Navigating the world of tax deductions can be a complex undertaking, particularly when it comes to insurance premiums. The question, “Are insurance premiums deductible?” isn’t a simple yes or no. The answer hinges on several factors, including the type of insurance, your employment status, and the specific tax laws of your country. This guide unravels the intricacies of insurance premium deductibility, offering clarity and insight into this often-confusing aspect of personal finance.
We’ll explore the various types of insurance premiums – from health and auto to home and life – examining the deductibility rules for each. We’ll delve into the significant differences in regulations across countries like the USA, Canada, and the UK, highlighting the specific requirements and limitations for claiming deductions. The guide also clarifies the distinctions between deductibility for self-employed individuals and those employed by a company, providing illustrative examples to solidify understanding.
Types of Insurance Premiums
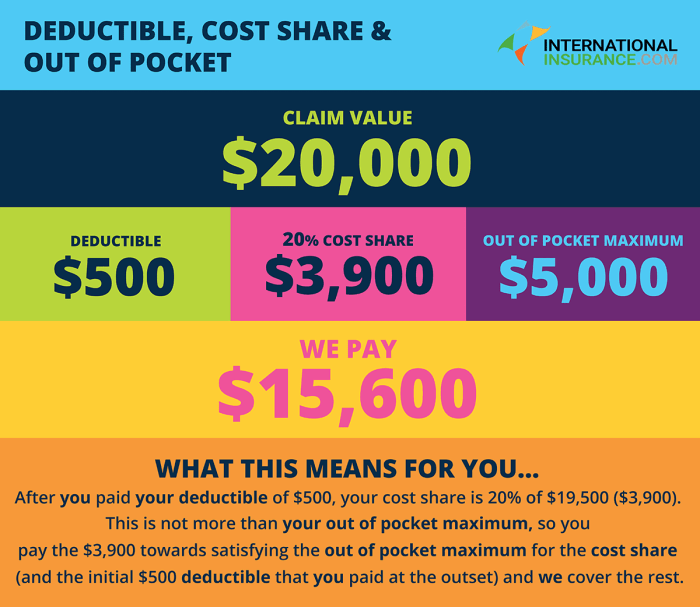
Understanding the different types of insurance premiums and the factors influencing their cost is crucial for effective financial planning. This section will explore various categories, highlighting their key features and cost determinants.
Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums cover medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription drugs. Examples include plans offered through employers, the Affordable Care Act marketplaces, and private insurers. The cost of health insurance premiums is significantly influenced by factors such as age, location, the type of plan (e.g., HMO, PPO), the level of coverage, and pre-existing conditions. Higher deductibles and co-pays generally result in lower premiums, while comprehensive coverage commands higher premiums.
Auto Insurance Premiums
Auto insurance premiums protect against financial losses resulting from car accidents. This includes liability coverage (for injuries or damage caused to others), collision coverage (for damage to your own vehicle), and comprehensive coverage (for non-collision damage, such as theft or vandalism). Factors influencing auto insurance premiums include driving history (accidents and tickets), age, location (higher crime rates often mean higher premiums), vehicle type (expensive cars often cost more to insure), and driving habits (mileage driven). Younger drivers and those with poor driving records typically pay higher premiums.
Home Insurance Premiums
Home insurance premiums cover damage or loss to your home and its contents due to events like fire, theft, or natural disasters. The cost of home insurance is affected by factors such as the location of the home (risk of natural disasters), the value of the home and its contents, the age and condition of the home, and security features (alarms, security systems). Homes in areas prone to hurricanes or earthquakes will generally have higher premiums than those in less risky areas.
