Securing a home loan can be a complex process, and understanding the intricacies of mortgage insurance is crucial for prospective homeowners. This guide delves into the world of FHA loan insurance premiums, demystifying the various components, influencing factors, and payment methods. We’ll explore how these premiums are calculated, the potential for savings, and how they compare to other mortgage insurance options. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or a seasoned investor, navigating the FHA loan insurance landscape is essential for making informed financial decisions.
From upfront premiums to annual payments, we’ll provide a clear and concise overview, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently approach the FHA loan process. We’ll address common concerns and provide practical examples to illustrate key concepts, ultimately empowering you to make the best choices for your financial future.
FHA Loan Insurance Premium Basics
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) insures mortgages, reducing the risk for lenders and making homeownership more accessible to borrowers who may not qualify for conventional loans. This insurance comes at a cost, paid through FHA loan insurance premiums. Understanding these premiums is crucial for anyone considering an FHA loan.
FHA Loan Insurance Premium Types
FHA loan insurance premiums are divided into two main components: an upfront premium and an annual premium. The upfront premium is a one-time payment, while the annual premium is paid monthly along with your mortgage payment. Both premiums help to fund the FHA’s insurance fund, which protects lenders against potential losses from defaults.
Upfront Premium Calculation
The upfront premium is typically 1.75% of the base loan amount. This percentage can vary slightly depending on the loan terms and the FHA’s guidelines. The calculation is straightforward: Upfront Premium = 1.75% x Loan Amount. For example, on a $200,000 loan, the upfront premium would be $3,500 ($200,000 x 0.0175 = $3,500). This upfront premium can be paid at closing or financed into the loan amount, increasing the total loan balance. Financing the upfront premium means a slightly higher monthly payment.
Annual Premium Variation
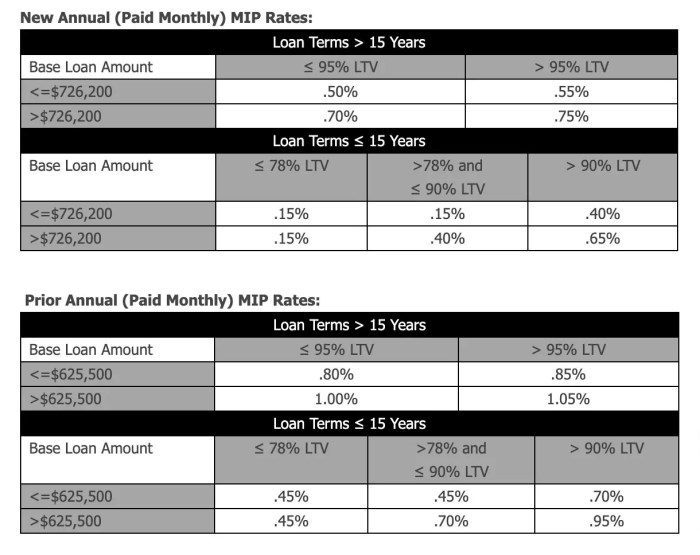
The annual premium is expressed as a percentage of the outstanding loan balance and is calculated annually. This percentage can vary based on several factors, including the loan term, the type of loan (e.g., fixed-rate, adjustable-rate), and the borrower’s credit score. A borrower with a higher credit score might qualify for a lower annual premium. Furthermore, the annual premium may be adjusted periodically by the FHA based on market conditions and the overall health of the FHA insurance fund. For instance, a longer loan term might result in a higher overall annual premium payment due to the longer period of insurance coverage.
Upfront and Annual Premium Comparison
The following table provides examples of upfront and annual premiums for different loan amounts, assuming a standard 1.75% upfront premium and a sample annual premium percentage. Remember that the actual annual premium will vary depending on the factors mentioned above. These figures are for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered definitive.
| Loan Amount | Upfront Premium (1.75%) | Annual Premium Rate (Example: 0.8%) | Approximate Annual Premium (Based on 0.8% rate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $150,000 | $2,625 | 0.8% | $1,200 |
| $200,000 | $3,500 | 0.8% | $1,600 |
| $250,000 | $4,375 | 0.8% | $2,000 |
| $300,000 | $5,250 | 0.8% | $2,400 |
Factors Affecting FHA Loan Insurance Premiums
Several key factors influence the amount you’ll pay for FHA loan insurance. Understanding these factors can help you better anticipate your monthly mortgage payments and plan accordingly. The primary drivers are your credit score, the loan-to-value ratio (LTV) of your mortgage, and the loan term.
