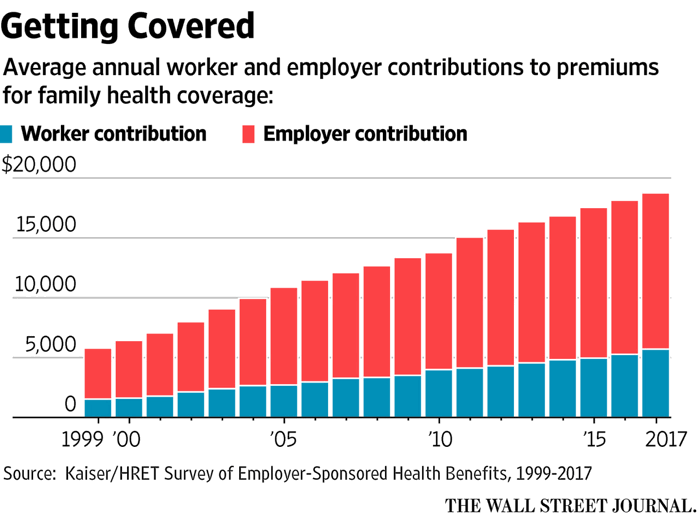
Insurance premiums, the amount you pay for coverage, aren’t arbitrary figures. They’re carefully calculated based on a variety of factors that assess your individual risk. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance choices and potentially lower your premiums.
Demographic Factors and Premiums
Several demographic factors significantly influence insurance premiums. Age, for example, is a key determinant. Younger drivers, statistically, are involved in more accidents, leading to higher premiums. As drivers age and gain experience, their premiums often decrease. Location also plays a crucial role. Premiums are generally higher in areas with higher crime rates, more traffic congestion, and a greater frequency of accidents. Gender can also be a factor, although this is becoming increasingly regulated and less impactful in many jurisdictions. Finally, factors such as marital status and occupation can indirectly influence premiums through their correlation with risk profiles.
Driving History and Credit Score’s Impact on Auto Insurance
Your driving history is a major factor in determining your auto insurance premium. A clean driving record with no accidents or traffic violations will result in lower premiums compared to someone with multiple accidents or speeding tickets. Similarly, your credit score, surprisingly, often plays a role in auto insurance pricing. Insurers believe that individuals with good credit are more likely to be responsible and less likely to file fraudulent claims. Therefore, a higher credit score can lead to lower premiums.
Health History and Lifestyle Choices and Health Insurance Premiums
In the realm of health insurance, your health history and lifestyle significantly impact premiums. Pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, typically lead to higher premiums because they increase the likelihood of future claims. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of exercise, also affect premiums. Insurers consider these factors as they contribute to increased health risks and potentially higher healthcare costs. For instance, a smoker might pay significantly more for health insurance than a non-smoker due to the increased risk of lung cancer and other smoking-related illnesses.
Claims History Across Different Insurance Types
Claims history consistently impacts premiums across all insurance types. Filing a claim, regardless of whether it’s for auto, home, or health insurance, typically results in a premium increase. This is because insurers view claims as indicators of higher risk. The impact of a claim can vary depending on the type of insurance and the nature of the claim. For example, a minor auto accident might result in a smaller premium increase than a major home insurance claim due to the potential for substantial payouts. Multiple claims within a short period significantly increase premiums more than a single incident.
Individual Risk Profiles and Premium Variations
Several aspects contribute to individual risk profiles and resulting premium variations.
- Age and Experience: Younger drivers and those with less experience generally face higher premiums due to increased accident risk.
- Location: Premiums are higher in areas with high accident rates or crime.
- Driving History: Accidents and traffic violations increase premiums.
- Credit Score (for some insurance types): A poor credit score can lead to higher premiums for certain types of insurance.
- Health History (for health insurance): Pre-existing conditions and lifestyle choices influence health insurance costs.
- Vehicle Type (for auto insurance): The type of car you drive affects premiums; sports cars often have higher premiums than sedans.
- Home Security Features (for home insurance): Security systems and other safety features can lower home insurance premiums.
Trends and Predictions in Average Premiums
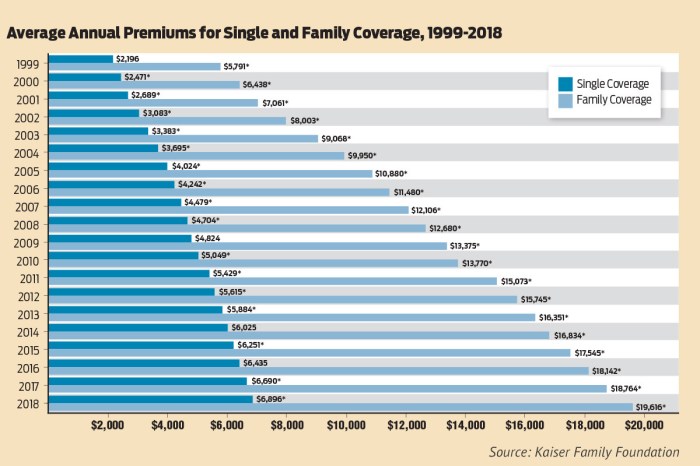
Average insurance premiums have experienced significant fluctuations over the past decade, influenced by a complex interplay of economic, social, and technological factors. Understanding these trends and predicting future movements is crucial for both insurers and consumers to effectively manage risk and financial planning. This section will explore historical premium changes, anticipate future trends, and analyze the potential impact of regulatory shifts.