Life Insurance Premiums
Life insurance premiums provide a financial benefit to designated beneficiaries upon the death of the insured individual. There are various types of life insurance, including term life insurance (coverage for a specific period) and whole life insurance (permanent coverage). The cost of life insurance premiums is influenced by factors such as age, health, lifestyle (smoking, risky hobbies), the amount of coverage, and the type of policy. Younger, healthier individuals typically qualify for lower premiums.
| Insurance Type | Deductibility Rules | Limitations | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance | Generally deductible as an itemized medical expense, subject to AGI limitations. | Subject to 7.5% AGI threshold for medical expense deductions. | Premiums paid through an employer or the marketplace. |
| Auto Insurance | Generally not deductible. | N/A | Liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage. |
| Home Insurance | Generally not deductible. | N/A | Coverage for fire, theft, and other damages. |
| Life Insurance | Premiums are generally not deductible, except in certain circumstances (e.g., business insurance). | Specific requirements and limitations apply to deductible business life insurance premiums. | Term life insurance, whole life insurance. |
Tax Deductibility Rules and Regulations
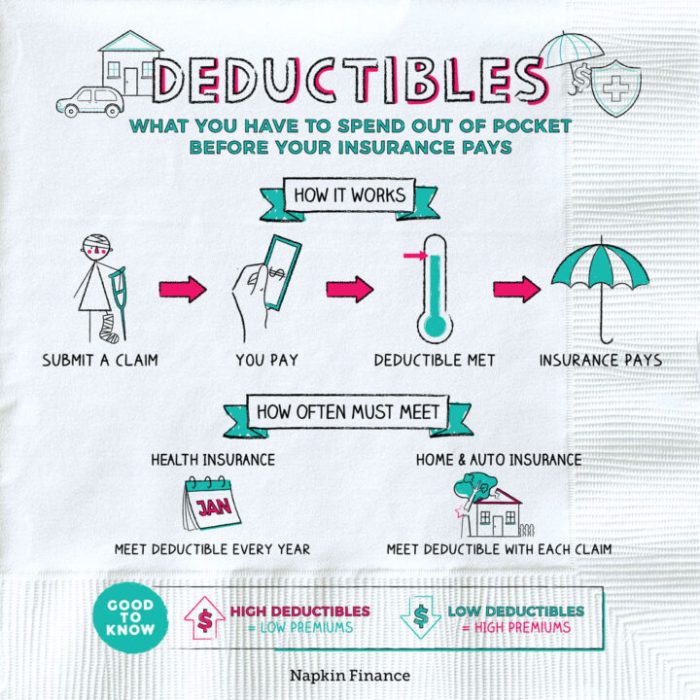
The deductibility of insurance premiums varies significantly across countries, depending on the type of insurance, the taxpayer’s circumstances, and specific tax laws. Understanding these rules is crucial for maximizing tax benefits and ensuring compliance. This section Artikels general rules and key differences in the USA, Canada, and the UK, focusing on significant variations.
Insurance Premium Deductibility: General Rules
Generally, insurance premiums are deductible if the insurance covers business-related expenses or protects against risks associated with income-generating activities. Personal insurance premiums, such as those for health or life insurance, are typically not deductible, with exceptions sometimes made for specific circumstances such as disability insurance related to work. The specific requirements and limitations vary considerably between countries.
Deductibility in the USA
In the USA, the deductibility of insurance premiums depends heavily on the type of insurance. Premiums for health insurance purchased through the Marketplace may be partially deductible through tax credits. Business insurance premiums are generally deductible as business expenses, subject to limitations. However, premiums for personal life insurance are typically not deductible, except in certain situations like Key Person Life Insurance. Detailed documentation, including receipts and policy information, is required for claiming deductions.
Deductibility in Canada
Canadian tax rules allow deductions for insurance premiums related to business activities or income-generating property. This includes premiums for business liability insurance, property insurance, and professional liability insurance. Specific forms and documentation are required to support these deductions. Personal insurance premiums, including life and health insurance, are generally not deductible. However, premiums for disability insurance purchased to replace lost income due to illness or injury may be deductible in certain cases.
Deductibility in the UK
In the UK, the deductibility of insurance premiums largely depends on the nature of the insured asset or activity. Premiums for insurance covering business assets or income-generating activities are generally deductible as business expenses. Personal insurance premiums are usually not deductible. Specific requirements and evidence of expenditure are necessary for claiming deductions.
Requirements for Claiming Deductions
To claim deductions for insurance premiums, taxpayers generally need to provide proof of payment, such as receipts or bank statements, along with details of the insurance policy, including the policy number and the period covered. Tax forms specific to each country will need to be completed accurately, providing details about the insurance premiums paid and their relationship to business or income-generating activities. Maintaining thorough records is essential for a successful claim.
