Navigating the world of insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. This guide demystifies the often-confusing concept of monthly insurance premiums, providing a clear and concise explanation of their components, influencing factors, and management strategies. We’ll explore various insurance types, payment methods, and cost-saving techniques, empowering you to make informed decisions about your financial protection.
From understanding the basic building blocks of your premium to exploring strategies for minimizing costs, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to confidently manage this essential aspect of personal finance. This guide will cover everything from the impact of age and health history on your premium to the advantages and disadvantages of different payment options, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this critical financial element.
Defining “Monthly Insurance Premium”
A monthly insurance premium is the recurring payment you make to an insurance company in exchange for coverage under an insurance policy. This payment secures your financial protection against unforeseen events, such as accidents, illnesses, or property damage, depending on the type of insurance. The amount you pay is calculated based on several factors, ensuring a fair and accurate reflection of your risk profile.
Components of a Monthly Insurance Premium
Several factors contribute to the final cost of your monthly insurance premium. These components work together to determine the overall price you pay. The primary components typically include administrative costs (covering the insurer’s operational expenses), claims payouts (funds set aside to cover insured losses), and profit margins (the insurer’s desired return on investment). Actuaries meticulously analyze these factors to calculate premiums that balance risk and profitability. In addition to these core elements, some policies may also include additional fees or surcharges.
Factors Influencing Premium Variations
Numerous variables influence how much you pay monthly for insurance. Your age, health status (for health insurance), driving history (for auto insurance), location (considering crime rates and disaster risks), and the coverage level you choose all play a significant role. For example, a young driver with a history of accidents will generally pay a higher auto insurance premium than an older driver with a clean record. Similarly, individuals living in high-risk areas might face higher home insurance premiums due to increased chances of theft or natural disasters. The amount of coverage you select also directly impacts your premium; higher coverage levels typically mean higher monthly payments.
Examples of Different Insurance Types and Premium Structures
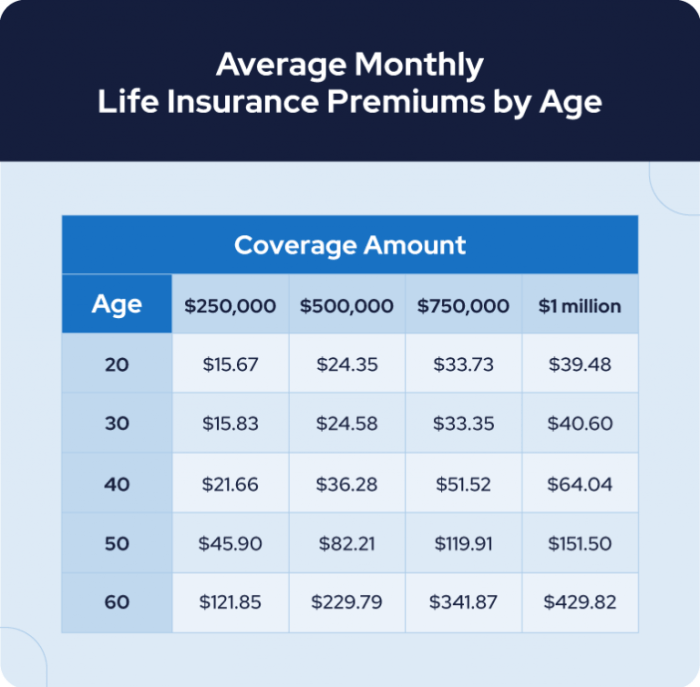
Different types of insurance have distinct premium structures. For example, health insurance premiums are often influenced by factors such as pre-existing conditions, chosen plan type (e.g., HMO, PPO), and the deductible. Auto insurance premiums are heavily reliant on driving history, vehicle type, and location. Homeowners insurance premiums are affected by the value of the property, its location, and the level of coverage selected. Life insurance premiums are calculated based on age, health, and the desired death benefit amount. The complexity of these calculations underscores the importance of understanding the factors involved in your specific policy.
Premium Comparison Table for Various Coverage Levels
The following table illustrates how premiums can vary based on coverage level for a hypothetical auto insurance policy. Remember that these are illustrative examples and actual premiums will vary widely depending on the insurer and individual circumstances.
