Securing affordable auto insurance is a crucial financial consideration for most drivers. Navigating the complexities of premiums, however, can be daunting. This guide delves into the factors that influence the average six-month auto insurance premium, providing insights into how various elements contribute to the overall cost. We’ll explore demographic influences, coverage options, and the methods used to calculate these averages, empowering you to make informed decisions about your own insurance needs.
From understanding the impact of your driving record and the type of vehicle you drive to appreciating the role of location and coverage choices, we aim to demystify the process of estimating your six-month premium. By examining real-world examples and data, this guide will help you navigate the insurance landscape with greater confidence and clarity.
Factors Influencing Average 6-Month Auto Insurance Premiums
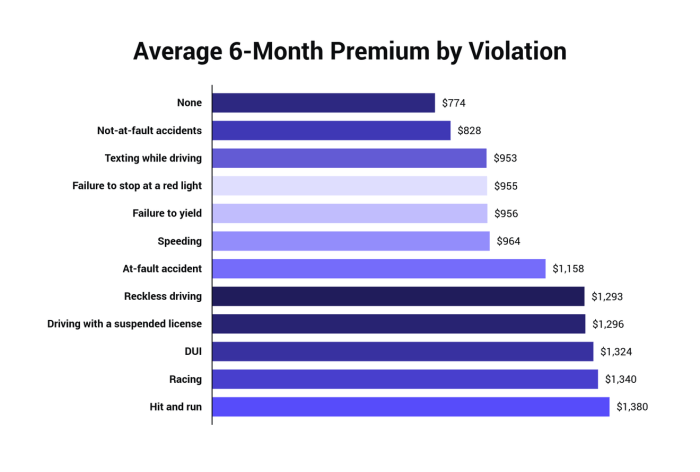
Understanding the cost of auto insurance can seem complex, but several key factors significantly influence the average six-month premium. These factors interact to determine your individual rate, so it’s helpful to understand their individual impact. This information can empower you to make informed decisions about your coverage and potentially lower your costs.
Top Five Factors Affecting Auto Insurance Premiums
The cost of your six-month auto insurance policy is a product of many variables. However, five factors consistently stand out as the most influential. The following table summarizes these factors, their impact, and provides illustrative examples.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Premium | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driving History | Accidents, tickets, and claims filed in the past. | Higher frequency of incidents leads to higher premiums. | A driver with three accidents in the past three years will pay significantly more than a driver with a clean record. |
| Age and Gender | Statistically, younger drivers and males tend to have higher accident rates. | Younger drivers and males typically pay more. | A 20-year-old male driver will generally pay more than a 40-year-old female driver. |
| Credit Score | Insurance companies often use credit scores to assess risk. | Higher credit scores generally correlate with lower premiums. | Individuals with excellent credit scores often qualify for discounts and lower rates. |
| Vehicle Type and Features | The type of vehicle, its safety features, and engine size influence the cost of repairs and likelihood of accidents. | Higher-value vehicles, sports cars, and vehicles with less safety features usually lead to higher premiums. | Insuring a new luxury SUV will cost more than insuring a used economy car. |
| Location | Geographic location impacts accident rates and the cost of repairs. | Areas with high crime rates or frequent accidents typically have higher premiums. | Insurance in a large city with high traffic density will usually be more expensive than in a rural area. |
Driving History’s Influence on Premiums
Your driving history is a crucial determinant of your insurance premium. Insurance companies meticulously track accidents, speeding tickets, and any claims filed against your policy. A clean driving record translates to lower premiums, while incidents like accidents or traffic violations significantly increase your cost.
For instance, a single at-fault accident could lead to a premium increase of 20-40%, depending on the severity of the accident and the insurer. Multiple accidents or serious violations like DUI convictions can result in even more substantial increases, sometimes doubling or tripling the premium. Conversely, maintaining a spotless record for several years can earn you discounts and lower rates.
Vehicle Type and Features’ Impact on Premiums
The type of vehicle you drive plays a significant role in your insurance costs. Factors such as the vehicle’s make, model, year, safety features, and engine size all contribute to the premium calculation.
- Vehicle Value: More expensive vehicles cost more to repair and replace, resulting in higher premiums.