Situations Where Insurance Premiums Are Not Deductible
Insurance premiums are generally not deductible when they relate to personal expenses unrelated to business or income generation. This typically includes personal life insurance, health insurance (with exceptions noted above), and homeowner’s insurance (unless it covers rental properties used for income). Premiums for insurance covering illegal activities are also not deductible. Penalties and fines associated with non-compliance with insurance requirements are likewise not deductible.
Flowchart for Determining Deductibility
[The following describes a flowchart. A visual flowchart would be beneficial but is outside the scope of this text-based response.]
Start: Is the insurance related to a business or income-generating activity?
Yes: Does the country’s tax law allow deduction for this type of insurance?
Yes: Do you have sufficient documentation (receipts, policy details)?
Yes: Deductible.
No: Not Deductible.
No (to either of the first two questions): Is there a specific exception in the tax law allowing deduction for this type of insurance?
Yes: Do you meet the specific criteria for the exception?
Yes: Deductible.
No: Not Deductible.
End
Impact of Health Insurance Premiums
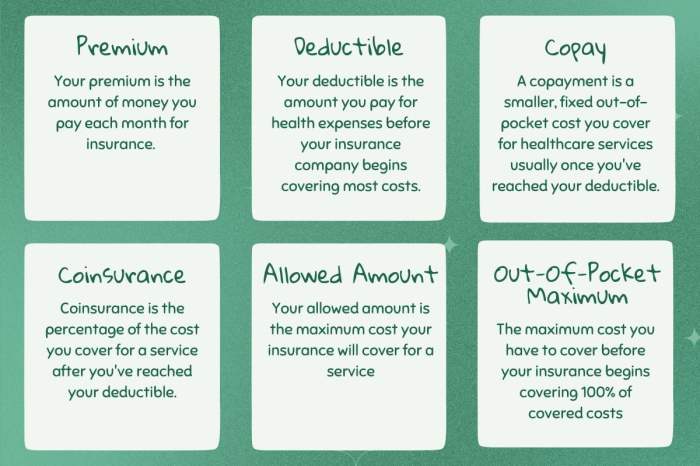
Health insurance premiums represent a significant expense for many individuals and families. Understanding the tax implications of these premiums is crucial for effective financial planning. The deductibility of health insurance premiums varies depending on the type of plan and the applicable tax laws.
The deductibility of health insurance premiums is largely determined by whether the plan is self-purchased or employer-sponsored. This distinction significantly affects the tax benefits individuals can claim. Furthermore, legislation like the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States, or equivalent legislation in other countries, plays a substantial role in shaping the rules and regulations surrounding premium deductibility.
Deductibility of Self-Purchased Health Insurance Premiums
Individuals who purchase health insurance plans independently, rather than through an employer, may be able to deduct the premiums paid as a medical expense. However, this deduction is subject to limitations. The deduction is only allowed for amounts exceeding a certain percentage of the taxpayer’s adjusted gross income (AGI). For example, in the US, only the amount exceeding 7.5% of AGI is deductible. This means that a significant portion of the premium may not be deductible, reducing the overall tax benefit. Taxpayers should consult the specific rules and regulations applicable to their tax jurisdiction to determine the exact limitations.
Deductibility of Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance Premiums
Generally, premiums paid by employers for employee health insurance are not deductible by the employee. The employer may be able to deduct the premiums as a business expense, but this is separate from the employee’s tax liability. However, the employee’s share of the premiums, if any, may be deductible under certain circumstances and subject to the same AGI limitations as self-purchased plans. The specific rules vary by country and tax code.
Impact of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) on Deductibility
The ACA significantly impacted the US healthcare landscape, including the tax treatment of health insurance premiums. While it didn’t directly alter the deductibility rules for self-purchased premiums, it indirectly influenced them through subsidies and tax credits. The ACA made health insurance more accessible and affordable for many, reducing the overall premium burden for some and consequently affecting the amount potentially deductible. The tax credits available under the ACA are designed to offset the cost of health insurance, effectively reducing the amount of premium expenses individuals are left to pay out-of-pocket.
