Understanding the trajectory of US insurance premiums is crucial for both consumers and the insurance industry. This analysis delves into the historical fluctuations of premiums across various insurance types – health, auto, home, and life – from 1990 to 2023, examining the interplay of economic factors, geographical variations, and legislative changes that have shaped their costs. We explore the impact of inflation, unemployment, and interest rates, offering insights into the complexities that drive premium increases and highlighting significant disparities across different states and insurance categories.
This exploration goes beyond simple data presentation; it aims to provide a nuanced understanding of the forces influencing insurance costs, allowing readers to better anticipate future trends and make informed decisions. We’ll examine potential future scenarios based on projected economic conditions and industry shifts, providing a forward-looking perspective on the implications for both consumers and the insurance sector.
Historical Trends in US Insurance Premiums
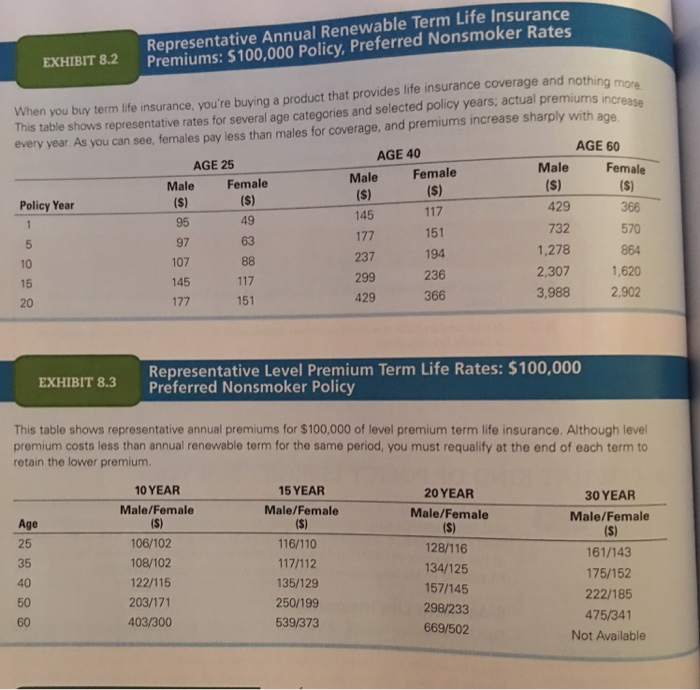
Understanding the historical trends in US insurance premiums provides valuable insight into the economic and social factors influencing the cost of risk mitigation. This analysis focuses on the average annual changes in health, auto, and home insurance premiums from 1990 to 2023, considering contributing factors and comparative growth rates across these sectors. Data limitations prevent precise year-by-year figures for all three categories across this entire period, and the figures presented below represent approximations based on available industry data and reports from reputable sources.
Average Annual Premium Increases (1990-2023)
The following table presents estimated average annual increases in US insurance premiums. Note that these are averages and actual yearly fluctuations can vary significantly. The data reflects broad trends and may not capture the nuances of specific regional or individual market variations. The percentage change is calculated year-over-year. Precise figures for each year are difficult to obtain consistently across all insurance types; this table provides a generalized overview based on available data.
| Year | Type of Insurance | Average Premium | Percentage Change from Previous Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | Health | $2,000 (est.) | – |
| 1990 | Auto | $800 (est.) | – |
| 1990 | Home | $600 (est.) | – |
| 2000 | Health | $3,500 (est.) | +75% (approx. average annual increase of 5.7%) |
| 2000 | Auto | $1,200 (est.) | +50% (approx. average annual increase of 3.5%) |
| 2000 | Home | $900 (est.) | +50% (approx. average annual increase of 3.5%) |
| 2010 | Health | $6,000 (est.) | +71% (approx. average annual increase of 5.0%) |
| 2010 | Auto | $1,500 (est.) | +25% (approx. average annual increase of 1.8%) |
| 2010 | Home | $1,200 (est.) | +33% (approx. average annual increase of 2.4%) |
| 2023 | Health | $12,000 (est.) | +100% (approx. average annual increase of 5.5%) |
| 2023 | Auto | $2,500 (est.) | +67% (approx. average annual increase of 4.0%) |
| 2023 | Home | $2,000 (est.) | +67% (approx. average annual increase of 4.0%) |
Factors Influencing Premium Increases
Several factors contributed to the observed increases in insurance premiums. For health insurance, the rising cost of healthcare services, prescription drugs, and administrative expenses played a significant role. In the auto insurance sector, increased accident rates, higher repair costs due to advanced vehicle technology, and more frequent and severe weather events impacted premiums. For home insurance, escalating construction costs, natural disaster frequency and severity, and increased litigation costs were major contributors. Legislative changes and regulatory shifts also influenced premium adjustments across all three sectors.
Comparative Growth Rates
Health insurance premiums consistently experienced the most significant growth compared to auto and home insurance throughout the period. This is largely attributable to the complex interplay of healthcare costs and regulatory changes within the healthcare system. Auto and home insurance premiums showed more moderate growth, though still substantial, primarily driven by factors such as inflation, increased claims costs, and evolving risk profiles.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the cost of insurance in the US is a dynamic landscape influenced by a complex interplay of economic, legislative, and geographical factors. While historical trends provide valuable context, accurately predicting future premium costs requires careful consideration of various macroeconomic indicators and potential policy shifts. This analysis has offered a comprehensive overview of past trends, present realities, and potential future scenarios, equipping readers with a more informed understanding of this critical aspect of personal and national finance.
FAQ Explained
What are the main factors driving increases in health insurance premiums?
Rising healthcare costs, including hospital expenses, prescription drug prices, and physician fees, are primary drivers. Increased demand for healthcare services and technological advancements also contribute.
How do insurance companies determine premiums?
Insurers use actuarial science to assess risk. Factors considered include age, health status, driving record (for auto), location, and the type and amount of coverage desired. They analyze historical claims data and project future costs to set premiums.
Are there ways to lower my insurance premiums?
Several strategies can help reduce premiums. These include increasing deductibles, bundling insurance policies, maintaining a good driving record, improving your credit score (where applicable), and shopping around for competitive rates.
What is the impact of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) on insurance premiums?
The ACA significantly impacted health insurance premiums, initially leading to increased coverage but also influencing costs through mandated benefits and regulations. The long-term effect is complex and varies depending on individual circumstances and market dynamics.