- Safety Features: Vehicles equipped with advanced safety features like anti-lock brakes, airbags, and electronic stability control may qualify for discounts.
- Engine Size and Performance: High-performance vehicles with larger engines are often associated with higher risk and thus higher premiums.
- Vehicle Theft Rate: Vehicles with a higher theft rate in your area will generally have higher premiums.
Geographic Location and Insurance Premiums
Insurance rates vary significantly across different geographic locations. This variation stems from several factors, including accident rates, crime rates, the cost of vehicle repairs, and the prevalence of natural disasters.
For example, states with high population densities and congested roadways often have higher premiums due to increased accident frequency. Conversely, rural areas with lower accident rates tend to have lower premiums. States like Florida and California are often cited as having relatively high average premiums, partly due to high population density, severe weather, and higher repair costs. On the other hand, some Midwestern and Southern states may have lower average premiums. These differences reflect the varied risk profiles associated with each location.
Comparing Average Premiums Across Demographics
Auto insurance premiums are not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Several demographic factors significantly influence the average cost, leading to considerable variation in six-month premiums across different segments of the population. Understanding these variations can help individuals better understand their own insurance costs and potentially find ways to save money.
Average Premiums by Age Group
Age is a powerful predictor of auto insurance premiums. Younger drivers, typically those under 25, generally face higher premiums due to statistically higher accident rates and a perceived higher risk profile among this demographic. Conversely, drivers in middle age (approximately 30-60) often benefit from lower premiums as their accident history tends to be more favorable. Senior drivers (65 and older) may experience premium fluctuations; while some insurers offer discounts for mature drivers with clean records, others may increase premiums due to potential health concerns impacting driving abilities. The following bar chart illustrates these differences:
Illustrative Bar Chart: Average Six-Month Auto Insurance Premiums by Age Group
Imagine a bar chart with the horizontal axis representing age groups (e.g., 16-25, 26-35, 36-55, 56-65, 65+). The vertical axis represents the average six-month premium in US dollars. The bars would visually demonstrate that the 16-25 age group has the tallest bar (highest premium), followed by a gradual decrease in bar height for subsequent age groups. The bar representing the 36-55 age group would likely be the shortest, representing the lowest average premium. The bar for the 65+ age group would be slightly taller than the 36-55 group, reflecting the potential for increased premiums for senior drivers.
Impact of Marital Status on Premiums
Married individuals often enjoy lower auto insurance premiums compared to their single counterparts. Insurers often view married individuals as having a lower risk profile, possibly due to increased stability, shared responsibility, and potentially safer driving habits. This is not a universal rule, however, as individual driving records and other factors still play a significant role. The exact premium difference varies considerably based on other factors like age, location, and driving history.
Influence of Gender on Auto Insurance Premiums
Historically, studies have shown a slight tendency for men to pay higher premiums than women. This disparity has been attributed to various factors, including statistically higher accident rates and claims among male drivers. However, it’s crucial to note that this difference is not consistently observed across all insurance companies and jurisdictions, and regulations are increasingly addressing potential gender bias in insurance pricing. Further, individual driving history and other factors play a far more significant role than gender alone in determining premiums. Any observed differences are often marginal compared to the impact of other factors like age and driving record.
Finding and Understanding Average Premium Data
Understanding average six-month auto insurance premiums requires a careful examination of the data collection methods and inherent limitations. While averages provide a general benchmark, they shouldn’t be the sole factor in determining your personal insurance needs.
Calculating average six-month auto insurance premiums involves aggregating data from various sources and applying statistical methods. Data sources typically include insurance companies’ internal records, industry-wide surveys conducted by organizations like the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), and publicly available data from insurance comparison websites. Methodologies usually involve weighting premiums based on factors like policyholder demographics and vehicle characteristics to arrive at a representative average. The process often involves cleaning and standardizing the data to ensure consistency and accuracy before averaging. Different methodologies might yield slightly different results, highlighting the importance of understanding the specific approach used when interpreting the data.