Tax Benefits of Health Insurance Premium Deductions
The ability to deduct health insurance premiums can provide substantial tax savings. By reducing taxable income, taxpayers can lower their overall tax liability. The exact amount saved depends on the taxpayer’s tax bracket and the amount of premiums deducted. For example, a taxpayer in a higher tax bracket will benefit more from a deduction than a taxpayer in a lower tax bracket. This tax savings can free up funds for other financial priorities or contribute to overall financial security.
Illustrative Examples and Scenarios
Understanding the deductibility of insurance premiums can be complex, varying based on the type of insurance, your employment status, and specific tax regulations. The following examples illustrate how these factors interact to determine the deductible portion of your premiums. Remember to always consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
Self-Employed Individual Deducting Health Insurance Premiums
Self-employed individuals can often deduct the cost of health insurance premiums as a business expense. This deduction is taken on Schedule C (Profit or Loss from Business) of Form 1040. The deduction is limited to the amount of net earnings from self-employment.
Example 1: Self-Employed Photographer
Maria, a self-employed photographer, paid $7,200 in health insurance premiums during the tax year. Her net earnings from self-employment were $10,000. She can deduct the full $7,200 in health insurance premiums because it’s less than her net earnings.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance and Deductibility
Generally, premiums paid by employers for employee health insurance are not deductible by the employee. However, if an employee pays additional premiums for a higher level of coverage or for a family plan beyond what the employer provides, those additional premiums might be deductible under certain circumstances, but this is often complex and fact-specific.
Example 2: Employee with Supplemental Insurance
John works for a company that provides basic health insurance. He chooses to pay an additional $1,500 annually for a more comprehensive plan that includes dental and vision coverage. While John cannot deduct the premiums paid by his employer, he may be able to deduct the $1,500 he paid for the supplemental coverage, depending on the specifics of his employer’s plan and the applicable tax laws. This may require careful examination of his W-2 and related documentation.
Deductibility of Long-Term Care Insurance Premiums
Long-term care insurance premiums may be deductible, but the rules are intricate. Deductibility often depends on the age of the policyholder. There may be limitations based on the policy’s face amount and other factors.
Example 3: Long-Term Care Insurance for a Retiree
Susan, a 68-year-old retiree, paid $3,000 in long-term care insurance premiums. Depending on her adjusted gross income (AGI) and other relevant factors, a portion or all of these premiums may be deductible as a medical expense. However, the deduction is subject to a 7.5% AGI threshold; only amounts exceeding 7.5% of her AGI can be deducted. This means that if her AGI is $50,000, she must first deduct $3,750 (7.5% of $50,000) from the $3,000 before she can claim any deduction.
Summary Table
| Scenario | Deductible Amount | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Employed Photographer (Maria) | $7,200 | Full deduction allowed as a business expense, limited to net self-employment income. |
| Employee with Supplemental Insurance (John) | Potentially $1,500 | Deductibility depends on the specifics of the employer-sponsored plan and additional premiums paid. Requires careful review of documentation. |
| Retiree with Long-Term Care Insurance (Susan) | Potentially a portion | Deduction is subject to a 7.5% AGI threshold for medical expenses. The actual deductible amount depends on her AGI. |
Summary
Understanding the deductibility of your insurance premiums can significantly impact your tax liability. While the rules can seem complicated, this guide has provided a framework for navigating the process. By understanding the various factors influencing deductibility – your employment status, the type of insurance, and relevant tax laws – you can confidently assess your eligibility for deductions and potentially reduce your tax burden. Remember to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice tailored to your specific circumstances.
FAQ Corner
Can I deduct insurance premiums for a pet?
Generally, pet insurance premiums are not deductible for personal use. However, if the pet is used for business purposes (e.g., a service animal), deductions may be possible under specific circumstances.
What if I pay my insurance premiums in installments?
The deductibility is determined by the total premiums paid during the tax year, regardless of how the payments are structured.
Are life insurance premiums deductible?
Generally, life insurance premiums are not deductible, except in limited situations, such as those involving business insurance policies.
Where can I find more detailed information specific to my country?
Consult your country’s tax authority website or a qualified tax professional for the most up-to-date and specific information regarding insurance premium deductibility.