Ever wondered what determines the cost of your insurance? Understanding insurance premiums is crucial for managing your finances and securing the right coverage. This guide delves into the intricacies of insurance premiums, explaining what they are, how they’re calculated, and what factors influence their cost. We’ll explore various types of insurance, payment options, and provide insights into how to navigate your policy effectively.
From the fundamental definition of insurance premiums to the various components that contribute to their final price, this guide aims to demystify the often-complex world of insurance costs. We’ll explore the impact of personal factors, such as age and driving history, and how insurance companies use this information to assess risk and determine your premium.
Defining Insurance Premiums

Insurance premiums are essentially the payments you make to an insurance company in exchange for financial protection against potential losses. Think of it as a pre-paid agreement: you pay a regular fee, and the insurer agrees to cover specific costs should a covered event occur. This protects you from potentially devastating financial burdens.
Insurance premiums are calculated based on a complex assessment of risk. The more likely you are to make a claim, the higher your premium will be. This is a fundamental principle of insurance; it’s a system of risk pooling, where those who are less likely to make claims essentially subsidize those who are more likely.
Types of Insurance Premiums
Different types of insurance carry different premiums reflecting the varying levels of risk involved. For instance, health insurance premiums are typically higher for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those in high-risk demographics because these individuals are statistically more likely to require expensive medical care. Similarly, auto insurance premiums vary widely depending on factors like driving history, vehicle type, and location. Homeowners insurance premiums are influenced by factors such as the value of the home, its location (e.g., proximity to fire hazards), and the level of coverage chosen. Each type of insurance has its own unique risk assessment methodology.
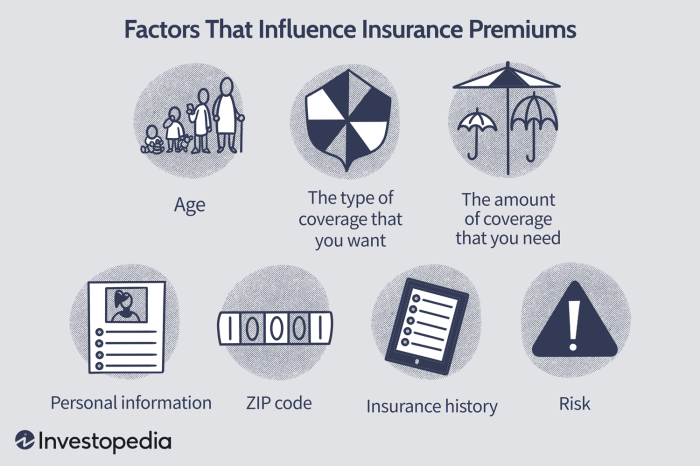
Factors Influencing Premium Calculation
Numerous factors contribute to the final premium amount. These can be broadly categorized into risk-related factors and administrative costs. Risk-related factors include demographic data (age, location, health history), the insured item’s characteristics (vehicle type, home value), and the level of coverage selected. Administrative costs encompass the insurer’s operating expenses, claims processing, and profit margins. A more detailed breakdown of these factors is presented below.
| Factor Category | Specific Factors | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic Data | Age, location, health history, driving record | A younger driver with a clean record will likely pay less for car insurance than an older driver with multiple accidents. |
| Insured Item Characteristics | Vehicle type, home value, building materials | A luxury car will typically have higher insurance premiums than an economical car. A larger home made of wood will likely have higher homeowners insurance than a smaller brick home. |
| Coverage Level | Deductible amount, coverage limits | Choosing a higher deductible will usually result in a lower premium, as you’re accepting more of the financial risk. |
| Administrative Costs | Operating expenses, claims processing, profit margin | These costs are built into the premium to ensure the insurer remains financially solvent. |
The calculation of insurance premiums is a complex process, involving statistical modeling, actuarial analysis, and consideration of numerous variables.
Types of Insurance Premiums and Payment Options
Choosing the right payment plan for your insurance premiums can significantly impact your budget and overall financial planning. Understanding the various options available and their associated benefits and drawbacks is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will explore the different ways you can pay your insurance premiums and the factors to consider when selecting a payment method.
Premium Payment Frequency
The frequency with which you pay your insurance premiums—monthly, quarterly, or annually—directly affects your cash flow and, in some cases, the overall cost. Each option presents a unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
- Monthly Payments: This option offers the most flexibility, allowing for smaller, more manageable payments spread throughout the year. However, it typically results in higher overall costs due to administrative fees associated with more frequent processing.
- Quarterly Payments: Quarterly payments represent a middle ground, balancing affordability with reduced administrative fees compared to monthly payments. They require slightly larger payments than monthly installments but offer more breathing room than annual payments.
- Annual Payments: Paying your premiums annually often results in the lowest overall cost, as insurers frequently offer discounts for this option. However, it requires a larger upfront payment, which may not be feasible for everyone.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Payment Options
The choice between monthly, quarterly, and annual payments depends largely on personal financial circumstances and preferences.
- Monthly Payments:
- Advantages: Easier budget management, smaller payments.
- Disadvantages: Higher total cost due to potential administrative fees.
- Quarterly Payments:
- Advantages: Balance between affordability and cost savings compared to monthly payments.
- Disadvantages: Requires larger payments than monthly installments.
- Annual Payments:
- Advantages: Lowest overall cost due to potential discounts.
- Disadvantages: Requires a significant upfront payment.
Payment Methods and Their Impact on Cost
While the frequency of payment significantly affects the total cost, the payment method itself can also have a minor influence. For example, some insurers might offer a slight discount for automatic payments through electronic fund transfers (EFT) or online banking, as these methods reduce administrative overhead.
- Automatic Payments (EFT/Online Banking): These methods often come with the convenience of automated payments and, in some cases, a small discount. They eliminate the risk of missed payments and late fees.
- Checks: Paying by check is a traditional method, but it can be less convenient and may not offer discounts. There’s also a risk of lost or delayed payments, potentially incurring late fees.
- Credit/Debit Cards: Using credit or debit cards might incur additional processing fees, negating any potential discounts. However, it offers convenience and a record of payment.
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, understanding insurance premiums involves more than just knowing the monthly amount due. It requires grasping the underlying factors that influence cost and how those factors can change over time. By understanding the components of your premium, how different payment options affect your overall cost, and how to interpret your policy, you can make informed decisions about your insurance coverage and manage your finances more effectively. Being proactive and informed allows you to find the best value for your insurance needs.
FAQ Overview
What happens if I miss an insurance premium payment?
Missing a payment can lead to a lapse in coverage, leaving you financially vulnerable in case of an accident or unforeseen event. Late fees may also apply. Contact your insurer immediately if you anticipate difficulty making a payment to explore possible solutions.
Can I negotiate my insurance premium?
While not always guaranteed, you might be able to negotiate your premium. This often involves shopping around for different insurers, demonstrating a good driving or health record, and bundling multiple policies.
How often are insurance premiums reviewed?
The frequency of premium reviews varies depending on the insurer and type of insurance. Some insurers review premiums annually, while others may do so more frequently or less frequently, depending on factors such as claims history and risk assessment.
What is the difference between a deductible and a premium?
A premium is the amount you pay regularly to maintain your insurance coverage. A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in after a claim.