Data Sources and Methodologies
Reliable average premium data often comes from large-scale surveys or aggregated data from multiple insurance companies. Insurance comparison websites, while convenient for consumers, may not always represent a completely unbiased sample of the entire market. Government agencies, such as the NAIC, may release aggregate data, but this information is usually broad and may not reflect regional variations in premiums. Academic studies can also provide valuable insights, but it is crucial to consider the study’s methodology, sample size, and year of publication when interpreting the findings. For instance, a study focusing solely on urban areas may not accurately reflect average premiums in rural regions. The methodology employed will often involve statistical techniques like weighted averages to account for the different distributions of policyholders across various risk categories.
Limitations of Average Premium Data
Using average premium data alone to make personal insurance decisions can be misleading. Average data masks the wide range of premiums individuals actually pay. This is because insurance premiums are highly personalized, depending on many factors not captured in a simple average. For example, a young, inexperienced driver with a sports car will likely pay significantly more than an older, experienced driver with a smaller, safer vehicle, even if they live in the same area. Similarly, average data may not reflect the impact of discounts, such as safe driver discounts or bundling discounts, which can substantially lower individual premiums. Averages also fail to account for the varying levels of coverage offered by different insurance policies. A comprehensive policy naturally costs more than a minimum liability policy, even for individuals with similar risk profiles.
Resources for Finding Reliable Information
Several resources provide reliable information on average auto insurance premiums. While precise regional averages are difficult to find publicly, comparison websites like NerdWallet, The Zebra, and Insurify allow users to input their information to receive personalized quotes and gain insight into the range of premiums in their area. These sites don’t directly provide average premiums, but they give a sense of the market range. State-level insurance departments often publish reports on the overall cost of insurance within their jurisdiction, providing a broader context. Finally, consulting with an independent insurance agent can provide a more personalized assessment, taking into account your specific circumstances and helping you navigate the complexities of insurance pricing.
Conclusive Thoughts
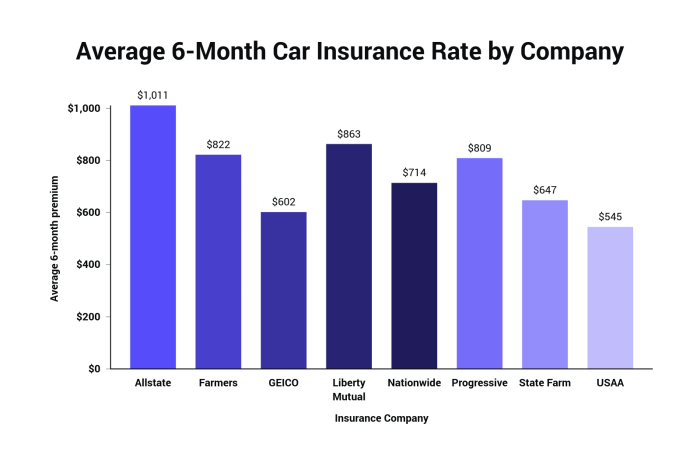
Determining your individual six-month auto insurance premium requires a nuanced understanding of various interconnected factors. While average premium data offers a valuable benchmark, it’s crucial to remember that individual circumstances significantly impact the final cost. By considering the factors Artikeld in this guide – driving history, vehicle type, location, demographics, and coverage choices – you can gain a clearer picture of what influences your premium and make more informed decisions to secure the best possible coverage at a price that aligns with your budget. Remember to consult multiple insurers and compare quotes to find the most suitable policy for your specific needs.
FAQ Resource
What is the average increase in premiums after an at-fault accident?
The increase varies greatly depending on the severity of the accident and your insurer, but expect a substantial rise, potentially doubling or tripling your premiums.
How does my credit score affect my auto insurance premium?
In many states, insurers use credit-based insurance scores to assess risk. A lower credit score generally leads to higher premiums.
Can I get a discount for bundling my auto and home insurance?
Yes, many insurers offer discounts for bundling policies, saving you money on both your auto and homeowners insurance.
What are the consequences of driving without car insurance?
Driving without insurance is illegal and can result in hefty fines, license suspension, and even jail time depending on your location and the circumstances.
How often can I expect my auto insurance premiums to change?
Premiums can change annually, or even more frequently, depending on your driving record, claims history, and changes in your insurer’s rates.