Credit Score Impact on FHA Premiums
Your credit score significantly impacts your FHA loan insurance premium. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower premium. Lenders view borrowers with strong credit histories as less risky, thus justifying a lower insurance cost. For example, a borrower with a credit score above 700 might qualify for a lower premium compared to someone with a score below 620. The specific impact varies by lender and the FHA program’s guidelines. Scores below a certain threshold may even result in loan denial.
Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV) and Premiums
The loan-to-value ratio (LTV) represents the size of your loan relative to the home’s value. It’s calculated by dividing the loan amount by the appraised value of the property. A higher LTV indicates a larger loan compared to the property’s worth, representing a higher risk for the lender and therefore a higher premium. For instance, a loan with an LTV of 90% (meaning you borrowed 90% of the home’s value) will typically have a higher premium than a loan with an LTV of 80%.
Loan Term and Premium Differences
The length of your loan term also affects the premium. Generally, longer-term loans (like 30-year mortgages) will result in higher overall premiums compared to shorter-term loans (like 15-year mortgages). This is because the lender assumes more risk over a longer period. While the monthly premium might be lower on a 30-year loan, the total amount paid in premiums over the life of the loan will be significantly higher.
LTV Ratio and Premium Relationship
The following table illustrates how different LTV ratios can affect your FHA insurance premiums. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual premiums may vary based on other factors such as credit score and the specific FHA program.
| LTV Ratio | Annual Premium (Example Percentage) | Monthly Premium (Example, based on $200,000 loan) | Total Premium (30-year loan, example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80% | 0.8% | $133.33 | $48,000 |
| 90% | 1.0% | $166.67 | $60,000 |
| 96.5% | 1.0% + Upfront MIP | $166.67 + Upfront MIP | $60,000 + Upfront MIP |
FHA Loan Insurance Premium Payment Methods
Paying your FHA loan insurance premiums is a crucial aspect of maintaining your mortgage. Understanding the available payment methods and adhering to the payment schedule ensures you avoid penalties and maintain your good standing with your lender. This section details the various ways you can pay your premiums and addresses potential consequences of late payments.
FHA loan insurance premiums can be paid in several ways, most commonly integrated directly into your monthly mortgage payment. This simplifies the process by consolidating all payments into a single monthly bill. Alternatively, you may have the option to pay separately, depending on your lender’s policies and the specific terms of your loan agreement. Let’s explore these methods in more detail.
Methods for Paying FHA Loan Insurance Premiums
Your lender will typically offer several methods for paying your FHA loan insurance premiums. These may include paying through your monthly mortgage payment, paying online through a lender portal, or using other methods like mail or in-person payments. The availability of each method depends on your lender and the loan agreement.
Including Premiums in the Monthly Mortgage Payment
This is the most common and convenient method. Your lender adds the FHA insurance premium to your principal, interest, taxes, and insurance (PITI) payment. This means you make one single monthly payment encompassing all these costs. This simplifies budgeting and payment management, as you only need to track one payment. The lender then distributes the payment accordingly. For example, if your monthly PITI is $1,500 and your FHA premium is $100, your total monthly payment would be $1,600.
Paying Premiums Through an Online Portal
Many lenders provide online portals for managing your mortgage account. These portals often allow you to pay your FHA insurance premiums electronically. A step-by-step process might look like this:
- Log in to your lender’s online portal using your username and password.
- Navigate to the “Payments” or “Billing” section.
- Select “FHA Insurance Premium” as the payment type.
- Enter the amount of the premium due.
- Choose your payment method (e.g., checking account, savings account).
- Review the payment details and confirm the transaction.
- You’ll typically receive a confirmation email or notification once the payment is processed.
Penalties for Late FHA Loan Insurance Premium Payments
Late payments can result in significant penalties. These penalties can vary depending on your lender and the terms of your loan. Common consequences include late fees, an increase in your insurance premium, or even foreclosure proceedings in severe cases. It’s crucial to make timely payments to avoid these negative consequences. Always refer to your loan documents for specific details regarding late payment penalties.
Comparison of FHA Loan Insurance Premium Payment Methods
Choosing the best payment method depends on individual preferences and circumstances. Consider the following pros and cons:
- Monthly Mortgage Payment:
- Pros: Convenient, simplifies budgeting, single payment.
- Cons: Less control over individual payment amounts.
- Online Portal:
- Pros: Convenient, fast, accessible 24/7.
- Cons: Requires internet access and online banking capabilities.
- Mail or In-Person Payment (if offered):
- Pros: Suitable for those without online access.
- Cons: Less convenient, potential for delays in processing.