| Coverage Level | Liability Coverage | Collision Coverage | Comprehensive Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | $50 | $25 | $15 |
| Standard | $75 | $50 | $30 |
| Premium | $100 | $75 | $45 |
| Comprehensive Plus | $150 | $100 | $70 |
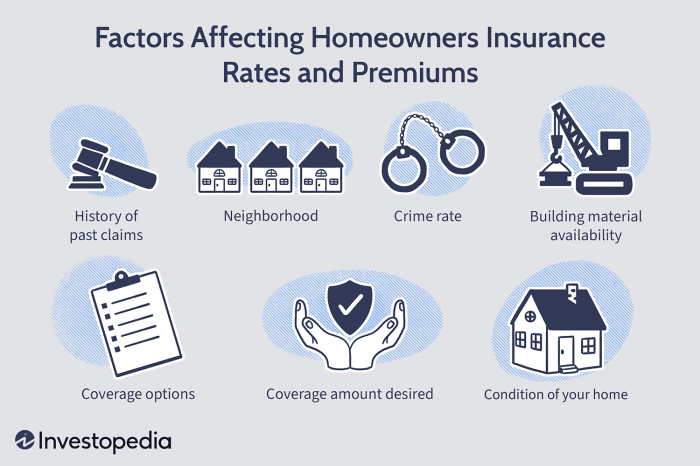
Factors Affecting Monthly Premiums
Several interconnected factors influence the cost of your monthly insurance premium. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your coverage and budget. This section will explore the key elements that insurance companies consider when calculating your premium.
Age
Age is a significant factor in determining insurance premiums. Generally, older individuals tend to have higher premiums than younger individuals. This is because the likelihood of needing medical care increases with age, leading to higher potential claims costs for the insurance company. For example, a 60-year-old might pay considerably more for health insurance than a 30-year-old, even if both are in excellent health. This is reflected in actuarial tables used by insurance companies to assess risk.
Health History
Pre-existing conditions and past medical history play a crucial role in premium calculations. Individuals with a history of serious illnesses or chronic conditions typically face higher premiums. This is because these conditions increase the probability of future claims. For instance, someone with a history of heart disease will likely pay more than someone with a clean bill of health. Similarly, a history of frequent hospitalizations or expensive treatments can significantly impact premium costs. Insurance companies carefully review medical records to assess the level of risk associated with each individual.
Location
Geographic location influences premiums due to variations in healthcare costs and the prevalence of certain health risks. Areas with high healthcare costs, such as major metropolitan areas, generally have higher premiums than those in rural areas with lower healthcare expenses. Furthermore, the prevalence of specific diseases or health issues in a particular region can also influence premiums. For example, areas with high rates of certain cancers might see higher premiums for health insurance policies.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity, can impact insurance premiums. These habits increase the risk of developing health problems, thus leading to higher premiums. Insurance companies often incorporate lifestyle factors into their risk assessment models, rewarding healthier lifestyles with lower premiums and penalizing riskier behaviors with higher premiums. Many insurers offer discounts for non-smokers, for example.
Occupation
Certain occupations are considered higher risk than others, leading to variations in insurance premiums. Jobs involving hazardous materials, strenuous physical activity, or high stress levels may result in higher premiums. For instance, a construction worker might pay more for life insurance than an office worker due to the inherent risks associated with their profession. Insurance companies assess the occupational hazards and incorporate this into their risk calculations.
Comparison of Premiums Across Providers
Different insurance providers offer varying levels of coverage and pricing. A policy with comprehensive coverage from one company might cost more than a policy with more limited coverage from another. It’s essential to compare quotes from multiple providers to find the best value for your needs. Factors such as deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums significantly affect the overall cost and should be carefully considered when comparing policies. For example, a policy with a lower monthly premium might have a very high deductible, resulting in higher out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a claim.
Understanding Premium Payment Methods

Paying your monthly insurance premium is a crucial aspect of maintaining your coverage. Understanding the various payment methods available and their associated advantages and disadvantages can help you choose the option that best suits your financial habits and preferences. This section Artikels several common payment methods and their key features.
Available Payment Methods
Several methods exist for paying insurance premiums, each offering a unique set of benefits and drawbacks. Choosing the right method depends on individual circumstances and preferences. Consider factors such as convenience, fees, and security when making your selection.
- Automatic Bank Payments (ACH): This method involves automatically deducting the premium amount from your checking or savings account on the due date. It’s convenient and ensures timely payments, preventing late fees. However, it requires providing your bank account information, posing a potential security risk if the system is compromised. It also lacks flexibility if you need to adjust the payment amount or stop payments.
- Credit or Debit Card Payments: Many insurers accept credit or debit card payments online or by phone. This offers flexibility and immediate payment confirmation. However, some credit cards may charge processing fees, and using a debit card exposes your bank account directly. Also, some insurers may impose transaction limits.
- Mail Payments (Check or Money Order): This traditional method involves mailing a check or money order to the insurance company. It’s generally accepted, but it’s slower than electronic methods and lacks immediate confirmation. There’s also a risk of lost or delayed mail, potentially leading to late payment fees.
- Online Payment Portals: Most insurance companies provide secure online portals for premium payments. These portals typically offer various payment options, including credit/debit cards, electronic bank transfers, and sometimes even payment apps. The convenience is a major advantage, but it requires internet access and familiarity with online banking.