Historical Overview of Average Premium Changes
Over the past ten years, average insurance premiums across various lines – including auto, home, and health – have generally shown an upward trend. While specific rates vary significantly by location, coverage type, and insurer, a consistent pattern of yearly increases is observable. For example, auto insurance premiums in many regions experienced a 2-5% annual increase, largely driven by factors such as increased healthcare costs (in the case of liability claims) and the rising cost of vehicle repairs. Similarly, home insurance premiums have been impacted by factors such as increased frequency and severity of weather-related events, leading to higher claim payouts and subsequently higher premiums. Health insurance premiums have seen more dramatic fluctuations, often tied to changes in healthcare legislation and the overall cost of healthcare services.
Anticipated Future Trends in Average Premiums
Several factors suggest continued growth in average insurance premiums over the next five years. Inflationary pressures, particularly in the cost of labor and materials, will directly impact insurers’ operational expenses and claim payouts. Technological advancements, while offering potential for efficiency gains, also necessitate significant investments in new systems and cybersecurity measures, adding to overall costs. Furthermore, the increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events, fueled by climate change, will likely lead to higher premiums for homeowners and businesses in vulnerable areas. These escalating costs will inevitably be passed on to consumers in the form of higher premiums.
Projected Growth of Average Premiums
The following describes a line graph illustrating projected average premium growth for the next five years. The horizontal axis represents the year (Year 0 being the present year, Year 1 being next year, and so on until Year 5). The vertical axis represents the average premium amount, expressed as a percentage increase from the current average. The graph would show a generally upward sloping line, starting at 0% increase in Year 0. The line would increase gradually, perhaps showing a steeper incline in Years 3-5, reflecting the accelerating impact of inflation and extreme weather events. For instance, a possible data point could be a 3% increase in Year 1, rising to 5% in Year 3, and reaching approximately 8% in Year 5. This projected growth is based on conservative estimates, assuming moderate inflationary pressures and a gradual increase in catastrophic events. Significant unforeseen events, such as a major pandemic or widespread economic recession, could significantly alter this projection.
Potential Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes at both the state and federal levels can significantly impact average insurance premiums. For example, new regulations aimed at increasing transparency and consumer protection could increase administrative costs for insurers, potentially leading to higher premiums. Conversely, deregulation in certain areas might lead to increased competition and lower premiums for consumers. Furthermore, changes in mandated coverage levels (such as minimum auto insurance requirements) could also significantly influence premium levels. For example, a mandated increase in minimum liability coverage would likely increase premiums, as insurers would need to cover larger potential payouts. The ongoing debate around healthcare reform continues to significantly influence health insurance premiums, highlighting the considerable impact of regulatory decisions.
Wrap-Up
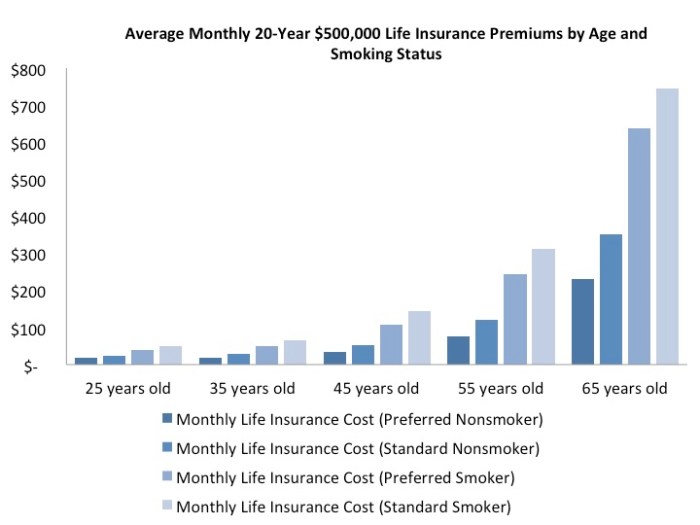
In conclusion, understanding average insurance premiums is crucial for both consumers and industry professionals. While the average provides a benchmark, individual premiums are highly personalized, reflecting a complex interplay of factors. By recognizing these influences and staying informed about market trends, individuals can better manage their insurance costs and secure appropriate coverage. The future of insurance premiums will likely be shaped by evolving technologies, regulatory changes, and societal shifts, making continuous learning essential in this dynamic landscape.
FAQ Summary
What is the difference between an average premium and my individual premium?
The average premium represents a statistical average across a large population. Your individual premium is tailored to your specific risk profile, which includes factors like age, location, driving history (for auto insurance), health history (for health insurance), and claims history.
How often do average insurance premiums change?
Average premiums fluctuate regularly, influenced by various factors such as inflation, claims costs, and regulatory changes. Insurance companies typically adjust rates periodically, sometimes annually or even more frequently.
Can I negotiate my insurance premium?
While you can’t directly negotiate the base rate, you can often influence your premium by improving your risk profile (e.g., taking a defensive driving course, improving your credit score). Comparing quotes from multiple insurers is also crucial for securing the best possible rate.
What is the impact of inflation on average insurance premiums?
Inflation directly affects the cost of providing insurance, leading to increased claims costs and operational expenses. This often translates to higher premiums over time.