Cancellation of FHA Loan Insurance

Cancelling FHA loan insurance isn’t as simple as just stopping payments. It depends heavily on your loan’s status and how much of the loan has been repaid. Understanding the conditions and process is crucial for homeowners looking to eliminate this ongoing expense.
Conditions for FHA Loan Insurance Cancellation
FHA loan insurance premiums are typically paid for the life of the loan, unless certain conditions are met. The primary method for cancellation involves paying off a significant portion of the loan, usually reaching a certain loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. This ratio represents the outstanding loan balance compared to the home’s current appraised value. Once the LTV reaches a specific threshold (typically 78%), the annual premium may be cancelled, and only the upfront premium is required. Complete cancellation is usually only possible upon full loan payoff. Other situations, such as a sale of the property, would also lead to the termination of the insurance coverage.
Process of Cancelling FHA Loan Insurance
The process for canceling FHA loan insurance is generally handled automatically by your mortgage servicer once the LTV ratio reaches the required threshold. No separate application is typically required. Your servicer will monitor your loan balance and the home’s appraised value to determine when the cancellation criteria are met. They will then notify you of the cancellation and adjust your monthly mortgage payment accordingly. If you are paying off the loan completely, the final payment will include a final adjustment for the insurance premium.
Requirements for Loan Refinancing to Eliminate FHA Insurance
Refinancing your FHA loan to a conventional loan is another way to eliminate FHA mortgage insurance premiums. This typically requires meeting specific credit score and LTV requirements. Your credit score needs to be high enough to qualify for a conventional loan, and the appraised value of your home must be sufficient to lower your LTV to the point where you no longer need the insurance. This process involves applying for a new mortgage with a conventional lender and using the proceeds to pay off your existing FHA loan. The new loan will have its own closing costs and potentially a higher interest rate, depending on market conditions and your financial profile.
Costs and Benefits of Refinancing to Remove FHA Insurance
Refinancing to remove FHA insurance involves weighing the costs against the long-term benefits. The costs include closing costs associated with the new loan, which can be substantial. There may also be prepayment penalties on your existing FHA loan, depending on its terms. However, the benefits include eliminating the ongoing FHA mortgage insurance premiums, which can result in significant savings over the remaining loan term. The net benefit depends on factors such as the interest rate difference between the FHA and conventional loans, the remaining loan term, and the closing costs of refinancing. For example, if a homeowner has a 15-year FHA loan with high insurance premiums and can refinance into a 15-year conventional loan with a slightly higher interest rate, the savings from eliminated premiums might still outweigh the slightly higher interest cost. Conversely, if refinancing results in a significantly higher interest rate, the cost savings from eliminating premiums might be offset by increased interest payments.
Flowchart Illustrating the Steps Involved in Cancelling FHA Insurance
[A textual description of a flowchart is provided here as image creation is outside the scope of this response. The flowchart would visually represent the decision points and steps involved in canceling FHA insurance. It would start with the initial assessment of the loan’s LTV ratio. If the LTV is below the threshold for cancellation (e.g., 78%), the flowchart would indicate the need for either continued payments or refinancing. If the LTV is at or below the threshold, the flowchart would show the automatic cancellation process initiated by the servicer, followed by notification to the borrower and adjustment of monthly payments. A separate branch would illustrate the refinancing process, showing the application for a conventional loan, the appraisal, the loan approval, and the payoff of the FHA loan.]
Last Recap

Successfully navigating the FHA loan insurance process requires a thorough understanding of its various facets. By carefully considering the factors that influence premium calculations, exploring available payment options, and comparing FHA insurance to alternatives, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. Remember, proper planning and a clear understanding of FHA loan insurance premiums are key to a smooth and successful home-buying experience. This guide serves as a valuable resource to help you confidently embark on your journey towards homeownership.
FAQ Summary
Can I refinance my FHA loan to eliminate the insurance premium?
Yes, you can refinance your FHA loan into a conventional loan once you achieve a certain loan-to-value (LTV) ratio, typically 80% or less. This will eliminate the FHA mortgage insurance premium, but refinancing involves closing costs and may require a higher credit score.
What happens if I miss an FHA loan insurance premium payment?
Late payments can result in penalties and negatively impact your credit score. Contact your lender immediately if you anticipate difficulties making a payment to explore available options.
How is the annual FHA MIP calculated?
The annual FHA MIP is calculated as a percentage of the outstanding loan balance. The percentage varies based on the loan term and the type of FHA loan.
Are there any tax benefits associated with FHA loan insurance premiums?
Generally, FHA mortgage insurance premiums are not tax deductible. Consult a tax professional for specific guidance.