- In-Person Payments: Some insurers allow in-person payments at their offices or designated locations. This method offers immediate confirmation but is less convenient for those geographically distant from the insurer’s offices. It also may not be available for all insurers.
Online Payment System Flowchart
The following describes a typical online insurance premium payment process:
1. Access the Payment Portal: The customer logs into the insurer’s online portal using their credentials.
2. Select Payment Method: The customer chooses their preferred payment method (credit card, debit card, bank transfer, etc.).
3. Enter Payment Details: The customer enters the required information for their chosen payment method (card number, expiry date, bank account details, etc.).
4. Review and Confirm: The customer reviews the payment details and confirms the transaction.
5. Payment Processing: The system processes the payment and updates the customer’s account.
6. Confirmation: The customer receives a confirmation message or email indicating successful payment.
7. Payment Record: The payment is recorded in both the insurer’s and the customer’s records.
Common Payment Processing Fees
Payment processing fees vary depending on the method and the insurer. While some methods are free, others may incur charges.
| Payment Method | Potential Fees |
|---|---|
| Credit Card | Transaction fee (percentage of payment amount) |
| Debit Card | May have a small transaction fee or none |
| ACH Transfer | Usually no fee |
| Mail (Check/Money Order) | Typically no fee, but potential for late fees if payment is delayed |
| Online Payment Portal | Usually no fee, but some portals may charge for specific payment methods. |
Managing Monthly Insurance Costs
Managing your monthly insurance costs effectively requires a proactive approach, balancing coverage needs with affordability. Several strategies can help you reduce your premiums without sacrificing essential protection. Understanding the factors influencing your premium and exploring different options can significantly impact your overall insurance expenses.
Strategies for Lowering Monthly Insurance Premiums
Several approaches can help lower your monthly insurance premiums. Improving your credit score, for instance, can lead to lower rates as insurers often consider credit history a measure of risk. Maintaining a safe driving record, if it’s auto insurance, is another crucial factor. Discounts are frequently offered for drivers with clean records. Bundling your insurance policies (home and auto, for example) with the same provider often results in significant savings. Increasing your deductible, while carrying the risk of higher out-of-pocket expenses in case of a claim, can considerably lower your monthly premiums. Finally, shopping around and comparing quotes from different insurers is essential to finding the best rates for your specific needs.
Implications of Choosing Higher Deductibles on Monthly Premiums
Opting for a higher deductible directly translates to lower monthly insurance premiums. A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. By agreeing to pay a larger portion of any claim yourself, you reduce the insurer’s risk and, consequently, your premium. For example, choosing a $1,000 deductible instead of a $500 deductible for your car insurance might result in a noticeable reduction in your monthly payment. However, it’s crucial to weigh this cost savings against the potential for a significant out-of-pocket expense should you need to file a claim. Carefully consider your financial situation and risk tolerance before making this decision.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Bundled Insurance Packages
Bundling your insurance policies, such as home and auto insurance, with a single provider often offers substantial cost savings. Insurers frequently provide discounts for bundling, recognizing the reduced administrative costs associated with managing multiple policies for a single customer. This convenience also simplifies billing and communication. However, bundling might limit your options. You may not find the best rates for each individual policy if you’re locked into a single provider. It’s essential to compare bundled packages with purchasing individual policies to determine the most cost-effective approach for your specific needs.
Resources for Finding Affordable Insurance Options
Finding affordable insurance requires research and comparison. Several resources can assist in this process.
- Independent Insurance Agents: These agents work with multiple insurance companies, allowing them to compare options and find the best rates for you.
- Online Comparison Websites: Numerous websites allow you to enter your information and compare quotes from various insurers simultaneously.
- Your State’s Insurance Department: These departments often have resources and tools to help consumers find affordable insurance options and file complaints.
- Consumer Advocacy Groups: Organizations like the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) provide information and resources on insurance issues.
Final Review
Successfully managing your monthly insurance premium requires a proactive approach to understanding its components and the factors that influence its cost. By employing the strategies and insights discussed in this guide, you can gain greater control over your insurance expenses, ensuring adequate coverage without unnecessary financial strain. Remember, informed choices lead to better financial outcomes, so take the time to understand your policy and explore options for optimizing your premium.
Questions Often Asked
What happens if I miss a monthly insurance premium payment?
Missing a payment can result in late fees, suspension of coverage, or even policy cancellation. Contact your insurer immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment to explore options.
Can I change my insurance plan mid-year?
Generally, you can, but there might be penalties or limitations depending on your insurer and the specific policy. Check your policy documents or contact your insurer for details.
How often are insurance premiums reviewed and adjusted?
This varies depending on the insurer and type of insurance. Some policies have annual reviews, while others may adjust premiums more frequently based on factors like claims history or market conditions.
What is a deductible, and how does it affect my monthly premium?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Choosing a higher deductible typically lowers your monthly premium, but increases your upfront cost in case of a claim.